Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... • rocks, gases and events from observed eruptions compared to similar lavas elsewhere to infer the nature of past activity ...
... • rocks, gases and events from observed eruptions compared to similar lavas elsewhere to infer the nature of past activity ...
Explosive eruptions
... II bunker with a bird's eye view of Honolulu. (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Diamond-HeadHawaii-Nov-2001.jpg) ...
... II bunker with a bird's eye view of Honolulu. (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Diamond-HeadHawaii-Nov-2001.jpg) ...
Chapter 4 volcanoes powerpoint notes
... Lava plateaus are formed by highly fluid (i.e. runny) basaltic lava during numerous successive eruptions through numerous linear fissures or rifts. See the layers or flows of lava? ...
... Lava plateaus are formed by highly fluid (i.e. runny) basaltic lava during numerous successive eruptions through numerous linear fissures or rifts. See the layers or flows of lava? ...
Types of Volcanoes
... An eruption begins when pressure on a magma chamber forces magma up through the conduit and out the volcano's vents. When the magma chamber has been completely filled, the type of eruption partly depends on the amount of gases and silica in the magma. The amount of silica determines how sticky (leve ...
... An eruption begins when pressure on a magma chamber forces magma up through the conduit and out the volcano's vents. When the magma chamber has been completely filled, the type of eruption partly depends on the amount of gases and silica in the magma. The amount of silica determines how sticky (leve ...
File
... 3. A composite volcano is formed when both lava and ash erupt from a vent. The materials pile up in alternate layers around the vent and form a cone-shaped mountain that comes to a point on top. (Examples: Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount Vesuvius in Italy.) 4. Divide your class into three groups, and ass ...
... 3. A composite volcano is formed when both lava and ash erupt from a vent. The materials pile up in alternate layers around the vent and form a cone-shaped mountain that comes to a point on top. (Examples: Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount Vesuvius in Italy.) 4. Divide your class into three groups, and ass ...
What can low frequency seismicity tell us about eruption processes
... Frequently-active subduction zone volcanoes of intermediate composition (andesite to dacite) exhibit a range of different eruption mechanisms. They can pose a significant hazard to surrounding populations, and a considerable challenge to management agencies. Activity at these volcanoes can also gene ...
... Frequently-active subduction zone volcanoes of intermediate composition (andesite to dacite) exhibit a range of different eruption mechanisms. They can pose a significant hazard to surrounding populations, and a considerable challenge to management agencies. Activity at these volcanoes can also gene ...
Cinder Cone Volcanoes!
... material (tephra) and water that flows down the side of a volcano Can flow down the side of the volcano at 60 mph. At Pinatubo, Lahars were formed by the typhoon that was passing through the area at the time, increasing ...
... material (tephra) and water that flows down the side of a volcano Can flow down the side of the volcano at 60 mph. At Pinatubo, Lahars were formed by the typhoon that was passing through the area at the time, increasing ...
Volcanic Eruptions 3.3
... Pumice forms when lava cools quick and traps air bubbles inside Obsidian forms when lava cools quick leaving the surface smooth and glass-like ...
... Pumice forms when lava cools quick and traps air bubbles inside Obsidian forms when lava cools quick leaving the surface smooth and glass-like ...
Volume II: Hazard Annex Volcanic Eruption
... ships in port, and closed the ports of Portland, Vancouver, and Kalama for over a month. Several water and sewage treatment facilities were also damaged or destroyed. The estimated damage attributed to the eruption was $1.1 billion.197 The May 18, 1980 eruption was preceded by about two months of pr ...
... ships in port, and closed the ports of Portland, Vancouver, and Kalama for over a month. Several water and sewage treatment facilities were also damaged or destroyed. The estimated damage attributed to the eruption was $1.1 billion.197 The May 18, 1980 eruption was preceded by about two months of pr ...
WebQuest Questions - Tenafly Public Schools
... 5. Pompeii lay untouched and undiscovered until its discovery in the _______________ and excavation beginning in the ____________________________. 6. Click on Public Life: Pompeii was a _____________________ town. It included a _______________, an open square of marketplace. This part of the city is ...
... 5. Pompeii lay untouched and undiscovered until its discovery in the _______________ and excavation beginning in the ____________________________. 6. Click on Public Life: Pompeii was a _____________________ town. It included a _______________, an open square of marketplace. This part of the city is ...
76 Volcanism and Igneous Processes I. Introduction A. Volcanism
... Composite cones or Strato Volcano- Volcanos comprised of a mixture or alternating layers of lava and pyroclastic material, generally form large Volcanos, often associated with violent eruptions (e.g. MT. St. Helens) and andesitic magmas (sl. more siliceous than basalt). a. ...
... Composite cones or Strato Volcano- Volcanos comprised of a mixture or alternating layers of lava and pyroclastic material, generally form large Volcanos, often associated with violent eruptions (e.g. MT. St. Helens) and andesitic magmas (sl. more siliceous than basalt). a. ...
Slide 1
... • Much rarer than non-explosive eruptions • Incredibly destructive • Clouds of hot debris, ash, and gas rapidly shoot out from a volcano • Causes molten rock to be blown into tiny particles that harden in the air • Blast millions of tons of lava and rock • Can demolish an entire mountainside ...
... • Much rarer than non-explosive eruptions • Incredibly destructive • Clouds of hot debris, ash, and gas rapidly shoot out from a volcano • Causes molten rock to be blown into tiny particles that harden in the air • Blast millions of tons of lava and rock • Can demolish an entire mountainside ...
Study questions for Exam #2
... 10) About how long a time period did this precursor activity occur for prior to the May 18th eruption? 11) Whys did the volcano erupt with a lateral blast directed to the north? 12) How much magma was erupted by Mt St Helens on May 18th, 1980. 13) Over how long a time period did the eruption last? 1 ...
... 10) About how long a time period did this precursor activity occur for prior to the May 18th eruption? 11) Whys did the volcano erupt with a lateral blast directed to the north? 12) How much magma was erupted by Mt St Helens on May 18th, 1980. 13) Over how long a time period did the eruption last? 1 ...
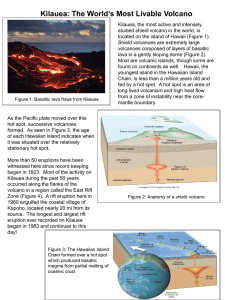
Kilauea: The World`s Most Livable Volcano
... Chain, is less than a million years old and fed by a hot spot. A hot spot is an area of long lived volcanism and high heat flow from a zone of instability near the coremantle boundary. ...
... Chain, is less than a million years old and fed by a hot spot. A hot spot is an area of long lived volcanism and high heat flow from a zone of instability near the coremantle boundary. ...
Mount Etna Kilauea
... volcano. Paricutin had an active lifespan of 9 years, killing 3 people in this time period. Paricutin formed as part of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic belt, which includes many other volcanoes. In its first eruption, Paricutin rose 50 m high, spraying rock fragments ranging from the size of cinders to v ...
... volcano. Paricutin had an active lifespan of 9 years, killing 3 people in this time period. Paricutin formed as part of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic belt, which includes many other volcanoes. In its first eruption, Paricutin rose 50 m high, spraying rock fragments ranging from the size of cinders to v ...
Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
... Composite Volcanoes • Composite cones or stratovolcanoes – Located around the Ring of Fire ...
... Composite Volcanoes • Composite cones or stratovolcanoes – Located around the Ring of Fire ...
3 types of Volcanoes Reading
... than Mount Everest, the tallest mountain on land. Cinder cone volcanoes are small volcanic cones made entirely of pyroclastic material from moderately explosive eruptions. The pyroclastic material forms steeper slopes with a narrower base than the lava flows of shield volcanoes, as you can see in th ...
... than Mount Everest, the tallest mountain on land. Cinder cone volcanoes are small volcanic cones made entirely of pyroclastic material from moderately explosive eruptions. The pyroclastic material forms steeper slopes with a narrower base than the lava flows of shield volcanoes, as you can see in th ...
Unit 3 Section 2 Volcanoes Answer Key - WAHS
... plugged, gasses cannot escape and pressure builds. The pressure can be released in a volcanic eruption that blasts pieces of lava and rock into the atmosphere. (pyroclastics) A composite cone forms by many eruptions of material with medium or high-silica content. They erupt violently when pressure b ...
... plugged, gasses cannot escape and pressure builds. The pressure can be released in a volcanic eruption that blasts pieces of lava and rock into the atmosphere. (pyroclastics) A composite cone forms by many eruptions of material with medium or high-silica content. They erupt violently when pressure b ...
Volcanism 3
... • Dynamic types related to magma/water interactions • Dynamic types related to dissolved bubbles • Dynamic types related to domes growth and collapse • Dynamic types related to lava flows etc. • Complex edifices • Destruction of volcanic edifices ...
... • Dynamic types related to magma/water interactions • Dynamic types related to dissolved bubbles • Dynamic types related to domes growth and collapse • Dynamic types related to lava flows etc. • Complex edifices • Destruction of volcanic edifices ...
Exam 2 Review Sheet Handout Page
... 1) What are the 2 most abundant elements in Earth’s crust? 2) What is a mineral (definition)? 3) What is a mineraloid? 4) What is an atom? What is it composed of? 5) What is the atomic number? The atomic mass? 6) What is an isotope? 7) Be able to calculate the number of protons and neutrons if given ...
... 1) What are the 2 most abundant elements in Earth’s crust? 2) What is a mineral (definition)? 3) What is a mineraloid? 4) What is an atom? What is it composed of? 5) What is the atomic number? The atomic mass? 6) What is an isotope? 7) Be able to calculate the number of protons and neutrons if given ...
Volcanic Landforms (pages 217*223)
... often found in areas of present or past volcanic activity. ...
... often found in areas of present or past volcanic activity. ...
Teacher`s Guide - Discovery Education
... and in all directions, floating on a hot layer of rocks. pyroclastic flow Definition: Eruption from a volcano consisting primarily of fragmented rock. Context: The blast wave traveled downslope at the speed of sound, flattening whole forests and blasting 600 tons of ash into the atmosphere. Pyroclas ...
... and in all directions, floating on a hot layer of rocks. pyroclastic flow Definition: Eruption from a volcano consisting primarily of fragmented rock. Context: The blast wave traveled downslope at the speed of sound, flattening whole forests and blasting 600 tons of ash into the atmosphere. Pyroclas ...
3-2 Notes: Volcanoes Eruptions • Volcano
... • Cone-shaped; built up by alternating ___________________ of lava and rock fragments. • Magma is high in ___________________ • Tends to be steep near the top and flattens out toward the ____________________. – Example: Mt. Fuji, Japan • Composite volcanoes have _____________________ eruptions becau ...
... • Cone-shaped; built up by alternating ___________________ of lava and rock fragments. • Magma is high in ___________________ • Tends to be steep near the top and flattens out toward the ____________________. – Example: Mt. Fuji, Japan • Composite volcanoes have _____________________ eruptions becau ...
Volcano - Curriculum Visions
... The molten material from inside the Earth that rises to form a volcano The solid rock core of an extinct volcano A volcano near Naples, Italy that once buried Roman Pompeii A pebble-sized lump of rock thrown out of a volcano A famous geyser in Yellowstone National Park (2 Words) A rock formed when a ...
... The molten material from inside the Earth that rises to form a volcano The solid rock core of an extinct volcano A volcano near Naples, Italy that once buried Roman Pompeii A pebble-sized lump of rock thrown out of a volcano A famous geyser in Yellowstone National Park (2 Words) A rock formed when a ...
Mount St. Helens

Mount St. Helens or Louwala-Clough (known as Lawetlat'la to the indigenous Cowlitz people, and Loowit to the Klickitat) is an active stratovolcano located in Skamania County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is 96 miles (154 km) south of Seattle, Washington, and 50 miles (80 km) northeast of Portland, Oregon. Mount St. Helens takes its English name from the British diplomat Lord St Helens, a friend of explorer George Vancouver who made a survey of the area in the late 18th century. The volcano is located in the Cascade Range and is part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, a segment of the Pacific Ring of Fire that includes over 160 active volcanoes. This volcano is well known for its ash explosions and pyroclastic flows.Mount St. Helens is most notorious for its catastrophic eruption on May 18, 1980, at 8:32 a.m. PDT, the deadliest and most economically destructive volcanic event in the history of the United States. Fifty-seven people were killed; 250 homes, 47 bridges, 15 miles (24 km) of railways, and 185 miles (298 km) of highway were destroyed. A massive debris avalanche triggered by an earthquake measuring 5.1 on the Richter scale caused an eruption that reduced the elevation of the mountain's summit from 9,677 ft (2,950 m) to 8,363 ft (2,549 m), replacing it with a 1 mile (1.6 km) wide horseshoe-shaped crater. The debris avalanche was up to 0.7 cubic miles (2.9 km3) in volume. The Mount St. Helens National Volcanic Monument was created to preserve the volcano and allow for its aftermath to be scientifically studied.As with most other volcanoes in the Cascade Range, Mount St. Helens is a large eruptive cone consisting of lava rock interlayered with ash, pumice, and other deposits. The mountain includes layers of basalt and andesite through which several domes of dacite lava have erupted. The largest of the dacite domes formed the previous summit, and off its northern flank sat the smaller Goat Rocks dome. Both were destroyed in the 1980 eruption.