Macroeconomics
... These criticisms were generated from suffering of the Great Depression of the 1930’s which was one of the most disruptive economic crises in history, that resulted in mass unemployment and greatly reduced levels of GDP in the major Western countries. • Keynes presented a new way of analyzing the eco ...
... These criticisms were generated from suffering of the Great Depression of the 1930’s which was one of the most disruptive economic crises in history, that resulted in mass unemployment and greatly reduced levels of GDP in the major Western countries. • Keynes presented a new way of analyzing the eco ...
Unit 3: Microeconomic Concepts
... investment more workers & businesses ◦ Less spending decreases government investment less workers & businesses ◦ Spending can also increase/decrease transfer payments (welfare, social security, etc.) ...
... investment more workers & businesses ◦ Less spending decreases government investment less workers & businesses ◦ Spending can also increase/decrease transfer payments (welfare, social security, etc.) ...
Macro_3.4-_Classical_vs._Keynesian
... “The long run is a misleading guide to current affairs. In the long run we are all dead. Economists set themselves too easy, too useless a task if in tempestuous seasons they can only tell us that when the storm is past the ocean is ...
... “The long run is a misleading guide to current affairs. In the long run we are all dead. Economists set themselves too easy, too useless a task if in tempestuous seasons they can only tell us that when the storm is past the ocean is ...
Chapter 11
... Aggregate supply curve is a curve that shows the amount of real output or GDP that is for sale at various prices. In this case, Aggregate supply (AS) curve can be divided into 3 ranges. a- Horizontal range: This portion of AS curve is horizontal and the price level is fixed. It is called Keynisian s ...
... Aggregate supply curve is a curve that shows the amount of real output or GDP that is for sale at various prices. In this case, Aggregate supply (AS) curve can be divided into 3 ranges. a- Horizontal range: This portion of AS curve is horizontal and the price level is fixed. It is called Keynisian s ...
EconomicPolicy AP2013
... statement about the government and the economy? “Capitalism is the astounding belief that the most wickedest of men will do the most wickedest of things for the greatest good of ...
... statement about the government and the economy? “Capitalism is the astounding belief that the most wickedest of men will do the most wickedest of things for the greatest good of ...
13 Overall economic Activity
... Leakages and Injections This model is very simplified What is it not taking into consideration? Do people spend all of their income? No, they save some in the bank or other financial institutions This is known as a leakage from the circular flow If households don’t buy all the output that is ...
... Leakages and Injections This model is very simplified What is it not taking into consideration? Do people spend all of their income? No, they save some in the bank or other financial institutions This is known as a leakage from the circular flow If households don’t buy all the output that is ...
Income and Expenditure
... notion of autonomous consumer spending. In particular, students often question how consumer spending can be positive even when income is zero. Emphasize to students that when disposable income is zero, consumers are financing their spending with their savings. • The link between investment and consu ...
... notion of autonomous consumer spending. In particular, students often question how consumer spending can be positive even when income is zero. Emphasize to students that when disposable income is zero, consumers are financing their spending with their savings. • The link between investment and consu ...
Chapter 5
... Effectiveness of monetary policy depends upon The sensitivity (elasticity) of economy to changes In interest rates Advocates fiscal policy ...
... Effectiveness of monetary policy depends upon The sensitivity (elasticity) of economy to changes In interest rates Advocates fiscal policy ...
Fiscal Policy During and After the Crisis
... stimulus measures were implemented in response to the largest global recession since the 1930s Discretionary Measures in 2009 and 2010, G7 countries P centt off GDP Per ...
... stimulus measures were implemented in response to the largest global recession since the 1930s Discretionary Measures in 2009 and 2010, G7 countries P centt off GDP Per ...
New Keynesian versus Old Keynesian Government Spending
... numerical estimates of the impact of an increase in government spending on GDP and employment in the United States. Such estimates are a crucial input for the policy making process. They help determine the appropriate size and timing of countercyclical fiscal policy packages and they help inform mem ...
... numerical estimates of the impact of an increase in government spending on GDP and employment in the United States. Such estimates are a crucial input for the policy making process. They help determine the appropriate size and timing of countercyclical fiscal policy packages and they help inform mem ...
1600547EE_Bahamas_en PDF - CEPAL
... modest at 2.0% as the pass-through effects of lower fuel prices partly offset higher prices resulting from the introduction of value added tax (VAT) in 2015. The fiscal position improved in fiscal year 2014/15 owing mainly to VAT receipts. The fiscal deficit narrowed by 20.4%, but an uptick in spend ...
... modest at 2.0% as the pass-through effects of lower fuel prices partly offset higher prices resulting from the introduction of value added tax (VAT) in 2015. The fiscal position improved in fiscal year 2014/15 owing mainly to VAT receipts. The fiscal deficit narrowed by 20.4%, but an uptick in spend ...
Chapter 12 – Macroeconomic Performance
... produced by a country’s citizens (whether within our borders or not) Disposable Personal Income (DPI) – Total consumer income minus income taxes (represents amount of money consumers have to spend) All of our country’s output (GDP) is purchased by one of four sectors. We use the Output Expenditure m ...
... produced by a country’s citizens (whether within our borders or not) Disposable Personal Income (DPI) – Total consumer income minus income taxes (represents amount of money consumers have to spend) All of our country’s output (GDP) is purchased by one of four sectors. We use the Output Expenditure m ...
AS 2.3 Practice Assessment Marking Schedule File
... negative effects may be larger than the economic effects (explained in b above) causing the net social welfare index to fall (E) And so our economic growth would decrease (Q) ...
... negative effects may be larger than the economic effects (explained in b above) causing the net social welfare index to fall (E) And so our economic growth would decrease (Q) ...
2.3 Practice Marking schedule File
... negative effects may be larger than the economic effects (explained in b above) causing the net social welfare index to fall (E) And so our economic growth would decrease (Q) ...
... negative effects may be larger than the economic effects (explained in b above) causing the net social welfare index to fall (E) And so our economic growth would decrease (Q) ...
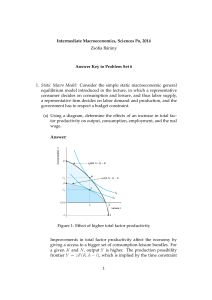
Intermediate Macroeconomics, Sciences Po, 2014 Zsófia Bárány
... When T = G/z, the consumption possibilities frontier is given by C = Y − T = zF (K, h − l) − G/z. Note: for z = 1 the frontier is the same as in the previous part of the problem set. When z increases, the private sector is more productive (as in part (a)), but now there is also an effect on the gove ...
... When T = G/z, the consumption possibilities frontier is given by C = Y − T = zF (K, h − l) − G/z. Note: for z = 1 the frontier is the same as in the previous part of the problem set. When z increases, the private sector is more productive (as in part (a)), but now there is also an effect on the gove ...
The Economic Cycle
... or spending levels. Exogenous demand shocks are external influences on the components of aggregate demand (consumption, investment, government spending, exports and imports) and they may result from a wideranging set of changes. They include, for example, a change in household taxation, shifting opp ...
... or spending levels. Exogenous demand shocks are external influences on the components of aggregate demand (consumption, investment, government spending, exports and imports) and they may result from a wideranging set of changes. They include, for example, a change in household taxation, shifting opp ...
Presentation_Barrell_ppt
... sovereign bonds had a zero risk weights. Domestic holders of Greek debt had a more realistic perception of risks, so returns looked high to banks elsewhere ...
... sovereign bonds had a zero risk weights. Domestic holders of Greek debt had a more realistic perception of risks, so returns looked high to banks elsewhere ...
0324236956_122417
... The interest-rate effect helps explain why the aggregate-demand curve slopes downward: An increase in the price level raises money demand, which raises the interest rate, which reduces investment, which reduces the aggregate quantity of goods & services demanded. ...
... The interest-rate effect helps explain why the aggregate-demand curve slopes downward: An increase in the price level raises money demand, which raises the interest rate, which reduces investment, which reduces the aggregate quantity of goods & services demanded. ...
chapter 10 - Spring Branch ISD
... (a) If full employment in this economy is 65 million, will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap? What will be the consequence of this gap? By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain. (b) ...
... (a) If full employment in this economy is 65 million, will there be an inflationary or recessionary gap? What will be the consequence of this gap? By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the inflationary or recessionary gap? Explain. (b) ...
March 19, 2001
... The Canadian economy is in a short and long run equilibrium position with Aggregate Demand equal to Aggregate Supply at Potential GDP. Now, U.S. GDP shoots upwards, and as a result, Canada’s Aggregate Demand curve shifts to the right. Consider the following statements about what happens: I) the pric ...
... The Canadian economy is in a short and long run equilibrium position with Aggregate Demand equal to Aggregate Supply at Potential GDP. Now, U.S. GDP shoots upwards, and as a result, Canada’s Aggregate Demand curve shifts to the right. Consider the following statements about what happens: I) the pric ...
References - E
... used during the period of low demand and also its work load will not fall as much as that of small firms. Similarly, any reduction in the level of building activity would give rise to unemployment and even some workers in the industry will leave the industry to work elsewhere since the employment in ...
... used during the period of low demand and also its work load will not fall as much as that of small firms. Similarly, any reduction in the level of building activity would give rise to unemployment and even some workers in the industry will leave the industry to work elsewhere since the employment in ...
Macroeconomics (AGEC 512)
... • But, it had very little to say about aggregate demand, it perceived no problem of unemployment and it envisaged no role for any form of macro policy other than control of money supply to prevent inflation. • The essential reason for all this was that classical economics concentrated, at least in i ...
... • But, it had very little to say about aggregate demand, it perceived no problem of unemployment and it envisaged no role for any form of macro policy other than control of money supply to prevent inflation. • The essential reason for all this was that classical economics concentrated, at least in i ...
14.02 Principles of Macroeconomics Problem Set 2 Spring 2003
... 3. If we want to consider the effects of price changes in the short run, we can use the ISLM model. 4. The government of Macronesia decides to permanently increase unemployment benefits. The AS-AD model shows that there will be a short run effect on output, but no medium run effect. 5. Suppose worke ...
... 3. If we want to consider the effects of price changes in the short run, we can use the ISLM model. 4. The government of Macronesia decides to permanently increase unemployment benefits. The AS-AD model shows that there will be a short run effect on output, but no medium run effect. 5. Suppose worke ...
Slide 1
... and force reorganisation of national expenditures...’ ‘’ because interest rates will soon be roughly the same everywhere, the mobility of labour across European frontiers is (still) slight, and financial transfers have not been provided for, the countries in the EMU will soon have only one instrumen ...
... and force reorganisation of national expenditures...’ ‘’ because interest rates will soon be roughly the same everywhere, the mobility of labour across European frontiers is (still) slight, and financial transfers have not been provided for, the countries in the EMU will soon have only one instrumen ...