Questions on Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
... 18. Classical economist David Hume observed that as the money supply expanded after gold discoveries a. prices and output both increased immediately. b. prices increased immediately while output remained unchanged. c. it took time for prices to rise; in the meantime output was lower. d. it took tim ...
... 18. Classical economist David Hume observed that as the money supply expanded after gold discoveries a. prices and output both increased immediately. b. prices increased immediately while output remained unchanged. c. it took time for prices to rise; in the meantime output was lower. d. it took tim ...
CHAP1.WP (Word5)
... objective of the Fed is to restrain inflation, which it does by instituting restrictive policies that work to raise interest rates. In Figure 9-1, Gordon presents an historical graph of the inflation rate and the output ratio, which is the ratio of actual real GDP to natural real GDP. From the graph ...
... objective of the Fed is to restrain inflation, which it does by instituting restrictive policies that work to raise interest rates. In Figure 9-1, Gordon presents an historical graph of the inflation rate and the output ratio, which is the ratio of actual real GDP to natural real GDP. From the graph ...
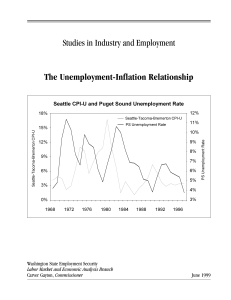
Unemployment-Inflation Relationship
... non-economists accepted—tight labor markets lead to wage and price pressures—though few could cite the NAIRU as the theoretical basis of the phenomenon. That was then. Today, the NAIRU is widely believed to be askew. Though clearly the case nationally, it is perhaps even more obvious in high-flying ...
... non-economists accepted—tight labor markets lead to wage and price pressures—though few could cite the NAIRU as the theoretical basis of the phenomenon. That was then. Today, the NAIRU is widely believed to be askew. Though clearly the case nationally, it is perhaps even more obvious in high-flying ...
MacroeconoMics for a Modern econoMy
... expected and its wage increase was not bringing it any of the reduced quit rate it had expected. Moreover, following the initial impact of the velocity shock on demand prices, any firm supplying a specialized assortment of goods would experience a secondary increase in its demand price (at the init ...
... expected and its wage increase was not bringing it any of the reduced quit rate it had expected. Moreover, following the initial impact of the velocity shock on demand prices, any firm supplying a specialized assortment of goods would experience a secondary increase in its demand price (at the init ...
Estimating The Optimal Level of Inflation (Inflation Threshold) in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
... countries is 10%, with the exception of countries developed where the rate dropped significantly from previous average. Possible separation between exporting and non-oil exporter, where it became clear that increasing the level of inflation in oil-exporting countries by 3% would lead to a decrease i ...
... countries is 10%, with the exception of countries developed where the rate dropped significantly from previous average. Possible separation between exporting and non-oil exporter, where it became clear that increasing the level of inflation in oil-exporting countries by 3% would lead to a decrease i ...
Economics Explorer Series No. 3 - Inflation
... substitution bias. DOS attempts to alleviate this problem by updating the CPI basket every five years. Another measurement problem arises with the emergence of new retail chains, discount stores and on-line shopping. The so-called new outlet bias refers to an overstatement in the CPI as a result of ...
... substitution bias. DOS attempts to alleviate this problem by updating the CPI basket every five years. Another measurement problem arises with the emergence of new retail chains, discount stores and on-line shopping. The so-called new outlet bias refers to an overstatement in the CPI as a result of ...
NBE WO~G PAPER SERIES THE TIME-VARYING NAIRU AND ITS
... 1. Even though the actual unemployment rate averaged 5.6 percent in the 21 months ending in May, 1996, below the Fed’s previous NAIRU estimate of 6.0 percent, the inflation rate did not accelerate. Indeed, one key measure of inflation, the personal consumption deflator (on the new chain-weighted bas ...
... 1. Even though the actual unemployment rate averaged 5.6 percent in the 21 months ending in May, 1996, below the Fed’s previous NAIRU estimate of 6.0 percent, the inflation rate did not accelerate. Indeed, one key measure of inflation, the personal consumption deflator (on the new chain-weighted bas ...
aggregate-supply curve
... Think of potential output as the maximum speed that a marathoner can run without becoming “overheated” and dropping out from exhaustion. Clearly, the runner can run faster than the sustainable pace for a while, just as the U.S. economy grew faster than its potential growth rate during the 1990s. But ...
... Think of potential output as the maximum speed that a marathoner can run without becoming “overheated” and dropping out from exhaustion. Clearly, the runner can run faster than the sustainable pace for a while, just as the U.S. economy grew faster than its potential growth rate during the 1990s. But ...
Declines in the Volatility of the U. S. Economy: A Detailed Look
... effect of macro shocks, plus some increase in variance in Electronics, Communications, and Finance due to ...
... effect of macro shocks, plus some increase in variance in Electronics, Communications, and Finance due to ...
MERCATUS RESEARCH THE CASE FOR NOMINAL GDP TARGETING Scott Sumner
... wisdom, the fact that NGDP fell during 2009 at the fastest rate since the 1930s suggests that monetary policy failure was at the center of the crisis. Like Hetzel, I do not believe financial distress alone can explain the crisis of 2008 and its aftermath.11 Instead, I see an almost perfect storm of ...
... wisdom, the fact that NGDP fell during 2009 at the fastest rate since the 1930s suggests that monetary policy failure was at the center of the crisis. Like Hetzel, I do not believe financial distress alone can explain the crisis of 2008 and its aftermath.11 Instead, I see an almost perfect storm of ...
Chapter 23 Employment and Unemployment
... 2. Joe performed 15 hours of unpaid work on his family farm. He would be considered to be an ____________ person, according to the BLS. 3. Marwan lost his job as an airline mechanic, and has been sending out his resume to other potential employers. He would be willing to start working in a new job i ...
... 2. Joe performed 15 hours of unpaid work on his family farm. He would be considered to be an ____________ person, according to the BLS. 3. Marwan lost his job as an airline mechanic, and has been sending out his resume to other potential employers. He would be willing to start working in a new job i ...
EMPLOYMENT AND UNEMPLOYMENT
... 2. Joe performed 15 hours of unpaid work on his family farm. He would be considered to be an ____________ person, according to the BLS. 3. Marwan lost his job as an airline mechanic, and has been sending out his resume to other potential employers. He would be willing to start working in a new job i ...
... 2. Joe performed 15 hours of unpaid work on his family farm. He would be considered to be an ____________ person, according to the BLS. 3. Marwan lost his job as an airline mechanic, and has been sending out his resume to other potential employers. He would be willing to start working in a new job i ...
4. Supply and Demand Developments
... in confidence indices points to lower propensity to spend. Attenuated employment expectations indicate that the income channel may also be less supportive than projected. Against this background, private consumption is estimated to remain weak in the first quarter and register a mild and gradual imp ...
... in confidence indices points to lower propensity to spend. Attenuated employment expectations indicate that the income channel may also be less supportive than projected. Against this background, private consumption is estimated to remain weak in the first quarter and register a mild and gradual imp ...
What Is Price Level Stability?
... There are two price level problems When the price level is stable, the problem is to prevent inflation from breaking out. When inflation is already present, the problem is to reduce its rate and restore price level stability while doing the least possible damage to real GDP growth. ...
... There are two price level problems When the price level is stable, the problem is to prevent inflation from breaking out. When inflation is already present, the problem is to reduce its rate and restore price level stability while doing the least possible damage to real GDP growth. ...
aggregate supply curve
... The period of time in which prices do not change or do not change very much. We call these prices “sticky”. • sticky prices If wages are sticky, firms’ overall costs will be sticky as well. Sticky wages cause sticky prices and hamper the economy’s ability to bring demand and supply into balance in t ...
... The period of time in which prices do not change or do not change very much. We call these prices “sticky”. • sticky prices If wages are sticky, firms’ overall costs will be sticky as well. Sticky wages cause sticky prices and hamper the economy’s ability to bring demand and supply into balance in t ...
Phillips curve

In economics, the Phillips curve is a historical inverse relationship between rates of unemployment and corresponding rates of inflation that result in an economy. Stated simply, decreased unemployment, (i.e., increased levels of employment) in an economy will correlate with higher rates of inflation.While there is a short run tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, it has not been observed in the long run. In 1968, Milton Friedman asserted that the Phillips Curve was only applicable in the short-run and that in the long-run, inflationary policies will not decrease unemployment. Friedman then correctly predicted that, in the upcoming years after 1968, both inflation and unemployment would increase. The long-run Phillips Curve is now seen as a vertical line at the natural rate of unemployment, where the rate of inflation has no effect on unemployment. Accordingly, the Phillips curve is now seen as too simplistic, with the unemployment rate supplanted by more accurate predictors of inflation based on velocity of money supply measures such as the MZM (""money zero maturity"") velocity, which is affected by unemployment in the short but not the long term.