2. Volcanism 2.1. Volcanoes and plate tectonics
... 2.5. Types of eruptions and volcanoes Two categories of eruptions can be distinguished: central eruptions and fissure eruptions. The former are associated with volcanoes in which lava and other volcanic material are ejected from a central vent. The latter are eruptions during which lava erupts from ...
... 2.5. Types of eruptions and volcanoes Two categories of eruptions can be distinguished: central eruptions and fissure eruptions. The former are associated with volcanoes in which lava and other volcanic material are ejected from a central vent. The latter are eruptions during which lava erupts from ...
Identifying volcanic rocks
... What to do Which rock? Completed chart Introduction/background There are many different types of volcanoes around New Zealand, from volcanic fields in the north, to cone volcanoes and calderas in the south. Each type of volcano is associated with a different type of lava, which cools to form rocks. ...
... What to do Which rock? Completed chart Introduction/background There are many different types of volcanoes around New Zealand, from volcanic fields in the north, to cone volcanoes and calderas in the south. Each type of volcano is associated with a different type of lava, which cools to form rocks. ...
Debris Avalanches
... Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an eruption or an earthquake. They can travel up to 50 miles from their source, burying everythin ...
... Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an eruption or an earthquake. They can travel up to 50 miles from their source, burying everythin ...
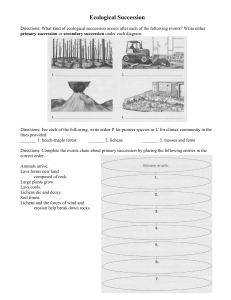
Ecological Succession
... species over time? A. An ecosystem with only pioneer species B. An ecosystem that is in primary succession C. An ecosystem that is in secondary succession D. An ecosystem with a climax community ...
... species over time? A. An ecosystem with only pioneer species B. An ecosystem that is in primary succession C. An ecosystem that is in secondary succession D. An ecosystem with a climax community ...
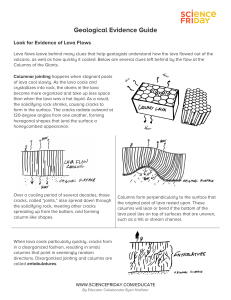
Geological Evidence Guide
... Igneous rocks that contain large interlocking mineral crystals (what geologists call a coarsegrained texture) formed from magma that slowly cooled and solidified miles beneath earth’s surface over a period of millions of years. ...
... Igneous rocks that contain large interlocking mineral crystals (what geologists call a coarsegrained texture) formed from magma that slowly cooled and solidified miles beneath earth’s surface over a period of millions of years. ...
Lecture Outlines Natural Disasters, 6th edition
... Plate-Tectonic Setting of Volcanoes Revisited • Spreading centers have abundant volcanism because: – Sit above hot asthenosphere – Asthenosphere has low SiO2 – Plates pull apart so asthenosphere rises and melts under low pressure, changing to high-temperature, low SiO2, low volatile, low viscosity ...
... Plate-Tectonic Setting of Volcanoes Revisited • Spreading centers have abundant volcanism because: – Sit above hot asthenosphere – Asthenosphere has low SiO2 – Plates pull apart so asthenosphere rises and melts under low pressure, changing to high-temperature, low SiO2, low volatile, low viscosity ...
Types of Rocks
... Small Plutons (body of plutonic rock of any size or shape, intrusive rock - i.e. have intruded into the host rock) i) Dikes - discordant - cut across layers ii) Sills - concordant - parallel to layers Laccolith - concordant - more or less circular in shape, up to 3 km across b) Deep Batholith - cont ...
... Small Plutons (body of plutonic rock of any size or shape, intrusive rock - i.e. have intruded into the host rock) i) Dikes - discordant - cut across layers ii) Sills - concordant - parallel to layers Laccolith - concordant - more or less circular in shape, up to 3 km across b) Deep Batholith - cont ...
No Slide Title
... 8:33:00 a.m. A cubic mile of mountain gives way, traveling at 70 to 150 mph, and superheated rocks in the volcano's core are suddenly exposed, shooting a lateral blast of gas north, incinerating everything in its path. Huge glaciers on the mountain's peak melt instantly. ...
... 8:33:00 a.m. A cubic mile of mountain gives way, traveling at 70 to 150 mph, and superheated rocks in the volcano's core are suddenly exposed, shooting a lateral blast of gas north, incinerating everything in its path. Huge glaciers on the mountain's peak melt instantly. ...
The Critical Zone What is a caldera? The Valles Caldera
... Teacher’s Notes: 1) Circular feature seen is the Valles Caldera— have the students right click, select Measure Distance, note distance of caldera width, and right click to clear the measurement. Students should repeat for examples in step 2. 2) Mauna Loa is an example of shield volcano collapse with ...
... Teacher’s Notes: 1) Circular feature seen is the Valles Caldera— have the students right click, select Measure Distance, note distance of caldera width, and right click to clear the measurement. Students should repeat for examples in step 2. 2) Mauna Loa is an example of shield volcano collapse with ...
TURNING 2011`S DISASTERS INTO EDUCATIONAL SURGES
... divergent boundary between the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates that is marked by volcanic eruptions and the associated volcano hazards. ...
... divergent boundary between the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates that is marked by volcanic eruptions and the associated volcano hazards. ...
Mt. Vesuvius - Central Square School District
... Herculaneum and Pompeii. • The city was abandoned and its location forgotten until 1595. ...
... Herculaneum and Pompeii. • The city was abandoned and its location forgotten until 1595. ...
SSSI citation
... area has multiple geological interest. Sediments occur as a thin sequence beneath lava flows and the significant volcanic rocks occur as thin sheets or sills which cut through pre-existing rocks. The abundantly vegetated cliffs are covered with coastal grassland with occasional coastal heath. Cliff ...
... area has multiple geological interest. Sediments occur as a thin sequence beneath lava flows and the significant volcanic rocks occur as thin sheets or sills which cut through pre-existing rocks. The abundantly vegetated cliffs are covered with coastal grassland with occasional coastal heath. Cliff ...
SiO 2 - Bakersfield College
... •Western U.S. coast, Western South American coast, Japan • typically form in the ocean along continent convergent boundaries • found along the ring of fire Steep high angle flanks ...
... •Western U.S. coast, Western South American coast, Japan • typically form in the ocean along continent convergent boundaries • found along the ring of fire Steep high angle flanks ...
CASCADES OF LAVA. 441 through these numerous craters into the
... plete silence, and without any convulsion of the ground. Of the mountain, Mouna Loa, itself, a fearful ertiption took place in 1840, and it has since given repeated evidences of its activity. An eruption also occurred in 1843 from a crater about 2000 feet below the summit. A river of lava pouring do ...
... plete silence, and without any convulsion of the ground. Of the mountain, Mouna Loa, itself, a fearful ertiption took place in 1840, and it has since given repeated evidences of its activity. An eruption also occurred in 1843 from a crater about 2000 feet below the summit. A river of lava pouring do ...
Geo 102 Practice Exam 1: True or false, to be considered a mineral
... 25. True or false, Mafic rocks are high in iron and magnesium, but low in silica content. 26. True or false, explosive volcanoes have high viscosity magma. 27. Scenario: You are a prominent Volcanologist and are studying a volcano that is on the verge of an eruption. You are trying to determine whic ...
... 25. True or false, Mafic rocks are high in iron and magnesium, but low in silica content. 26. True or false, explosive volcanoes have high viscosity magma. 27. Scenario: You are a prominent Volcanologist and are studying a volcano that is on the verge of an eruption. You are trying to determine whic ...
Subduction Tephra - Centralia College
... Pahto (Mount Adams) and Wy-east (Mount Hood) fought over a young maiden, Loo-wit Lat-kla An eruption from the Goat Rocks dome as painted by Paul Kane in 1847 ...
... Pahto (Mount Adams) and Wy-east (Mount Hood) fought over a young maiden, Loo-wit Lat-kla An eruption from the Goat Rocks dome as painted by Paul Kane in 1847 ...
Review - WordPress.com
... composite volcano flowing an explosive eruption • Yellowstone-type: collapse of large area, caused by discharge of huge volumes of silica-rich pumice and ash along ring fractures ...
... composite volcano flowing an explosive eruption • Yellowstone-type: collapse of large area, caused by discharge of huge volumes of silica-rich pumice and ash along ring fractures ...
(from Mountain site or ones you find) Image of example
... to the surface. A volcano is a type of mountain. There are about 1,510 active volcanoes in the world. Over half are located around the Pacific Ocean on the Ring of Fire. The crust is made of Plates that sometimes move. When one plate is forced under another, Magma can be squeezed up through two plat ...
... to the surface. A volcano is a type of mountain. There are about 1,510 active volcanoes in the world. Over half are located around the Pacific Ocean on the Ring of Fire. The crust is made of Plates that sometimes move. When one plate is forced under another, Magma can be squeezed up through two plat ...
Mid-Atlantic Ridge Volcanic Processes How Erupting Lava Forms Earth’s Anatomy
... Joe Cann says he is old enough to remember before there were any plate tectonics, but still young enough to enjoy research on mid-ocean ridges. He visits Woods Hole out of season, when the rents on the Cape are lower, from his base in the UK at the University of Leeds. ...
... Joe Cann says he is old enough to remember before there were any plate tectonics, but still young enough to enjoy research on mid-ocean ridges. He visits Woods Hole out of season, when the rents on the Cape are lower, from his base in the UK at the University of Leeds. ...
mid-oceanic ridges
... Joe Cann says he is old enough to remember before there were any plate tectonics, but still young enough to enjoy research on mid-ocean ridges. He visits Woods Hole out of season, when the rents on the Cape are lower, from his base in the UK at the University of Leeds. ...
... Joe Cann says he is old enough to remember before there were any plate tectonics, but still young enough to enjoy research on mid-ocean ridges. He visits Woods Hole out of season, when the rents on the Cape are lower, from his base in the UK at the University of Leeds. ...
Partially Melt Mantle
... What happens when magma intrudes into rock? -Rock intruded into is “Country Rock” – could be anything. Heat from the magma will “bake” part of the country rock. Magma cools underground and has a coarse-grained (Phaneritic) texture. Hot rock up against the cool rock – it’ll cool quickly – so there is ...
... What happens when magma intrudes into rock? -Rock intruded into is “Country Rock” – could be anything. Heat from the magma will “bake” part of the country rock. Magma cools underground and has a coarse-grained (Phaneritic) texture. Hot rock up against the cool rock – it’ll cool quickly – so there is ...
Document
... since water usually slows down when going around the inner bank of a curve. In Iceland, however, oblique sand or gravel bars left by over· loaded glacial meltwaters are often present in the curves at such an angle that the force of the flow may be deflected inward, causing erosion. One of the world' ...
... since water usually slows down when going around the inner bank of a curve. In Iceland, however, oblique sand or gravel bars left by over· loaded glacial meltwaters are often present in the curves at such an angle that the force of the flow may be deflected inward, causing erosion. One of the world' ...
Erupting Volcano Model (916k PDF file)
... built by both loose fragmented material and lava flows. Conduit – The passage that the magma follows through a volcano. Crater – The hollow summit of a volcano above the vent; usually bowl-shaped and has steep sides. Dike – Sheet-like bodies of magma that cut through layers of adjacent rock. Domes – ...
... built by both loose fragmented material and lava flows. Conduit – The passage that the magma follows through a volcano. Crater – The hollow summit of a volcano above the vent; usually bowl-shaped and has steep sides. Dike – Sheet-like bodies of magma that cut through layers of adjacent rock. Domes – ...
Silverthrone Caldera

The Silverthrone Caldera is a potentially active caldera complex in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located over 350 kilometres (220 mi) northwest of the city of Vancouver and about 50 kilometres (31 mi) west of Mount Waddington in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The caldera is one of the largest of the few calderas in western Canada, measuring about 30 kilometres (19 mi) long (north-south) and 20 kilometres (12 mi) wide (east-west). Mount Silverthrone, an eroded lava dome on the caldera's northern flank that is 2,864 metres (9,396 ft) high may be the highest volcano in Canada.The main glaciers in the Silverthrone area are the Pashleth, Kingcome, Trudel, Klinaklini and Silverthrone glaciers. Most of the caldera lies in the Ha-Iltzuk Icefield, which is the largest icefield in the southern half of the Coast Mountains; it is one of the five icefields in southwestern British Columbia that thinned between the mid-1980s and 1999 due to global warming. Nearly half of the icefield is drained by the Klinaklini Glacier, which feeds the Klinaklini River.The Silverthrone Caldera is very remote and rarely visited or studied by geoscientists, such as volcanologists. It can be reached by helicopter or — with major difficulty — by hiking along one of the several river valleys extending from the British Columbia Coast or from the Interior Plateau.