Specific Objectives
... the intervention’s implementation: 1.Number of new business entities; 2.Rate of unemployment; 3.Volume of tax collection; ...
... the intervention’s implementation: 1.Number of new business entities; 2.Rate of unemployment; 3.Volume of tax collection; ...
China`s Recent Political and Socio
... debts among creditor banks, thus triggering a financial crisis. (3) Social risk: massive lay off may cause a new wave of unemployment, thus making the society even more unstable. According to the 13th Five-year Plan, it reveals the goal of comprehensively building a moderately prosperous society by ...
... debts among creditor banks, thus triggering a financial crisis. (3) Social risk: massive lay off may cause a new wave of unemployment, thus making the society even more unstable. According to the 13th Five-year Plan, it reveals the goal of comprehensively building a moderately prosperous society by ...
Causes of the Great Depression (1919-1933) - meister
... As businesses began to lose money, costs had to be cut. Often, these were in the form of wage reductions. Money failed to trickle well. ...
... As businesses began to lose money, costs had to be cut. Often, these were in the form of wage reductions. Money failed to trickle well. ...
Criticism of the Welfare State Concept and the Need for Liberal
... of 2010, no serious reforms have been implemented so far. The taxation reform that was launched in 2010 has failed to change economic climate. Moreover, it has had adverse effect on some sectors of the economy. III.3. Liberal reforms in Georgia and the feasibility of using this experience To illustr ...
... of 2010, no serious reforms have been implemented so far. The taxation reform that was launched in 2010 has failed to change economic climate. Moreover, it has had adverse effect on some sectors of the economy. III.3. Liberal reforms in Georgia and the feasibility of using this experience To illustr ...
Answer Key 3
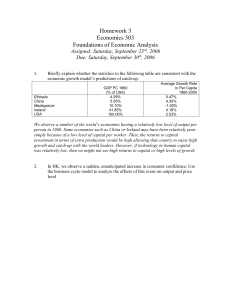
... We observe a number of the world’s economies having a relatively low level of output per person in 1960. Some economies such as China or Ireland may have been relatively poor simply because of a low level of capital per worker. Then, the returns to capital investment in terms of extra production wou ...
... We observe a number of the world’s economies having a relatively low level of output per person in 1960. Some economies such as China or Ireland may have been relatively poor simply because of a low level of capital per worker. Then, the returns to capital investment in terms of extra production wou ...
the fed, fiscal, monetary policy, keynes
... Portability, Divisibility, Uniformity, Limited Supply and Acceptability. How does it compare to the dollar? 5. What was the main difference between the philosophies of Adam Smith and John Meynard Keynes? **Did anyone check the stocks this morning? ...
... Portability, Divisibility, Uniformity, Limited Supply and Acceptability. How does it compare to the dollar? 5. What was the main difference between the philosophies of Adam Smith and John Meynard Keynes? **Did anyone check the stocks this morning? ...
The Great Depression of 1929 – 1933 from the point of view of
... A chronic problem throughout of interwar years, which had negative national and political effects, was the economic and social heterogeneity of the Czechoslovak Republic. There were considerable differences in the economic structure of the Czech Lands and of Slovakia. Until 1938, Slovakia – and the ...
... A chronic problem throughout of interwar years, which had negative national and political effects, was the economic and social heterogeneity of the Czechoslovak Republic. There were considerable differences in the economic structure of the Czech Lands and of Slovakia. Until 1938, Slovakia – and the ...
Chapter 28: Population, Labor and the Tertiary Sector
... 4. Note that the demand for labor in the service or tertiary sector of the economy is linked to the demand for labor in its primary and secondary sectors. So growth in those sectors fuels growth in the tertiary sector. Ask students to explain why growth in manufacturing, processing, and construction ...
... 4. Note that the demand for labor in the service or tertiary sector of the economy is linked to the demand for labor in its primary and secondary sectors. So growth in those sectors fuels growth in the tertiary sector. Ask students to explain why growth in manufacturing, processing, and construction ...
LECTURE 1 INTRODUCTION
... and informal “rules of the economic game”. If, for example, businesses will incur greater cost of hiring more workers, or their profitability will fall, they will be reluctant to hire more workers. If it is very difficult to fire young workers (the French example), businesses would be reluctant to h ...
... and informal “rules of the economic game”. If, for example, businesses will incur greater cost of hiring more workers, or their profitability will fall, they will be reluctant to hire more workers. If it is very difficult to fire young workers (the French example), businesses would be reluctant to h ...
Course Title: Public Finance Chapter 1: Introduction to public
... • subsidized education, • public health or health care, • social security, and • income redistribution. ...
... • subsidized education, • public health or health care, • social security, and • income redistribution. ...
Debate: Common Social concepts Anarchism: the state undesirable
... justified as an end in itself. It is best known in its first formulation: "Act only according to that maxim whereby you can at the same time will that it should become a universal law." The concept of the categorical imperative is a syllogism. The first premise is that a person acts morally if his o ...
... justified as an end in itself. It is best known in its first formulation: "Act only according to that maxim whereby you can at the same time will that it should become a universal law." The concept of the categorical imperative is a syllogism. The first premise is that a person acts morally if his o ...
Macroeconomics in Islamic Economy: A Theoretical Perspective
... level (safe-drinking water, streets, etc), local (roads and other means for transportation) and national levels (highways, bridges, dams, etc.) Maintenance of a credible deterrent • A small space for public works programs • Fine tuning of the economy through review of existing action. ...
... level (safe-drinking water, streets, etc), local (roads and other means for transportation) and national levels (highways, bridges, dams, etc.) Maintenance of a credible deterrent • A small space for public works programs • Fine tuning of the economy through review of existing action. ...
Instrument: A3 AMENDMENT TO THE CONSTITUTION
... Article 5 Article 7 of the Constitution, which reads: "The state economy is the sector of socialist economy under ownership by the whole people; it is the leading force in the national economy. The state ensures the consolidation and growth of the state economy," is revised as follows: "The state-o ...
... Article 5 Article 7 of the Constitution, which reads: "The state economy is the sector of socialist economy under ownership by the whole people; it is the leading force in the national economy. The state ensures the consolidation and growth of the state economy," is revised as follows: "The state-o ...
KOSOVO
... centrally planned to a market-based economy has proceeded steadily, and the government has engaged in a series of highprofile privatizations. Limited by political and geographic constraints, the young nation has opened its borders to trade and investment and now relies heavily on remittances and for ...
... centrally planned to a market-based economy has proceeded steadily, and the government has engaged in a series of highprofile privatizations. Limited by political and geographic constraints, the young nation has opened its borders to trade and investment and now relies heavily on remittances and for ...
Principles of Macroeconomics
... An economic system has given geographical boundaries, and is also known as a national economy. A national economy is endowed with a given amount of productive resources which are combined within a given state of technology in order to produce goods and services. A model of production-possibilities i ...
... An economic system has given geographical boundaries, and is also known as a national economy. A national economy is endowed with a given amount of productive resources which are combined within a given state of technology in order to produce goods and services. A model of production-possibilities i ...
Homework 3
... 2. Assume that the demand for M1 in Hong Kong was given by the equation PQ . Hong Kong’s central bank, the Hong Kong monetary M 1D 2 100i authority operates a fixed exchange rate. This implies that the interest rate in Hong Kong will be determined by the US interest rate denoted i*. Thus, a credib ...
... 2. Assume that the demand for M1 in Hong Kong was given by the equation PQ . Hong Kong’s central bank, the Hong Kong monetary M 1D 2 100i authority operates a fixed exchange rate. This implies that the interest rate in Hong Kong will be determined by the US interest rate denoted i*. Thus, a credib ...
The New Normal in the U.S. Economy is Slower Than You Think
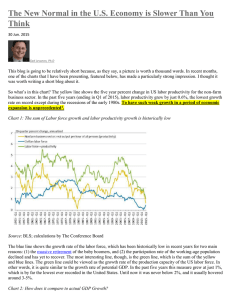
... more slowly than the sum of labor force and productivity growth2. So does that mean the new trend growth for the U.S. economy is just one percent? No, I wouldn’t go that far, but 1.5% sounds reasonable. Regarding labor force growth, I don’t expect it to accelerate in the coming years given the weak ...
... more slowly than the sum of labor force and productivity growth2. So does that mean the new trend growth for the U.S. economy is just one percent? No, I wouldn’t go that far, but 1.5% sounds reasonable. Regarding labor force growth, I don’t expect it to accelerate in the coming years given the weak ...
Business Cycles
... cycle, while low levels of investment contribute to contractions (decline in real GDP). Real GDP=The value of a nation’s gross domestic product (GDP) after it has been adjusted for inflation (in increase in overall prices that results from rising wages). ...
... cycle, while low levels of investment contribute to contractions (decline in real GDP). Real GDP=The value of a nation’s gross domestic product (GDP) after it has been adjusted for inflation (in increase in overall prices that results from rising wages). ...
Economy of Pakistan
... • Economic development generally refers to the sustained, concerted actions of policy makers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area. • Economic development can also be referred to as the quantitative and qualitative changes in the economy. ... ...
... • Economic development generally refers to the sustained, concerted actions of policy makers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area. • Economic development can also be referred to as the quantitative and qualitative changes in the economy. ... ...
Economic Environment
... • Aggregate Supply: – The total value of goods and services supplied in the economy. ...
... • Aggregate Supply: – The total value of goods and services supplied in the economy. ...