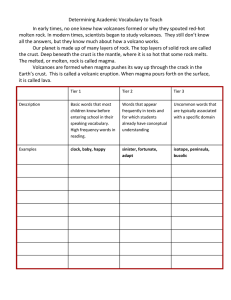
Section 1 - kjpederson
... 1. crater: a bowl-shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening; a large round pit caused by the impact of a meteroid 2. dormant: a volcano that is not currently active, but that may become active in the future 3. extinct: a volcano that is no longer active and is unlikely to erupt again ...
... 1. crater: a bowl-shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening; a large round pit caused by the impact of a meteroid 2. dormant: a volcano that is not currently active, but that may become active in the future 3. extinct: a volcano that is no longer active and is unlikely to erupt again ...
Vocabulary Handouts
... molten rock. In modern times, scientists began to study volcanoes. They still don’t know all the answers, but they know much about how a volcano works. Our planet is made up of many layers of rock. The top layers of solid rock are called the crust. Deep beneath the crust is the mantle, where it is s ...
... molten rock. In modern times, scientists began to study volcanoes. They still don’t know all the answers, but they know much about how a volcano works. Our planet is made up of many layers of rock. The top layers of solid rock are called the crust. Deep beneath the crust is the mantle, where it is s ...
Explosive Pyroclastic A volcano is a mountain formed beneath the
... Explosive Pyroclastic A volcano is a mountain formed beneath the ground when the Earth’s crust meets the mantle and magma collects there until it rises to the surface because magma is less dense than the surrounding rock is. Then the magma becomes liquid. Shield, cinder cone, and composite volcanoes ...
... Explosive Pyroclastic A volcano is a mountain formed beneath the ground when the Earth’s crust meets the mantle and magma collects there until it rises to the surface because magma is less dense than the surrounding rock is. Then the magma becomes liquid. Shield, cinder cone, and composite volcanoes ...
Name: Circle Period #: 7A / 7B Life in Ancient Rome Homework How
... destroyed many of the buildings of Pompeii. The city was still rebuilding seventeen years later when disaster struck. The Volcano Erupts On August 24, 79 AD Mount Vesuvius erupted. Scientists estimate that 1.5 million tons of ash and rock shot out of the volcano every second. The ash cloud likely to ...
... destroyed many of the buildings of Pompeii. The city was still rebuilding seventeen years later when disaster struck. The Volcano Erupts On August 24, 79 AD Mount Vesuvius erupted. Scientists estimate that 1.5 million tons of ash and rock shot out of the volcano every second. The ash cloud likely to ...
Volcanoes Week 2
... of the volcano when it blows apart. The pieces can be as big as a small car. Lava blocks are the largest pieces of pyroclastic material ejected during a violent eruption. Pumice Pumice is light-colored igneous rock blown into the air in a semi-liquid state. The rock cools so fast it does not have ti ...
... of the volcano when it blows apart. The pieces can be as big as a small car. Lava blocks are the largest pieces of pyroclastic material ejected during a violent eruption. Pumice Pumice is light-colored igneous rock blown into the air in a semi-liquid state. The rock cools so fast it does not have ti ...
Volcanoes
... Also known as pyroclastic rock fragments. There are many different possible sizes, from very small (volcanic ash or dust to much larger rocks (called volcanic bombs) ...
... Also known as pyroclastic rock fragments. There are many different possible sizes, from very small (volcanic ash or dust to much larger rocks (called volcanic bombs) ...
Volcanoes
... Why Volcanoes Erupt -Pressure builds as gases in Magma try to escape. -Enough pressure and Volcano erupts ...
... Why Volcanoes Erupt -Pressure builds as gases in Magma try to escape. -Enough pressure and Volcano erupts ...
Lesson Plan by : Laura Murphy, Arnone School Title : Volcanoes
... Review ten most important sentences by chanting. Reread the selection focusing on facts and opinions. Review facts and opinions by marking each sentence of the graphic organizer with “F” for a fact or “O” for opinion. Class decides as a whole by singing either “It’s a fact, it’s a fact, it’s a real ...
... Review ten most important sentences by chanting. Reread the selection focusing on facts and opinions. Review facts and opinions by marking each sentence of the graphic organizer with “F” for a fact or “O” for opinion. Class decides as a whole by singing either “It’s a fact, it’s a fact, it’s a real ...
Volcanoes
... •SiO2 content controls the viscosity of magma. •Viscosity controls the amount of gas that can be trapped in the magma. Viscosity: a measure of how easily a fluid flows. •Water has a low viscosity, honey has a much greater viscosity. ...
... •SiO2 content controls the viscosity of magma. •Viscosity controls the amount of gas that can be trapped in the magma. Viscosity: a measure of how easily a fluid flows. •Water has a low viscosity, honey has a much greater viscosity. ...
Volcanoes Booklet Info Basic Info
... Iceland is an island that sits right on a plate boundary. The pink line is the boundary between the two plates. ...
... Iceland is an island that sits right on a plate boundary. The pink line is the boundary between the two plates. ...
1150314LP 17 ES 2011
... 1. Identify where Earth’s volcanic regions are found and explain why they are found there. 2. Explain how hot spot volcanoes form. Pg 200 Section 1 “Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics” I. Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics II. Hot Spot volcanoes. Instructional method: Group discussion on section 1, students ...
... 1. Identify where Earth’s volcanic regions are found and explain why they are found there. 2. Explain how hot spot volcanoes form. Pg 200 Section 1 “Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics” I. Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics II. Hot Spot volcanoes. Instructional method: Group discussion on section 1, students ...
What IS A VOLCANO?
... Magma is molten rock which is still underground in vents. On the other hand, lava refers to molten rock which has found its way to the ground after an eruption. Lava occurs in active volcano while magma occurs in an inactive one. At the core of the earth is hot molten rock, magma. The molten rocks e ...
... Magma is molten rock which is still underground in vents. On the other hand, lava refers to molten rock which has found its way to the ground after an eruption. Lava occurs in active volcano while magma occurs in an inactive one. At the core of the earth is hot molten rock, magma. The molten rocks e ...
Volcano-Glacier Interactions during Historical Eruptions of Aleutian
... open melt pits with ephemeral lakes. Although catastrophic release of water and flooding did not occur, larger eruptions that produce more extensive lava flows could lead to outburst floods from the caldera ice field. This eruption highlights lava-flow interaction with glacier ice. Augustine Volcano ...
... open melt pits with ephemeral lakes. Although catastrophic release of water and flooding did not occur, larger eruptions that produce more extensive lava flows could lead to outburst floods from the caldera ice field. This eruption highlights lava-flow interaction with glacier ice. Augustine Volcano ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... Gas bubbles in the magma can expand until they explode When they explode ash and pumice are blasted from the vent ...
... Gas bubbles in the magma can expand until they explode When they explode ash and pumice are blasted from the vent ...
Types of Volcanoes Dangers from Composite Cones Pyroclastic
... Smooth “skin” with wrinkles. Pahoehoe flow - looks like twisted and braided rope. aa flow – rough, jagged blocks with sharp edges. Melted rhyolitic rock flows very slowly. ...
... Smooth “skin” with wrinkles. Pahoehoe flow - looks like twisted and braided rope. aa flow – rough, jagged blocks with sharp edges. Melted rhyolitic rock flows very slowly. ...
Volcanoes
... How are they formed? What are the types of volcanoes? How do volcanoes change the Earth’s surface? Stages of a volcano? What is the ring of fire? What are the differences between quiet eruptions and explosive eruptions? What are the volcanic related landforms? ...
... How are they formed? What are the types of volcanoes? How do volcanoes change the Earth’s surface? Stages of a volcano? What is the ring of fire? What are the differences between quiet eruptions and explosive eruptions? What are the volcanic related landforms? ...
Chapter 9
... Tambora, Indonesia, 1815 • Most violent and explosive eruption of last 200 years • Two extremely violent Plinian eruptions tore open the volcano so that 50 km3 of magma erupted in pyroclastic flows over one week – Reduced elevation of mountain from 4,000 m to 2,650 m – Created 6 km wide, 1 km deep c ...
... Tambora, Indonesia, 1815 • Most violent and explosive eruption of last 200 years • Two extremely violent Plinian eruptions tore open the volcano so that 50 km3 of magma erupted in pyroclastic flows over one week – Reduced elevation of mountain from 4,000 m to 2,650 m – Created 6 km wide, 1 km deep c ...
Chapter 7
... Tambora, Indonesia, 1815 • Most violent and explosive eruption of last 200 years • Two extremely violent Plinian eruptions tore open the volcano so that 50 km3 of magma erupted in pyroclastic flows over one week – Reduced elevation of mountain from 4,000 m to 2,650 m – Created 6 km wide, 1 km deep c ...
... Tambora, Indonesia, 1815 • Most violent and explosive eruption of last 200 years • Two extremely violent Plinian eruptions tore open the volcano so that 50 km3 of magma erupted in pyroclastic flows over one week – Reduced elevation of mountain from 4,000 m to 2,650 m – Created 6 km wide, 1 km deep c ...
lesson 24 effects of ash fall
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
Topic 8 Volcanoes
... Earth's surface. It is also a bowl-shaped depression at the top of the volcano where volcanic materials like, ash, lava, and other pyroclastic materials are released. ...
... Earth's surface. It is also a bowl-shaped depression at the top of the volcano where volcanic materials like, ash, lava, and other pyroclastic materials are released. ...
Subject
... Find a partner. Interview your partner to discover what he or she already knows about volcanoes. Together, create a quiz to test the knowledge of others on volcanoes. Parts of a volcano Kinds of volcanic eruptions Life cycle of a volcano 3 types of volcanoes ...
... Find a partner. Interview your partner to discover what he or she already knows about volcanoes. Together, create a quiz to test the knowledge of others on volcanoes. Parts of a volcano Kinds of volcanic eruptions Life cycle of a volcano 3 types of volcanoes ...
Physical Geology - Volcanoes and Volcanic Rocks
... magma chamber - an accumulation of molten rock beneath the Earth’s surface vent - the opening magma uses to move from the magma chamber to the Earth’s surface crater - the opening through which lava and tephra issues caldera - a very large crater created by explosion or collapse cone - a build-up of ...
... magma chamber - an accumulation of molten rock beneath the Earth’s surface vent - the opening magma uses to move from the magma chamber to the Earth’s surface crater - the opening through which lava and tephra issues caldera - a very large crater created by explosion or collapse cone - a build-up of ...
Volcanoes
... »Move down the slopes of a volcano at speeds up to 200 kilometers per hour »May produce a lahar, which is a volcanic mudflow ...
... »Move down the slopes of a volcano at speeds up to 200 kilometers per hour »May produce a lahar, which is a volcanic mudflow ...
volcanism - Geophile.net
... – Largest eruption in historic time (VEI = 7) – Caldera-forming eruption – Numerous pyroclastic flows • 10,000 deaths ...
... – Largest eruption in historic time (VEI = 7) – Caldera-forming eruption – Numerous pyroclastic flows • 10,000 deaths ...
Mount Vesuvius
.png?width=300)
Mount Vesuvius (Italian: Monte Vesuvio, Latin: Mons Vesuvius) is a stratovolcano in the Gulf of Naples, Italy, about 9 km (5.6 mi) east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of several volcanoes which form the Campanian volcanic arc. Vesuvius consists of a large cone partially encircled by the steep rim of a summit caldera caused by the collapse of an earlier and originally much higher structure.Mount Vesuvius is best known for its eruption in AD 79 that led to the burying and destruction of the Roman cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum and several other settlements. That eruption ejected a cloud of stones, ash and fumes to a height of 33 km (20.5 mi), spewing molten rock and pulverized pumice at the rate of 1.5 million tons per second, ultimately releasing a hundred thousand times the thermal energy released by the Hiroshima bombing. An estimated 16,000 people died due to hydrothermal pyroclastic flows. The only surviving eyewitness account of the event consists of two letters by Pliny the Younger to the historian Tacitus.Vesuvius has erupted many times since and is the only volcano on the European mainland to have erupted within the last hundred years. Today, it is regarded as one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world because of the population of 3,000,000 people living nearby and its tendency towards explosive (Plinian) eruptions. It is the most densely populated volcanic region in the world.