economics (hons) – sem-ii
... In terms of fish, what is the GDP of Gilligan’s Island? What are consumption and investment? What are the incomes of the Professor and Gilligan? ...
... In terms of fish, what is the GDP of Gilligan’s Island? What are consumption and investment? What are the incomes of the Professor and Gilligan? ...
Theory versus Reality
... • The trade-off between unemployment and inflation is a fiscal policy goal conflict. • The Fed wants fiscal stability, while the president and Congress may be unwilling to raise taxes or cut spending. • Some cutbacks affect the neediest and become politically impossible to enact. • All decisions hav ...
... • The trade-off between unemployment and inflation is a fiscal policy goal conflict. • The Fed wants fiscal stability, while the president and Congress may be unwilling to raise taxes or cut spending. • Some cutbacks affect the neediest and become politically impossible to enact. • All decisions hav ...
Fiscal Policy
... If there is a natural rate of unemployment, fiscal policy that increases aggregate demand will appear to succeed in the short run because output and employment will both expand But stimulating aggregate demand will, in the long run, result only in a higher price level, while the level of output will ...
... If there is a natural rate of unemployment, fiscal policy that increases aggregate demand will appear to succeed in the short run because output and employment will both expand But stimulating aggregate demand will, in the long run, result only in a higher price level, while the level of output will ...
Economics – Unit 3
... SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. ______a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions of households, businesses, government, and net exports. ______b. Define Gross Domestic P ...
... SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. ______a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions of households, businesses, government, and net exports. ______b. Define Gross Domestic P ...
Chapter 12 Fiscal Policy
... C) government spending is reduced. D) the income distribution becomes more unequal. E) the economy's expansion will be greater than it would have been without "crowding out." Answer: B 36) The lags in discretionary fiscal policy A) are desirable because they provide time for the economy to adjust to ...
... C) government spending is reduced. D) the income distribution becomes more unequal. E) the economy's expansion will be greater than it would have been without "crowding out." Answer: B 36) The lags in discretionary fiscal policy A) are desirable because they provide time for the economy to adjust to ...
Intro to Crowding Out
... vice versa. Investment decreases. As we know, a decrease in investment causes aggregate demand (real GDP) to decrease, as well. If the interest rate decreases, the opposite will happen. ...
... vice versa. Investment decreases. As we know, a decrease in investment causes aggregate demand (real GDP) to decrease, as well. If the interest rate decreases, the opposite will happen. ...
Fiscal Policy
... If there is a natural rate of unemployment, fiscal policy that increases aggregate demand will appear to succeed in the short run because output and employment will both expand But stimulating aggregate demand will, in the long run, result only in a higher price level, while the level of output will ...
... If there is a natural rate of unemployment, fiscal policy that increases aggregate demand will appear to succeed in the short run because output and employment will both expand But stimulating aggregate demand will, in the long run, result only in a higher price level, while the level of output will ...
class xii holiday homework
... 1. What will be the expenditure by the household on demand for food, clothing books, furniture etc. called? 2. What will expenditure on buildings, plants and equipment be called? 3. Can consumption be greater than income? If so what does it indicate? 4. What is consumption function? 5. What is auton ...
... 1. What will be the expenditure by the household on demand for food, clothing books, furniture etc. called? 2. What will expenditure on buildings, plants and equipment be called? 3. Can consumption be greater than income? If so what does it indicate? 4. What is consumption function? 5. What is auton ...
Chapter 12 LECTURE NOTES
... 3. Operational lag is the time elapsed between change in policy and its impact on the economy. B. Political considerations: Government has other goals besides economic stability, and these may conflict with stabilization policy. 1. A political business cycle may destabilize the economy: Election yea ...
... 3. Operational lag is the time elapsed between change in policy and its impact on the economy. B. Political considerations: Government has other goals besides economic stability, and these may conflict with stabilization policy. 1. A political business cycle may destabilize the economy: Election yea ...
Miami Dade College ECO 2013.003 Principles of Macroeconomics
... growing at a rate of 3%, and the unemployment rate is low by historical standards. The economy is expected to continue to grow in the near future, and the monetary authorities are concerned that inflation may increase. This economy is probably in the _____________ stage of the business cycle. A) exp ...
... growing at a rate of 3%, and the unemployment rate is low by historical standards. The economy is expected to continue to grow in the near future, and the monetary authorities are concerned that inflation may increase. This economy is probably in the _____________ stage of the business cycle. A) exp ...
Macro 3
... a) consumer wealth: When people have less money to save. This causes the curve to shift to the left. (decrease in AD) This has nothing to do with price. This is a change in real income due to nonmarket factors. (Decrease in stock prices will lead to less wealth.) b) consumer expectations: If people ...
... a) consumer wealth: When people have less money to save. This causes the curve to shift to the left. (decrease in AD) This has nothing to do with price. This is a change in real income due to nonmarket factors. (Decrease in stock prices will lead to less wealth.) b) consumer expectations: If people ...
Basic Macro Relationship
... because it is so volatile, but changes in consumption (unrelated to income), net exports, and government purchases also are subject to the multiplier effect. b. The initial change refers to an upward shift or downward shift in the aggregate expenditures schedule due to a change in one of its compone ...
... because it is so volatile, but changes in consumption (unrelated to income), net exports, and government purchases also are subject to the multiplier effect. b. The initial change refers to an upward shift or downward shift in the aggregate expenditures schedule due to a change in one of its compone ...
Principles of Macroeconomics, Case/Fair/Oster, 10e
... automatic destabilizer Revenue and expenditure items in the federal budget that automatically change with the state of the economy in such a way as to destabilize GDP. fiscal drag The negative effect on the economy that occurs when average tax rates increase because taxpayers have moved into higher ...
... automatic destabilizer Revenue and expenditure items in the federal budget that automatically change with the state of the economy in such a way as to destabilize GDP. fiscal drag The negative effect on the economy that occurs when average tax rates increase because taxpayers have moved into higher ...
Fiscal Policy
... Fiscal Policy We have already briefly talked about Keynesian arguments for government intervention, where we found that Keynesian Economist believes that because prices are sticky, it may take a sufficient lag in time before the economy rights its course and attain its potential output or target inc ...
... Fiscal Policy We have already briefly talked about Keynesian arguments for government intervention, where we found that Keynesian Economist believes that because prices are sticky, it may take a sufficient lag in time before the economy rights its course and attain its potential output or target inc ...
Shanghai American School
... >>Horizontal range: where the price level remains constant with substantial output variation. In this range substantial unemployment and excess capacity exist. Economy is far below full-employment output level. >>Intermediate (upsloping) range: where the expansion of real output is accompanied by r ...
... >>Horizontal range: where the price level remains constant with substantial output variation. In this range substantial unemployment and excess capacity exist. Economy is far below full-employment output level. >>Intermediate (upsloping) range: where the expansion of real output is accompanied by r ...
Bahamas_en.pdf
... outlays on wages and salaries, aimed partly at maintaining consumption during the downturn. Capital expenditure contracted by 6.7% owing partly to reduced acquisition of assets. Nevertheless, expenditure on capital formation, an important part of capital spending, rose by 8.8% and was associated wit ...
... outlays on wages and salaries, aimed partly at maintaining consumption during the downturn. Capital expenditure contracted by 6.7% owing partly to reduced acquisition of assets. Nevertheless, expenditure on capital formation, an important part of capital spending, rose by 8.8% and was associated wit ...
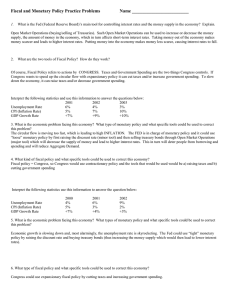
Answer Key--Fiscal and Monetary Policy Practice
... supply, the amount of money in the economy, which in turn affects short-term interest rates. Taking money out of the economy makes money scarcer and leads to higher interest rates. Putting money into the economy makes money less scarce, causing interest rates to fall. ...
... supply, the amount of money in the economy, which in turn affects short-term interest rates. Taking money out of the economy makes money scarcer and leads to higher interest rates. Putting money into the economy makes money less scarce, causing interest rates to fall. ...
PDF - Mercatus Center
... supposedly evidence of people’s opposition to severe cuts in spending. However, the growing antiausterity backlash in Europe ignores one fundamental point: If there is austerity in Europe, in most cases it hasn’t taken the form of massive spending cuts. The following collection of charts shows the e ...
... supposedly evidence of people’s opposition to severe cuts in spending. However, the growing antiausterity backlash in Europe ignores one fundamental point: If there is austerity in Europe, in most cases it hasn’t taken the form of massive spending cuts. The following collection of charts shows the e ...
Answer Key Section 5 and 6 practice test
... D) an increase in the government deficit 5. Suppose there is news of rising unemployment. Which scenario is most likely? A) Firms invest more in automation; the demand for loanable funds rises; interest rates rise; borrowing drops, which makes the anticipated bad times a reality. B) Households save ...
... D) an increase in the government deficit 5. Suppose there is news of rising unemployment. Which scenario is most likely? A) Firms invest more in automation; the demand for loanable funds rises; interest rates rise; borrowing drops, which makes the anticipated bad times a reality. B) Households save ...
Contradictions - EESC European Economic and Social Committee
... Joan Robinson: the central paradox of capitalism is that ‘each employer individually gains from a low real wage in terms of his product, but all suffer from the limited market for commodities which a low real-wage rate entails’. ...
... Joan Robinson: the central paradox of capitalism is that ‘each employer individually gains from a low real wage in terms of his product, but all suffer from the limited market for commodities which a low real-wage rate entails’. ...
PP-Chapter 11
... If the MPC is .98, the recessionary GDP gap is $200 billion, and the AD shortfall is $600 billion: 1. What is the fiscal target? 2. What size gov’t spending increase is needed to close the GDP gap? 3. What size tax decrease is needed to close the GDP gap? 4. What size transfer payment increase is ne ...
... If the MPC is .98, the recessionary GDP gap is $200 billion, and the AD shortfall is $600 billion: 1. What is the fiscal target? 2. What size gov’t spending increase is needed to close the GDP gap? 3. What size tax decrease is needed to close the GDP gap? 4. What size transfer payment increase is ne ...