4 - Weber State University
... increase by ____________ shifting the IS curve from IS0 to IS1 and crowding out is approximately ____________. A) 500, 500 B) 250, 500 C) 1000, 1000 D) 1000, 250 31) If spending is not responsive to changes in the interest rate then the A) LM curve is vertical. B) IS and LM curves are vertical. C) I ...
... increase by ____________ shifting the IS curve from IS0 to IS1 and crowding out is approximately ____________. A) 500, 500 B) 250, 500 C) 1000, 1000 D) 1000, 250 31) If spending is not responsive to changes in the interest rate then the A) LM curve is vertical. B) IS and LM curves are vertical. C) I ...
GROWTH AND INFLATION IN SOUTH AFRICA: IS THERE
... changes in the South African economy. The early 1970s present a breakpoint following the abandonment of the Bretton Woods system in 1971 and the oil price shock in 1973. In contrast to the low and stable inflation rates experienced during the 1960s, exchange rate devaluations during the early 1970s ...
... changes in the South African economy. The early 1970s present a breakpoint following the abandonment of the Bretton Woods system in 1971 and the oil price shock in 1973. In contrast to the low and stable inflation rates experienced during the 1960s, exchange rate devaluations during the early 1970s ...
Parkin-Bade Chapter 21
... New Goods Bias New goods that were not available in the base year appear and, if they are more expensive than the goods they replace, they put an upward bias into the CPI. Quality Change Bias Quality improvements occur every year. Part of the rise in the price is payment for improved quality and is ...
... New Goods Bias New goods that were not available in the base year appear and, if they are more expensive than the goods they replace, they put an upward bias into the CPI. Quality Change Bias Quality improvements occur every year. Part of the rise in the price is payment for improved quality and is ...
Chapter27 - Web.UVic.ca
... Interest Rates and Inflation Why Inflation Influences the Nominal Interest Rate On the average, and other things remaining the same, a 1 percentage point rise in the inflation rate leads to a 1 percentage point rise in the nominal interest rate. Why? The answer is that the financial capital market ...
... Interest Rates and Inflation Why Inflation Influences the Nominal Interest Rate On the average, and other things remaining the same, a 1 percentage point rise in the inflation rate leads to a 1 percentage point rise in the nominal interest rate. Why? The answer is that the financial capital market ...
PDF
... that population ageing modifies the decisions on environmental preservation (the willingness to preserve the environment increases if people die later) and increases the detrimental effect produced by an individual’s consumption. They also assume that the per capita environmental quality enters the ...
... that population ageing modifies the decisions on environmental preservation (the willingness to preserve the environment increases if people die later) and increases the detrimental effect produced by an individual’s consumption. They also assume that the per capita environmental quality enters the ...
7. Medium-Term Projections
... Accelerating capital inflows and weak global economic outlook may aggravate macro financial risks, should they persist for a while. The recent policies pursued by the CBRT aim to prevent the build-up of risks arising from long-lasting capital inflows. In this respect, in order to prevent rapid credi ...
... Accelerating capital inflows and weak global economic outlook may aggravate macro financial risks, should they persist for a while. The recent policies pursued by the CBRT aim to prevent the build-up of risks arising from long-lasting capital inflows. In this respect, in order to prevent rapid credi ...
ANALYSIS OF THE ZIMBABWEAN HYPERINFLATION CRISIS: A
... work in the field of hyperinflation. In particular, I will review the paper “Modern Hyperand High Inflations” by Fischer et al. (2002), which provides an overview of topics currently being researched, along with useful findings of its own. As seen by the title of their paper, Fischer et al. have bro ...
... work in the field of hyperinflation. In particular, I will review the paper “Modern Hyperand High Inflations” by Fischer et al. (2002), which provides an overview of topics currently being researched, along with useful findings of its own. As seen by the title of their paper, Fischer et al. have bro ...
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... continually bombarded by various shocks. These shocks have an immediate impact on the economy’s short-run equilibrium, and they also affect the subsequent path of output, inflation, and many other variables. The dynamic AD –AS model focuses attention on how output and inflation respond over time to ...
... continually bombarded by various shocks. These shocks have an immediate impact on the economy’s short-run equilibrium, and they also affect the subsequent path of output, inflation, and many other variables. The dynamic AD –AS model focuses attention on how output and inflation respond over time to ...
Slide 1
... 16. Which of the following policy choices represents a combination of fiscal and monetary policies designed to bring the economy out of a recession? (a) Decreasing both taxes and the money supply (b) Increasing both taxes and the money supply (c) Increasing government spending and decreasing the fe ...
... 16. Which of the following policy choices represents a combination of fiscal and monetary policies designed to bring the economy out of a recession? (a) Decreasing both taxes and the money supply (b) Increasing both taxes and the money supply (c) Increasing government spending and decreasing the fe ...
Stephen J. Working OF INTEREST RATES
... larger variance in policy will translate to a larger variance in the rates. Secondly, by influencing private speculative behavior, it also has another indirect effect. This may either reinforce or counteract the direct effect, depending upon the nature of the disturbance. The remainder of the paper ...
... larger variance in policy will translate to a larger variance in the rates. Secondly, by influencing private speculative behavior, it also has another indirect effect. This may either reinforce or counteract the direct effect, depending upon the nature of the disturbance. The remainder of the paper ...
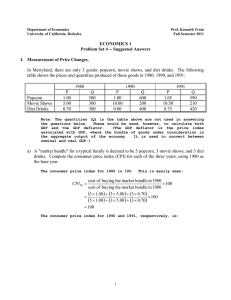
Answers. - University of California, Berkeley
... Note: The quantities (Q) in the table above are not used in answering the questions below. These would be used, however, to calculate both GDP and the GDP deflator. (The GDP deflator is the price index associated with GDP, where the bundle of goods under consideration is the aggregate output of the ...
... Note: The quantities (Q) in the table above are not used in answering the questions below. These would be used, however, to calculate both GDP and the GDP deflator. (The GDP deflator is the price index associated with GDP, where the bundle of goods under consideration is the aggregate output of the ...
Milton Friedman`s economics and political economy
... realism of assumptions for economic theory: “(T)he relevant question to ask about the “assumptions” of a theory is not whether they are descriptively “realistic,” for they never are, but whether they are sufficiently goo approximations for the purpose in hand. And this question can only be answered ...
... realism of assumptions for economic theory: “(T)he relevant question to ask about the “assumptions” of a theory is not whether they are descriptively “realistic,” for they never are, but whether they are sufficiently goo approximations for the purpose in hand. And this question can only be answered ...
Optimal fiscal and monetary policy action in a closed economy!
... embarked on the di¢ cult task of reducing their public debts at a time of stagnant or negative growth.1 What is the best policy reaction to economic conditions within this environment? In this paper, we search for the best mix of monetary and …scal policy actions in a closed economy, when the policy ...
... embarked on the di¢ cult task of reducing their public debts at a time of stagnant or negative growth.1 What is the best policy reaction to economic conditions within this environment? In this paper, we search for the best mix of monetary and …scal policy actions in a closed economy, when the policy ...
Macroecon_Practice_Exam
... 16. Which of the following policy choices represents a combination of fiscal and monetary policies designed to bring the economy out of a recession? (a) Decreasing both taxes and the money supply (b) Increasing both taxes and the money supply (c) Increasing government spending and decreasing the fe ...
... 16. Which of the following policy choices represents a combination of fiscal and monetary policies designed to bring the economy out of a recession? (a) Decreasing both taxes and the money supply (b) Increasing both taxes and the money supply (c) Increasing government spending and decreasing the fe ...
PPT - HNB
... and in 2012 they relate to the assumption of shipyards loans by the Ministry of Finance and the transaction of one bank which, aiming to reduce its partly recoverable and irrecoverable placements transferred a portion of its claims to a company indirectly owned by the parent bank. One-off effects in ...
... and in 2012 they relate to the assumption of shipyards loans by the Ministry of Finance and the transaction of one bank which, aiming to reduce its partly recoverable and irrecoverable placements transferred a portion of its claims to a company indirectly owned by the parent bank. One-off effects in ...
Chapter 24 The Open Economy with Fixed Exchange Rates
... of international trade. Thus, while the western countries liberalized their international trade regimes by reducing tariffs and eliminating quantitative restrictions on imports, they maintained substantial restrictions on the private export and import of capital. One motivation for this policy was th ...
... of international trade. Thus, while the western countries liberalized their international trade regimes by reducing tariffs and eliminating quantitative restrictions on imports, they maintained substantial restrictions on the private export and import of capital. One motivation for this policy was th ...
MacroPractice
... while the M2 money supply remains constant at the same time. 67. List and describe the three functions of money. 68. Describe the differences between M1 and M2. 69. Explain why it is not necessary for paper money to be backed by some commodity (e.g. gold) before it can ...
... while the M2 money supply remains constant at the same time. 67. List and describe the three functions of money. 68. Describe the differences between M1 and M2. 69. Explain why it is not necessary for paper money to be backed by some commodity (e.g. gold) before it can ...
Document
... Printing money to raise revenue causes inflation. Inflation is like a tax on people who hold money. © 2008 Worth Publishers ...
... Printing money to raise revenue causes inflation. Inflation is like a tax on people who hold money. © 2008 Worth Publishers ...
Monetary policy

Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting an inflation rate or interest rate to ensure price stability and general trust in the currency.Further goals of a monetary policy are usually to contribute to economic growth and stability, to lower unemployment, and to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies.Monetary economics provides insight into how to craft optimal monetary policy.Monetary policy is referred to as either being expansionary or contractionary, where an expansionary policy increases the total supply of money in the economy more rapidly than usual, and contractionary policy expands the money supply more slowly than usual or even shrinks it. Expansionary policy is traditionally used to try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates in the hope that easy credit will entice businesses into expanding. Contractionary policy is intended to slow inflation in order to avoid the resulting distortions and deterioration of asset values.Monetary policy differs from fiscal policy, which refers to taxation, government spending, and associated borrowing.