volcanism vent crater caldera quiet eruption explosive
... 2. Dormant Volcano- is a volcano that has not erupted recently, but has during recorded history. It is expected to erupt again in the future. 3. Extinct Volcano- is one that has not erupted in recorded history. It is unlikely to erupt again. VII. Volcanism Underground A. Intrusions- are flows of mag ...
... 2. Dormant Volcano- is a volcano that has not erupted recently, but has during recorded history. It is expected to erupt again in the future. 3. Extinct Volcano- is one that has not erupted in recorded history. It is unlikely to erupt again. VII. Volcanism Underground A. Intrusions- are flows of mag ...
Volcano Vocabulary - watertown.k12.wi.us
... 2. Dormant Volcano- is a volcano that has not erupted recently, but has during recorded history. It is expected to erupt again in the future. 3. Extinct Volcano- is one that has not erupted in recorded history. It is unlikely to erupt again. VII. Volcanism Underground A. Intrusions- are flows of mag ...
... 2. Dormant Volcano- is a volcano that has not erupted recently, but has during recorded history. It is expected to erupt again in the future. 3. Extinct Volcano- is one that has not erupted in recorded history. It is unlikely to erupt again. VII. Volcanism Underground A. Intrusions- are flows of mag ...
Lab 5 Lecture
... The magma chamber below is (partially or completely) emptied after an eruption The emptied magma chamber can no longer support the weight of the overlying rock The overlying rock collapses into itself, forming a circular basin ...
... The magma chamber below is (partially or completely) emptied after an eruption The emptied magma chamber can no longer support the weight of the overlying rock The overlying rock collapses into itself, forming a circular basin ...
Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions
... destructive boundaries: Crustal plate boundaries that converge (come together) with each other. May also be referred to as subduction zones. constructive boundaries: They exist between two crustal plates that are moving away from each other, causing new crustal rocks to form. May also be referred to ...
... destructive boundaries: Crustal plate boundaries that converge (come together) with each other. May also be referred to as subduction zones. constructive boundaries: They exist between two crustal plates that are moving away from each other, causing new crustal rocks to form. May also be referred to ...
Monitoring Methods
... Chemistry — As the molten material (magma) rises to shallow levels, gases are released and they rise to the surface. Gas — When molten material (magma) moves into a volcano it gives off volcanic gas emissions, sulphur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) which are measured ...
... Chemistry — As the molten material (magma) rises to shallow levels, gases are released and they rise to the surface. Gas — When molten material (magma) moves into a volcano it gives off volcanic gas emissions, sulphur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) which are measured ...
Chapter 6 study guide
... 1. Define volcano 2. Where are most volcanoes found? 3. What are two types of plate boundaries and how does the Earth’s crust move at these boundaries? 4. When lava or magma hardens it forms what type of rock? 5. How are igneous rocks classified? 6. What are the three textures an igneous rock can ha ...
... 1. Define volcano 2. Where are most volcanoes found? 3. What are two types of plate boundaries and how does the Earth’s crust move at these boundaries? 4. When lava or magma hardens it forms what type of rock? 5. How are igneous rocks classified? 6. What are the three textures an igneous rock can ha ...
why live enar a volcano
... • The wild, raw and barren volcanic landscapes also attract tourists who want to see what the early planet may have looked like. • Tourism creates jobs in shops, restaurants, hotels and tourist ...
... • The wild, raw and barren volcanic landscapes also attract tourists who want to see what the early planet may have looked like. • Tourism creates jobs in shops, restaurants, hotels and tourist ...
Chapter 10.1
... • Calderas - a large depression in a volcano. This is cause by the collapse of the top of a composite volcano or from the collapse of the top of a shield volcano. • Necks and Pipes – most volcanoes get magma through conduits called pipes that connect a magma chamber to the surface. A neck is when th ...
... • Calderas - a large depression in a volcano. This is cause by the collapse of the top of a composite volcano or from the collapse of the top of a shield volcano. • Necks and Pipes – most volcanoes get magma through conduits called pipes that connect a magma chamber to the surface. A neck is when th ...
Volcanoes: eruptive style and associated landforms
... 2. Large volume of material extruded 3. Magma chamber empties 4. Volcano collapses into the empty magma chamber ...
... 2. Large volume of material extruded 3. Magma chamber empties 4. Volcano collapses into the empty magma chamber ...
Volcanic Eruptions and Hazards
... • Melted water picks up rock and debris forming hot, fast moving mud flows known as lahars. • Lahars are a mixture of rocks, soil, boulders and other debris and can be very destructive. ...
... • Melted water picks up rock and debris forming hot, fast moving mud flows known as lahars. • Lahars are a mixture of rocks, soil, boulders and other debris and can be very destructive. ...
Rock and Lava: Felsic vs. Mafic
... fragments and hot gases • Travel at >80 km/hr • Temperature of 200-700°C • Pyroclastic flows – Destroy by direct impact – Bury sites with hot rock debris – Melt snow and ice to form ...
... fragments and hot gases • Travel at >80 km/hr • Temperature of 200-700°C • Pyroclastic flows – Destroy by direct impact – Bury sites with hot rock debris – Melt snow and ice to form ...
Volcanic Landforms
... millions of years, these layers of lava build up over a large area to form a lava plateau. An enormous eruption may empty a volcano’s main vent and magma chamber. With nothing to support it, the top of the mountain collapses inward. The huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain is called ...
... millions of years, these layers of lava build up over a large area to form a lava plateau. An enormous eruption may empty a volcano’s main vent and magma chamber. With nothing to support it, the top of the mountain collapses inward. The huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain is called ...
Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
... • The blast from an explosive eruption can knock down trees, destroy buildings, and kill humans and animals. ...
... • The blast from an explosive eruption can knock down trees, destroy buildings, and kill humans and animals. ...
Volcanic Landforms
... Composite Volcanoes • Sometimes called Stratovolcanoes, Composite volcanoes form when runny lava escapes through a fissure and flows a long way. Composite volcanoes are tall cone-shaped mountains that are typically steeplysided, symmetrical cones of large dimensions. The essential feature of a comp ...
... Composite Volcanoes • Sometimes called Stratovolcanoes, Composite volcanoes form when runny lava escapes through a fissure and flows a long way. Composite volcanoes are tall cone-shaped mountains that are typically steeplysided, symmetrical cones of large dimensions. The essential feature of a comp ...
Chapter 10
... 1. Viscosity= A measure of fluid’s substance to flow 2. Vent= A opening in the surface of earth through which molten rock and gases are released 3. Pyroclastic Material= Volcanic rock during an eruption, including ash, bombs, and blocks 4. Volcano= A mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic Materi ...
... 1. Viscosity= A measure of fluid’s substance to flow 2. Vent= A opening in the surface of earth through which molten rock and gases are released 3. Pyroclastic Material= Volcanic rock during an eruption, including ash, bombs, and blocks 4. Volcano= A mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic Materi ...
Volcano activity
... Monitoring Volcanoes • Geologists are more successful with predicting a volcanic eruption. • Changes around a volcano shows signs of an eruption and allow for a short warning time. – Monitor a volcano with: • Tiltmeters and Laser ranging devices to see ground changes due to shifting magma. • Monito ...
... Monitoring Volcanoes • Geologists are more successful with predicting a volcanic eruption. • Changes around a volcano shows signs of an eruption and allow for a short warning time. – Monitor a volcano with: • Tiltmeters and Laser ranging devices to see ground changes due to shifting magma. • Monito ...
powerpoint_Volcanoes Lava and Types of Eruptions
... Monitoring Volcanoes • Geologists are more successful with predicting a volcanic eruption. • Changes around a volcano shows signs of an eruption and allow for a short warning time. – Monitor a volcano with: • Tiltmeters and Laser ranging devices to see ground changes due to shifting magma. • Monito ...
... Monitoring Volcanoes • Geologists are more successful with predicting a volcanic eruption. • Changes around a volcano shows signs of an eruption and allow for a short warning time. – Monitor a volcano with: • Tiltmeters and Laser ranging devices to see ground changes due to shifting magma. • Monito ...
volcanoes-notes
... • It forms from a quiet eruption. • Lava flows out quietly and for great distances. ...
... • It forms from a quiet eruption. • Lava flows out quietly and for great distances. ...
Geysers: Types: cone (has a cone of “geyserite” around a small vent
... Most common on earth. happens when lava erupts under the ocean Occur mostly at the mid-ocean ridge ...
... Most common on earth. happens when lava erupts under the ocean Occur mostly at the mid-ocean ridge ...
Science 1 Notes: Volcanoes
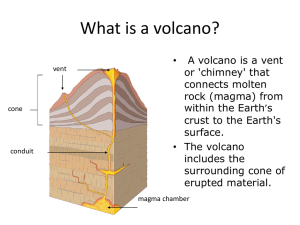
... I. What is a volcano? A volcano is basically a vent (hole in the ground) through which magma can rise to the earth’s surface. Lava flowing from fissures (long cracks in the ground) are more common than volcanoes. Magma is molten rock. Magma, which reaches the surface and flows, is called lava. Lava ...
... I. What is a volcano? A volcano is basically a vent (hole in the ground) through which magma can rise to the earth’s surface. Lava flowing from fissures (long cracks in the ground) are more common than volcanoes. Magma is molten rock. Magma, which reaches the surface and flows, is called lava. Lava ...