Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Biological Page
... Use with caution in individuals with a history of prior systemic allergic reactions following administration of human immunoglobulin preparations. Individuals with immunoglobulin A deficiency have a potential for developing IgA antibodies and could develop anaphylactic reactions to subsequent bl ...
... Use with caution in individuals with a history of prior systemic allergic reactions following administration of human immunoglobulin preparations. Individuals with immunoglobulin A deficiency have a potential for developing IgA antibodies and could develop anaphylactic reactions to subsequent bl ...
Hepatitis G - Haemosexual
... Causes and symptoms Some researchers believe that there may be a group of GB viruses, rather than just one. Others remain doubtful that HGV actually causes illness. If it does, the type of acute or chronic (long-lasting) illness that results is not clear. When diagnosed, acute HGV infection has usua ...
... Causes and symptoms Some researchers believe that there may be a group of GB viruses, rather than just one. Others remain doubtful that HGV actually causes illness. If it does, the type of acute or chronic (long-lasting) illness that results is not clear. When diagnosed, acute HGV infection has usua ...
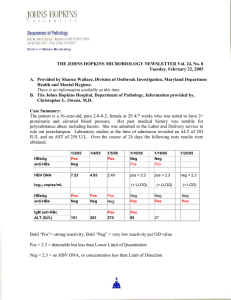
Northern Ireland Regional Hepatitis B & C Managed Care Network
... PWID: Ever-IDU * SVR rate among all patients aged <35yrs: genotype 1 was 54% (35/65); genotype 2/3 was 76% (121/159). ...
... PWID: Ever-IDU * SVR rate among all patients aged <35yrs: genotype 1 was 54% (35/65); genotype 2/3 was 76% (121/159). ...
Occupational Infections: A Risk for the Anesthesiologists
... hospitalization. The risk for HBV infection following an accidental needle stick, is 37 to 62%, if the source patient is HBeAg-positive and 23 to 37% if HBeAgnegative. The rate of transmission is significantly less after mucosal contact with infected oral secretions than after percutaneous exposure ...
... hospitalization. The risk for HBV infection following an accidental needle stick, is 37 to 62%, if the source patient is HBeAg-positive and 23 to 37% if HBeAgnegative. The rate of transmission is significantly less after mucosal contact with infected oral secretions than after percutaneous exposure ...
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard
... wash hands or other exposed skin with soap and water as soon as possible following an occupational exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials. Wash your hands with soap and water every ...
... wash hands or other exposed skin with soap and water as soon as possible following an occupational exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials. Wash your hands with soap and water every ...
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard
... l AIDS kills or damages cells of the body’s immune system. l HIV progressively destroys the body’s ability to fight infections and other diseases. ...
... l AIDS kills or damages cells of the body’s immune system. l HIV progressively destroys the body’s ability to fight infections and other diseases. ...
Timeline – Hepatitis Milestones
... Hepatitis A outbreak in Pennsylvania caused by green onions kills three and sickens at least 575 people; other hepatitis outbreaks in Georgia and Tennessee sicken over 300 people Actress Pamela Anderson announces she has HCV An estimated 40 million infants and children and 30 million adults in the U ...
... Hepatitis A outbreak in Pennsylvania caused by green onions kills three and sickens at least 575 people; other hepatitis outbreaks in Georgia and Tennessee sicken over 300 people Actress Pamela Anderson announces she has HCV An estimated 40 million infants and children and 30 million adults in the U ...
$doc.title
... All of these viruses cause acute, or shortterm, viral hepatitis. The hepatitis B, C, and D viruses can also cause chronic hepatitis, in which the infection is prolonged, some times lifelong. Chronic hepatitis can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Researchers are looking for other ...
... All of these viruses cause acute, or shortterm, viral hepatitis. The hepatitis B, C, and D viruses can also cause chronic hepatitis, in which the infection is prolonged, some times lifelong. Chronic hepatitis can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Researchers are looking for other ...
DECISION-MAKING IN VIRAL HEPATITIS RELATED ADVANCED
... Monitor for deterioration/decompensation • Patients with compensated disease should have 6-monthly blood tests including FBE, EUC, LFT, INR/PT in conjunction with HCC screening and a clinical review especially monitoring nutritional status • Gastroscopy surveillance for varices − see below for gui ...
... Monitor for deterioration/decompensation • Patients with compensated disease should have 6-monthly blood tests including FBE, EUC, LFT, INR/PT in conjunction with HCC screening and a clinical review especially monitoring nutritional status • Gastroscopy surveillance for varices − see below for gui ...
Bloodborne Pathogen Training - Comprehensive Sub Solutions
... body fluids MUST BE discarded as soon as possible in a designated sharps container. Containers will be found where sharps are used. Check with the School Nurse! Disposal is regulated by the Ohio EPA. ...
... body fluids MUST BE discarded as soon as possible in a designated sharps container. Containers will be found where sharps are used. Check with the School Nurse! Disposal is regulated by the Ohio EPA. ...
Hepatitis B Prevention
... Components of Strategies to Prevent HBV Transmission • Hepatitis B immunization – Universal infant immunization – Prevent perinatal transmission – Catch-up immunization ...
... Components of Strategies to Prevent HBV Transmission • Hepatitis B immunization – Universal infant immunization – Prevent perinatal transmission – Catch-up immunization ...
Immunological aspects of liver disease
... dangerous escalation of an already strong trait! Deborah Doniach, one of the grandparents of clinical immunology, was an important influence at this time. It was she who first introduced us to the work of Meyer zum Buschenfelde on liver specific antigens and experimental autoimmune hepatitis,4 and t ...
... dangerous escalation of an already strong trait! Deborah Doniach, one of the grandparents of clinical immunology, was an important influence at this time. It was she who first introduced us to the work of Meyer zum Buschenfelde on liver specific antigens and experimental autoimmune hepatitis,4 and t ...
HEPATITIS B VACCINATION KIT THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN INDIANA
... Persons with a history of allergic reactions to other vaccines are advised to seek further information regarding the components of this vaccine before receiving it. Individuals with immuno-deficiency disorders or those receiving immuno-suppressive therapy may require larger vaccine doses. Persons wh ...
... Persons with a history of allergic reactions to other vaccines are advised to seek further information regarding the components of this vaccine before receiving it. Individuals with immuno-deficiency disorders or those receiving immuno-suppressive therapy may require larger vaccine doses. Persons wh ...
Click to edit Master title style Hepatitis B Click to edit Master title style
... About 350 million worldwide live with chronic infection. An estimated 600,000 persons die each year due to the acute or chronic consequences of hepatitis B. About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood later die from liver cancer or cirrhosis caused by the chronic infec ...
... About 350 million worldwide live with chronic infection. An estimated 600,000 persons die each year due to the acute or chronic consequences of hepatitis B. About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood later die from liver cancer or cirrhosis caused by the chronic infec ...
Infections and Precautions
... infection. More than half of Hepatitis B infections occur and pass without noticeable symptoms. Sometimes, only mild symptoms such as a general discomfort occur. Rarely is medical attention needed. Often, the infection disappears without treatment. In fact, laboratory testing is often the only way o ...
... infection. More than half of Hepatitis B infections occur and pass without noticeable symptoms. Sometimes, only mild symptoms such as a general discomfort occur. Rarely is medical attention needed. Often, the infection disappears without treatment. In fact, laboratory testing is often the only way o ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) clinic attendees IV. ...
... Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) clinic attendees IV. ...
T or F - jan.ucc.nau.edu
... 2. Medical Abortion ●Can offer up to 9 weeks ● Consists of 2 drugs: ...
... 2. Medical Abortion ●Can offer up to 9 weeks ● Consists of 2 drugs: ...
the PDF here
... Despite improving therapies [8], our study found that deaths associated with HCV continued to rise while deaths associated with 60 ONNICs that are routinely reported to CDC declined. The great decline among deaths associated with HIV, pneumococcal disease, and tuberculosis from the ONNICs category w ...
... Despite improving therapies [8], our study found that deaths associated with HCV continued to rise while deaths associated with 60 ONNICs that are routinely reported to CDC declined. The great decline among deaths associated with HIV, pneumococcal disease, and tuberculosis from the ONNICs category w ...
comparative-analysis-of-serum-insulin
... Gastrointestinal system bleeding, Hepatic encephalopathy, hepatocellular carcinoma or any other malignancy, Any kind of infectious disease, Diabetes mellitus, Chronic renal failure, Hypertension were excluded from the study. Groups were compared using student's t-test and p < 0.01 was considered as ...
... Gastrointestinal system bleeding, Hepatic encephalopathy, hepatocellular carcinoma or any other malignancy, Any kind of infectious disease, Diabetes mellitus, Chronic renal failure, Hypertension were excluded from the study. Groups were compared using student's t-test and p < 0.01 was considered as ...
Hepatitis E virus as a newly identified cause of acute viral hepatitis
... chronic viral hepatitis and that it carries a poor prognosis in the context of chronic liver disease [2,9,10]. This might be critical in HIV-infected patients with high rates of chronic co-infections with hepatitis B virus and ⁄ or hepatitis C virus, especially those with a history of injecting drug ...
... chronic viral hepatitis and that it carries a poor prognosis in the context of chronic liver disease [2,9,10]. This might be critical in HIV-infected patients with high rates of chronic co-infections with hepatitis B virus and ⁄ or hepatitis C virus, especially those with a history of injecting drug ...
SPM 100 Skills Lab 1
... Good hand hygiene is the key to reducing nosocomial infections Wash before and after patient contact Wear gloves, a mask, eye protection, face shield and gown when contact with blood or other body fluids is likely ...
... Good hand hygiene is the key to reducing nosocomial infections Wash before and after patient contact Wear gloves, a mask, eye protection, face shield and gown when contact with blood or other body fluids is likely ...
Volume 24 - No 8: Hepatitis B
... HBV is a partially double stranded DNA virus classified as a hepadnavirus. The spectrum of clinical manifestations of HBV infection varies in acute and chronic disease. During the acute phase, manifestations range from subclinical or anicteric hepatitis to icteric hepatitis and, in rare cases, fulmi ...
... HBV is a partially double stranded DNA virus classified as a hepadnavirus. The spectrum of clinical manifestations of HBV infection varies in acute and chronic disease. During the acute phase, manifestations range from subclinical or anicteric hepatitis to icteric hepatitis and, in rare cases, fulmi ...
Commonwealth Health Corporation
... Hepatitis C (HCV) is a virus that, similar to Hepatitis B, attacks the liver. HCV causes liver disease that ranges in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. It is spread primarily through contact with the blood of an infected person. • Approximately 3.2 mill ...
... Hepatitis C (HCV) is a virus that, similar to Hepatitis B, attacks the liver. HCV causes liver disease that ranges in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. It is spread primarily through contact with the blood of an infected person. • Approximately 3.2 mill ...
Bacteria Department
... exposure to hepatitis c virus induces cellular immune responses without detectable viremia or seroconversion ...
... exposure to hepatitis c virus induces cellular immune responses without detectable viremia or seroconversion ...
Approximate questions to the topics:
... 7. How does Virus A hepatitis (Virus B hepatitis) spread? 8. When does epidemic hepatitis occur? 9. How long does the incubation period of Virus A hepatitis (Virus B hepatitis) last? 10. What does Botkin’s disease cause? Infectious Diseases 1. What are infectious diseases caused by? 2. What is human ...
... 7. How does Virus A hepatitis (Virus B hepatitis) spread? 8. When does epidemic hepatitis occur? 9. How long does the incubation period of Virus A hepatitis (Virus B hepatitis) last? 10. What does Botkin’s disease cause? Infectious Diseases 1. What are infectious diseases caused by? 2. What is human ...
Hepatitis

Hepatitis (plural: hepatitides) is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. Hepatitis may occur with limited or no symptoms, but often leads to jaundice (a yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membrane, and conjunctiva), poor appetite, and malaise. Hepatitis is acute when it lasts less than six months and chronic when it persists longer.Acute hepatitis can be self-limiting (healing on its own), can progress to chronic hepatitis, or, rarely, can cause acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may have no symptoms, or may progress over time to fibrosis (scarring of the liver) and cirrhosis (chronic liver failure). Cirrhosis of the liver increases the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (a form of liver cancer).Worldwide, viral hepatitis is the most common cause of liver inflammation. Other causes include autoimmune diseases and ingestion of toxic substances (notably alcohol), certain medications (such as paracetamol), some industrial organic solvents, and plants.The term is derived from the Greek hêpar (ἧπαρ), meaning ""liver"", and the suffix -itis (-ῖτις), meaning ""inflammation"" (c. 1727).