5.5 and 5.6 Volcanoes ppt
... builds up in the pipe and plugs it like a cork. When enough pressure builds, it explodes. Quiet eruptions: magma is hot or low in silica and thin and runny. The gases in the magma bubble out gently. This type formed the Hawaiian Islands. ...
... builds up in the pipe and plugs it like a cork. When enough pressure builds, it explodes. Quiet eruptions: magma is hot or low in silica and thin and runny. The gases in the magma bubble out gently. This type formed the Hawaiian Islands. ...
Basalt has a high melting point and is very runny (like honey) – in
... silica content of only 50%. Basalt is also very dense and has a high specific gravity. Examples of shield volcanoes include the Dunedin and Lyttleton volcanoes, and Rangitoto Island. The ‘Organ Pipes’ on Mt Cargill are an example of a basalt formation. Andesite is an intermediate type of magma, and ...
... silica content of only 50%. Basalt is also very dense and has a high specific gravity. Examples of shield volcanoes include the Dunedin and Lyttleton volcanoes, and Rangitoto Island. The ‘Organ Pipes’ on Mt Cargill are an example of a basalt formation. Andesite is an intermediate type of magma, and ...
The Fall of Minoan Civilization Just as an unknown cataclysm struck
... (1700 BC), destroying the palaces and prompting the Minoans to rebuild, another catastrophe occurred at the end of the Neopalatial period (1425 BC). Once again, we do not know what caused the destruction, but unlike the previous catastrophe, the Minoans did not rebuild or recover. Instead, their civ ...
... (1700 BC), destroying the palaces and prompting the Minoans to rebuild, another catastrophe occurred at the end of the Neopalatial period (1425 BC). Once again, we do not know what caused the destruction, but unlike the previous catastrophe, the Minoans did not rebuild or recover. Instead, their civ ...
ppt: volcano intro hook
... Why aren’t all volcanoes the same? Understanding why material comes out of a volcano explosively in one spot and not at another is related to what’s happening under the surface ...
... Why aren’t all volcanoes the same? Understanding why material comes out of a volcano explosively in one spot and not at another is related to what’s happening under the surface ...
Volume II: Hazard Annex Volcanic Eruption
... A.D. was approximately five times larger than the May 18, 1980 event.199 On the night of March 8, 2005, a plume of ash and steam spewed nearly seven miles high into the air. Glowing tendrils of lava were spotted inside the mountain's crater following the explosion.200 The plume rose nearly twice as ...
... A.D. was approximately five times larger than the May 18, 1980 event.199 On the night of March 8, 2005, a plume of ash and steam spewed nearly seven miles high into the air. Glowing tendrils of lava were spotted inside the mountain's crater following the explosion.200 The plume rose nearly twice as ...
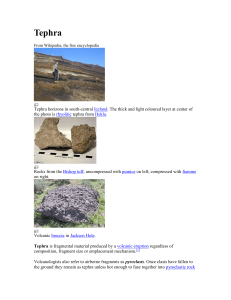
tephra - from wikipedia
... Rocks from the Bishop tuff, uncompressed with pumice on left; compressed with fiamme on right. ...
... Rocks from the Bishop tuff, uncompressed with pumice on left; compressed with fiamme on right. ...
Course Learning Outcomes for Unit IV Reading Assignment Igneous
... a diagram how using these principles can help understand the layers exposed in the Southwestern United States. Fossils and the correlation of rock layers also help geologists to find layers of rock of that formed in the same time and provide a geologic history of an area relative to other areas (USG ...
... a diagram how using these principles can help understand the layers exposed in the Southwestern United States. Fossils and the correlation of rock layers also help geologists to find layers of rock of that formed in the same time and provide a geologic history of an area relative to other areas (USG ...
Word
... 8. The three main classes of rocks are classified by how they formed. (1) _________ rocks form from molten rock. (2) _________ rocks form by surface processes. (3) _________ rocks form from existing rocks that are changed by pressure and temperature. A. (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic B. ...
... 8. The three main classes of rocks are classified by how they formed. (1) _________ rocks form from molten rock. (2) _________ rocks form by surface processes. (3) _________ rocks form from existing rocks that are changed by pressure and temperature. A. (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic B. ...
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 8
... 8. The three main classes of rocks are classified by how they formed. (1) _________ rocks form from molten rock. (2) _________ rocks form by surface processes. (3) _________ rocks form from existing rocks that are changed by pressure and temperature. A. (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic B. ...
... 8. The three main classes of rocks are classified by how they formed. (1) _________ rocks form from molten rock. (2) _________ rocks form by surface processes. (3) _________ rocks form from existing rocks that are changed by pressure and temperature. A. (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic B. ...
7-06 Garces Le Pichon - Laboratory for Atmospheric Acoustics
... technologies in an automated operational system, allowing a better statistical assessment of bolide detections and physical parameters. There appears to be substantial improvements in source models, with an introduction of a quasi-ballistic component of the radiated sound field. There seems to be a ...
... technologies in an automated operational system, allowing a better statistical assessment of bolide detections and physical parameters. There appears to be substantial improvements in source models, with an introduction of a quasi-ballistic component of the radiated sound field. There seems to be a ...
Volcanic Eruption Hazard Annex
... whose top collapsed and formed a huge depression, or caldera, that lies in the remains of Mount Mazama after a series of tremendous explosions occurred approximately 7,600 years ago – the largest kno ...
... whose top collapsed and formed a huge depression, or caldera, that lies in the remains of Mount Mazama after a series of tremendous explosions occurred approximately 7,600 years ago – the largest kno ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. A composite volcano are mostly steep-sided, symmetrical cones of large dimension made of bombs, blocks, cinders, volcanic a ...
... ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. A composite volcano are mostly steep-sided, symmetrical cones of large dimension made of bombs, blocks, cinders, volcanic a ...
chapter 7 - Geophile.net
... * climb the valley side to be above the flow 3. What is the driving force behind the explosive activity of a cinder cone? Where does it come from? * Water in the ground boils to steam. Expanding steam blows basalt cinders out of the vent. 4. On a huge shield volcano such as Mauna Loa, what is the ma ...
... * climb the valley side to be above the flow 3. What is the driving force behind the explosive activity of a cinder cone? Where does it come from? * Water in the ground boils to steam. Expanding steam blows basalt cinders out of the vent. 4. On a huge shield volcano such as Mauna Loa, what is the ma ...
Review for Exam 2
... Be able to define the following terms: aa, basalt plateau, caldera, cinder cone, columnar jointing, composite volcano, dike, extrusive, fissure eruption, lahar, lava, lava dome, lava flow, long period event, magma, nueé ardente, pahoehoe, pillow lava, pyroclastic sheet deposit, shield volcano, sill, ...
... Be able to define the following terms: aa, basalt plateau, caldera, cinder cone, columnar jointing, composite volcano, dike, extrusive, fissure eruption, lahar, lava, lava dome, lava flow, long period event, magma, nueé ardente, pahoehoe, pillow lava, pyroclastic sheet deposit, shield volcano, sill, ...
187 ― PPE For Volcanic Ash Exposures
... Depending on the type of volcano and the force of the eruption a number of different hazards may be present. They can include mudflows and flashfloods, landslides and rock falls, earthquakes, lava flow, falling ash, and the release of potentially harmful gases. According to the United States Centers ...
... Depending on the type of volcano and the force of the eruption a number of different hazards may be present. They can include mudflows and flashfloods, landslides and rock falls, earthquakes, lava flow, falling ash, and the release of potentially harmful gases. According to the United States Centers ...
an integrated framework for global volcano disaster resilience
... USE GLOBAL VOLCANIC ERUPTION DISASTER LABORATORIES AS A BASIS FOR PREPARING FROM “A” (Emergency Response) TO “Z” (Recovery and Reconstruction) ...
... USE GLOBAL VOLCANIC ERUPTION DISASTER LABORATORIES AS A BASIS FOR PREPARING FROM “A” (Emergency Response) TO “Z” (Recovery and Reconstruction) ...
KS4_Volcano_0 - Oxford Sparks
... The location of the best-fitting (spherical) pressure source at depth is shown by a red dot. This was found by comparing observations (left-hand image) to the model (right hand image), for a range of pressure-source locations. www.oxfordsparks.net/volcano ...
... The location of the best-fitting (spherical) pressure source at depth is shown by a red dot. This was found by comparing observations (left-hand image) to the model (right hand image), for a range of pressure-source locations. www.oxfordsparks.net/volcano ...
AP Physics SBHS Petyak
... Discuss the relationships between tsunamis and earthquakes. (9b) Describe two possible effects of a major earthquake on buildings.(9b) List three safety techniques to prevent injury caused by earthquake activity. (IE, 1m) Identify four methods scientists use to forecast earthquake risks. (9b ...
... Discuss the relationships between tsunamis and earthquakes. (9b) Describe two possible effects of a major earthquake on buildings.(9b) List three safety techniques to prevent injury caused by earthquake activity. (IE, 1m) Identify four methods scientists use to forecast earthquake risks. (9b ...
Lab 3: Volcanic Hazards
... Suppose you have been assigned a job with the Volcanic Hazards Program of the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and were asked to provide a hazard analysis of several active volcanic locations. What would you need to know in order to complete your analysis? How would you approach this study? Wh ...
... Suppose you have been assigned a job with the Volcanic Hazards Program of the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and were asked to provide a hazard analysis of several active volcanic locations. What would you need to know in order to complete your analysis? How would you approach this study? Wh ...
Kelud volcano
... The composition of the lake is rather unusual and corresponds to a near neutral (pH∼6), relatively diluted water with a TDS of a few g.kg-1 (Table 2.2). This neutral composition contrasts with the highly acidic waters (pH=0-3) most frequently observed in active crater lakes where the discharge of ma ...
... The composition of the lake is rather unusual and corresponds to a near neutral (pH∼6), relatively diluted water with a TDS of a few g.kg-1 (Table 2.2). This neutral composition contrasts with the highly acidic waters (pH=0-3) most frequently observed in active crater lakes where the discharge of ma ...
chapter 6 - Geophile.net
... * The ash gets into the engine and the engine heat melts it. It coats the inside of the engine and can stop it, causing the plane to crash. 10. What causes a big bulge to slowly grow on the flank of an active Cascades volcano? * It grows because rising magma is pushing it up 11. If you visit Mount S ...
... * The ash gets into the engine and the engine heat melts it. It coats the inside of the engine and can stop it, causing the plane to crash. 10. What causes a big bulge to slowly grow on the flank of an active Cascades volcano? * It grows because rising magma is pushing it up 11. If you visit Mount S ...
VOLCANOES AND IGNEOUS ENVIRONMENTS
... A volcano is an opening in the Earth’s crust where magma reaches Earth’s surface. Causes of Volcanic Eruptions 1. Magma has gases dissolved in it, such as H2O, SO2 (sulfur dioxide), and CO2 2. These gases expand and build up pressure as the magma rises through the lithosphere until finally enough pr ...
... A volcano is an opening in the Earth’s crust where magma reaches Earth’s surface. Causes of Volcanic Eruptions 1. Magma has gases dissolved in it, such as H2O, SO2 (sulfur dioxide), and CO2 2. These gases expand and build up pressure as the magma rises through the lithosphere until finally enough pr ...
Chapter 1 Study Questions
... 4. Explain fractional crystallization, partial melting, and assimilation. How do magma evolve by these three different mechanisms? 5. How do OIBs differ from MORBs and why? Chapter 3 ...
... 4. Explain fractional crystallization, partial melting, and assimilation. How do magma evolve by these three different mechanisms? 5. How do OIBs differ from MORBs and why? Chapter 3 ...
Volcano Lesson
... accumulation of material erupted through the conduit and increases in size as lava, cinders, ash, etc., are added to its slopes. Shield volcanoes, the third type of volcano, are built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or grou ...
... accumulation of material erupted through the conduit and increases in size as lava, cinders, ash, etc., are added to its slopes. Shield volcanoes, the third type of volcano, are built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or grou ...
Mount Etna

Mount Etna (Italian: Etna, Sicilian: Mungibeddu or â Muntagna, Latin: Aetna) is an active stratovolcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Province of Catania, between Messina and Catania. It lies above the convergent plate margin between the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is the tallest active volcano on the European continent, currently 3,329 m (10,922 ft) high, though this varies with summit eruptions. It is the highest mountain in Italy south of the Alps. Etna covers an area of 1,190 km2 (459 sq mi) with a basal circumference of 140 km. This makes it by far the largest of the three active volcanoes in Italy, being about two and a half times the height of the next largest, Mount Vesuvius. Only Mount Teide in Tenerife surpasses it in the whole of the European–North-African region. In Greek Mythology, the deadly monster Typhon was trapped under this mountain by Zeus, the god of the sky and thunder and king of gods, and the forges of Hephaestus were said to also be located underneath it.Mount Etna is one of the most active volcanoes in the world and is in an almost constant state of activity. The fertile volcanic soils support extensive agriculture, with vineyards and orchards spread across the lower slopes of the mountain and the broad Plain of Catania to the south. Due to its history of recent activity and nearby population, Mount Etna has been designated a Decade Volcano by the United Nations. In June 2013, it was added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.