Business Cycles
... breakthroughs that allow us to produce more with the same resources can stimulate the cycle’s expansion phase and put off contraction. ...
... breakthroughs that allow us to produce more with the same resources can stimulate the cycle’s expansion phase and put off contraction. ...
Business Cycle www.AssignmentPoint.com The Business Cycle (or
... Association, declared that the "central problem of depression-prevention has been solved, for all practical purposes." Unfortunately, this was followed by the 2008–2012 global recession. ...
... Association, declared that the "central problem of depression-prevention has been solved, for all practical purposes." Unfortunately, this was followed by the 2008–2012 global recession. ...
Economic Ups and Downs
... rise in the prices of goods and services. It often occurs during periods of rapid growth and expansion. Inflation affects consumers by reducing their purchasing powers. Money buys fewer things. Because inflation affects consumers who borrow, lend or invest money, they need to consider how it impacts ...
... rise in the prices of goods and services. It often occurs during periods of rapid growth and expansion. Inflation affects consumers by reducing their purchasing powers. Money buys fewer things. Because inflation affects consumers who borrow, lend or invest money, they need to consider how it impacts ...
The Root Beer Game Debrief
... •Retailer and Producers send misleading information about consumer demand. •Advances in tech, productivity, or resources. •Outside influences (wars, supply shocks, panic). Who cares? •Macroeconomics measures these fluctuations and guides policies to keep the economy stable. •The government has the r ...
... •Retailer and Producers send misleading information about consumer demand. •Advances in tech, productivity, or resources. •Outside influences (wars, supply shocks, panic). Who cares? •Macroeconomics measures these fluctuations and guides policies to keep the economy stable. •The government has the r ...
Notes on Economics
... counterproductive. The Austrian school holds a special view of the modern business cycle; it contends that boom cycles are actually a misallocation of capital resources caused by interfering monetary policy. When central banks effectively expand the money supply by lowering interest rates, it create ...
... counterproductive. The Austrian school holds a special view of the modern business cycle; it contends that boom cycles are actually a misallocation of capital resources caused by interfering monetary policy. When central banks effectively expand the money supply by lowering interest rates, it create ...
Course name
... Macroeconomics is the study of behaviour of the economy as a whole. Macroeconomics concerns business cycles that lead to unemployment and inflation as well as the longer-term trends in the output and living standards. In analyzing Macroeconomics we focus on a few key economic variables: gross nation ...
... Macroeconomics is the study of behaviour of the economy as a whole. Macroeconomics concerns business cycles that lead to unemployment and inflation as well as the longer-term trends in the output and living standards. In analyzing Macroeconomics we focus on a few key economic variables: gross nation ...
BUSINESS CYCLE, FEDERAL RESERVE, TAXATION
... rising. Inflation is a natural occurrence, but high rates of inflation can cause a decline in business activity. • Inflation is caused by an increase in the money supply. Money in circulation, or being spent. RECESSION • During a period of recession, consumers are not spending money, thus business p ...
... rising. Inflation is a natural occurrence, but high rates of inflation can cause a decline in business activity. • Inflation is caused by an increase in the money supply. Money in circulation, or being spent. RECESSION • During a period of recession, consumers are not spending money, thus business p ...
We Forgot Everything Keynes Taught Us
... (2) changes in aggregate demand have greatest short-run impact on real output and employment. (3) prices and wages respond slowly to changes in supply and demand, resulting in shortages and surpluses. (4) periods of recession/depression are economic maladies. (5) stabilization policy is necessary to ...
... (2) changes in aggregate demand have greatest short-run impact on real output and employment. (3) prices and wages respond slowly to changes in supply and demand, resulting in shortages and surpluses. (4) periods of recession/depression are economic maladies. (5) stabilization policy is necessary to ...
Study Guide - Cobb Learning
... Associate each of the economists studied with their main contributions to the field of Economics: ...
... Associate each of the economists studied with their main contributions to the field of Economics: ...
Eco 13/4
... Each year there are ups and downs in unemployment, world trade, inflation, etc. These are called business fluctuations or the business cycle. ...
... Each year there are ups and downs in unemployment, world trade, inflation, etc. These are called business fluctuations or the business cycle. ...
The Root Beer Game Debrief
... •Retailer and Producers send misleading information about consumer demand. •Advances in tech, productivity, or resources. •Outside influences (wars, supply shocks, panic). Who cares? •Macroeconomics measures these fluctuations and guides policies to keep the economy stable. •The government has the r ...
... •Retailer and Producers send misleading information about consumer demand. •Advances in tech, productivity, or resources. •Outside influences (wars, supply shocks, panic). Who cares? •Macroeconomics measures these fluctuations and guides policies to keep the economy stable. •The government has the r ...
Business Cycle Theory
... 2. Identify and explain the factors that cause business cycles 3. Analyze how economists use business cycle theory to predict what is going to happen 4. Analyze how the government uses predictions to make public policy ©2012, TESCCC ...
... 2. Identify and explain the factors that cause business cycles 3. Analyze how economists use business cycle theory to predict what is going to happen 4. Analyze how the government uses predictions to make public policy ©2012, TESCCC ...
Chapter 30: Business Fluctuations
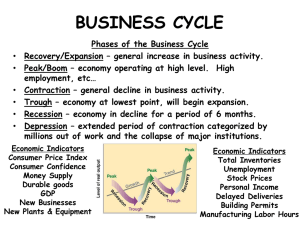
... - A Trough is the lowest point in a business cycle. - A Depression is a severe trough. Expansion - During a Expansion phase, output expands and income increases. Peak - In a Peak phase, real GDP is at its highest level. Recession - During the Recession phase, income and consumption decline. Length a ...
... - A Trough is the lowest point in a business cycle. - A Depression is a severe trough. Expansion - During a Expansion phase, output expands and income increases. Peak - In a Peak phase, real GDP is at its highest level. Recession - During the Recession phase, income and consumption decline. Length a ...
Macroeconomics: An Introduction
... The1960s: Continued growth with some inflation The 1970s’ stagflation Controlling inflation and supply side economics in the 1980s Prosperity in 1990s (Low inflation and low unemployment) Slow down in 2000-2001; mild recovery in the following years ...
... The1960s: Continued growth with some inflation The 1970s’ stagflation Controlling inflation and supply side economics in the 1980s Prosperity in 1990s (Low inflation and low unemployment) Slow down in 2000-2001; mild recovery in the following years ...
Business Cycles
... cycle, while low levels of investment contribute to contractions (decline in real GDP). Real GDP=The value of a nation’s gross domestic product (GDP) after it has been adjusted for inflation (in increase in overall prices that results from rising wages). ...
... cycle, while low levels of investment contribute to contractions (decline in real GDP). Real GDP=The value of a nation’s gross domestic product (GDP) after it has been adjusted for inflation (in increase in overall prices that results from rising wages). ...