Fall 2012
... the price for the economy when you add growth back in to the model. (B) Suppose that the economy is in a steady state, and declines. What happens to the quantities of steady state K1 and K2 , L1 and L2 , and steady state wage and rental prices of capital? What happens to the relative price of the ...
... the price for the economy when you add growth back in to the model. (B) Suppose that the economy is in a steady state, and declines. What happens to the quantities of steady state K1 and K2 , L1 and L2 , and steady state wage and rental prices of capital? What happens to the relative price of the ...
Sum_Up
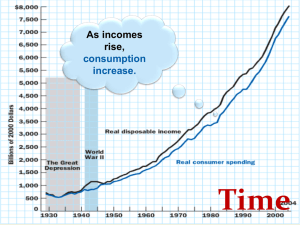
... (1936) says that there is not enough demand in the market. In his explanation of short run, it is the demand for goods and services that will determine the level of GDP, rather than the supply of factor inputs. The Great Depression was a result of low spending by consumer and business. The spe ...
... (1936) says that there is not enough demand in the market. In his explanation of short run, it is the demand for goods and services that will determine the level of GDP, rather than the supply of factor inputs. The Great Depression was a result of low spending by consumer and business. The spe ...
Economics Assessment Bank
... technology) and human capital (e.g., education) play in increasing productivity and how these influence the market. 1. An entrepreneur is considering spending money on research to develop an efficient way to increase productivity. What is the most important decision on whether or not to spend this m ...
... technology) and human capital (e.g., education) play in increasing productivity and how these influence the market. 1. An entrepreneur is considering spending money on research to develop an efficient way to increase productivity. What is the most important decision on whether or not to spend this m ...
Document
... The combined stimulus of federal spending on both the war in Vietnam and social programs in the late 1960s increased aggregate demand enough that the inflation rate began to increase The high inflation rates induced President Richard Nixon to introduce ceilings on prices and wages in 1971 To compoun ...
... The combined stimulus of federal spending on both the war in Vietnam and social programs in the late 1960s increased aggregate demand enough that the inflation rate began to increase The high inflation rates induced President Richard Nixon to introduce ceilings on prices and wages in 1971 To compoun ...
Institute of Business Management Semester: Summer Course
... model. What are the classical and Keynesian views about whether money is neutral in the short run? In the long run? Q#11 Drive aggregate demand (AD) curve? Why does the AD curve slope downward? Give two examples of changes in the economy that shift the AD curve up and to the right and explain why th ...
... model. What are the classical and Keynesian views about whether money is neutral in the short run? In the long run? Q#11 Drive aggregate demand (AD) curve? Why does the AD curve slope downward? Give two examples of changes in the economy that shift the AD curve up and to the right and explain why th ...
Fundamentals of Management
... Average non-oil primary deficit increased from 26 percent of nonoil GDP in 1999 to 38 percent in ...
... Average non-oil primary deficit increased from 26 percent of nonoil GDP in 1999 to 38 percent in ...
Bank of England Inflation Report February 2013
... (a) UK export prices divided by domestic currency export prices of goods and services of 52 countries weighted according to their shares in UK imports, divided by the average sterling effective exchange rate index over the quarter. The sample does not include any major oil exporters. The observation ...
... (a) UK export prices divided by domestic currency export prices of goods and services of 52 countries weighted according to their shares in UK imports, divided by the average sterling effective exchange rate index over the quarter. The sample does not include any major oil exporters. The observation ...
Timeline of Famous Economists Economic Theory
... classical economics!!). He argued that increases in the money supply would not inevitably lead to increases in inflation. Increasing M may instead lead to a decrease in V. In other words the average speed of circulation of money would fall because there was more of it about. Alternatively, the incre ...
... classical economics!!). He argued that increases in the money supply would not inevitably lead to increases in inflation. Increasing M may instead lead to a decrease in V. In other words the average speed of circulation of money would fall because there was more of it about. Alternatively, the incre ...
Current Economic Conditions
... Source: Federal Deficit/Surplus as a Percent of GDP (Fiscal year, %): Office of Management and Budget. ...
... Source: Federal Deficit/Surplus as a Percent of GDP (Fiscal year, %): Office of Management and Budget. ...
PRESIDENT'S REPORT TO THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS,
... Data since your previous Directors' meeting show an expanding economy. During the fourth quarter, real GDP posted a decent gain, led by growth in consumption, exports, equipment and software, inventory investment, and residential investment. Imports rose, subtracting from GDP. Core inflation for con ...
... Data since your previous Directors' meeting show an expanding economy. During the fourth quarter, real GDP posted a decent gain, led by growth in consumption, exports, equipment and software, inventory investment, and residential investment. Imports rose, subtracting from GDP. Core inflation for con ...
Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model Differences
... Oil prices are at record highs. And we wonder how is this going to affect the macroeconomy? What will be the effect on the aggregate price level and aggregate output as a result of this price shock? Well, oil prices affect the economy through the input prices that producers have to pay to make the g ...
... Oil prices are at record highs. And we wonder how is this going to affect the macroeconomy? What will be the effect on the aggregate price level and aggregate output as a result of this price shock? Well, oil prices affect the economy through the input prices that producers have to pay to make the g ...
2009 questions
... 17. Suppose a perfectly competitive market is in long run equilibrium. The market demand curve then shifts to the right. After a short run adjustment to the new equilibrium (a) ...
... 17. Suppose a perfectly competitive market is in long run equilibrium. The market demand curve then shifts to the right. After a short run adjustment to the new equilibrium (a) ...
Budget and the Economy
... and 2003 tax cuts, record deficits reemerged, reaching $455 billion in fiscal year 2008. Indeed, the deficits would be much larger if Social Security were excluded from the calculation. Furthermore, January 2009 projections by the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) of net deficits of $3.1 trillion ov ...
... and 2003 tax cuts, record deficits reemerged, reaching $455 billion in fiscal year 2008. Indeed, the deficits would be much larger if Social Security were excluded from the calculation. Furthermore, January 2009 projections by the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) of net deficits of $3.1 trillion ov ...
Government and Money
... money in taxes to the government. But reducing unemployment by increasing government spending or reducing taxes increases inflation, which is rapidly rising prices. Goods cost more, so people get less for their money. The government's fiscal policy is a powerful tool to guide the nation's economy. F ...
... money in taxes to the government. But reducing unemployment by increasing government spending or reducing taxes increases inflation, which is rapidly rising prices. Goods cost more, so people get less for their money. The government's fiscal policy is a powerful tool to guide the nation's economy. F ...
1 SPERI Panel: `The future of European varieties of capitalism
... Even if the impact of fiscal consolidation on growth can be so great, as to cause debt-GDP ratios to rise rather than fall (Delong and Summers, 2012)- results on the ground suggest that euro area government debt rose from 87.3 percent in 2011 to 90.6 percent in 2013 and is projected to rise further ...
... Even if the impact of fiscal consolidation on growth can be so great, as to cause debt-GDP ratios to rise rather than fall (Delong and Summers, 2012)- results on the ground suggest that euro area government debt rose from 87.3 percent in 2011 to 90.6 percent in 2013 and is projected to rise further ...
Powerpoints Macro Ch7 R
... of the assets of an economy measured by the goods and services it can produce now and in the future Nominal wealth is the value of these assets measured in current prices Asset price inflation is a rise in the price of assets unrelated to increases in their productive capacity ...
... of the assets of an economy measured by the goods and services it can produce now and in the future Nominal wealth is the value of these assets measured in current prices Asset price inflation is a rise in the price of assets unrelated to increases in their productive capacity ...
Power Point: Keynesian Model
... 5. Political Stability and the rule of law – Business cannot be conducted without a guarantee ...
... 5. Political Stability and the rule of law – Business cannot be conducted without a guarantee ...
Document
... The simple Keynesian model for a closed economy without its own currency: Assumption: The short-run supply curve is horizontal (= P is fixed), which implies that aggregate demand alone determines output. The model also assumes that the real interest rate is fixed; and that planned investment is an e ...
... The simple Keynesian model for a closed economy without its own currency: Assumption: The short-run supply curve is horizontal (= P is fixed), which implies that aggregate demand alone determines output. The model also assumes that the real interest rate is fixed; and that planned investment is an e ...
automatic social stabilizers what they are and
... and in the United States) and in different periods of time, however their mechanism of operation is still hiding important details that can reopen discussions or even new areas of research. An example can be given by the constraints imposed by the Maastricht criteria and the Stability and Growth Pac ...
... and in the United States) and in different periods of time, however their mechanism of operation is still hiding important details that can reopen discussions or even new areas of research. An example can be given by the constraints imposed by the Maastricht criteria and the Stability and Growth Pac ...
14.02 Principles of Macroeconomics Problem Set 2 Solutions Spring 2003
... this environment, monetary policy will no longer have an effect on output even in the short run. True. In this case P=Pe even in the short run. The AS curve is consequently vertical in the short and medium run. 6. An increase in the interest rate leads workers to ask for higher wages, leading to a s ...
... this environment, monetary policy will no longer have an effect on output even in the short run. True. In this case P=Pe even in the short run. The AS curve is consequently vertical in the short and medium run. 6. An increase in the interest rate leads workers to ask for higher wages, leading to a s ...
Chapter Objectives - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • The labor-pool effect of globalization has caused wages for low-skilled workers to fall. • At the same time, the market expansion impact of globalization has benefitted high-skilled workers. ...
... • The labor-pool effect of globalization has caused wages for low-skilled workers to fall. • At the same time, the market expansion impact of globalization has benefitted high-skilled workers. ...
Slide 1
... Vertical axis: average spread over the last 20 working days; in basis points. 2 Horizontal axis. 3 Forecast for 2011. 4 Domestic government debt with a remaining maturity of 1-3 years as per cent of total domestic government debt. 5 Average change in general ...
... Vertical axis: average spread over the last 20 working days; in basis points. 2 Horizontal axis. 3 Forecast for 2011. 4 Domestic government debt with a remaining maturity of 1-3 years as per cent of total domestic government debt. 5 Average change in general ...
Race to the Top or to the Bottom
... annual editions of the China Statistical Yearbook. Finally, proportion of the population under the age of 15 for each province was calculated from the results of the annual population sample survey reported in China Statistical Yearbooks. All three control variables are expected to be positively cor ...
... annual editions of the China Statistical Yearbook. Finally, proportion of the population under the age of 15 for each province was calculated from the results of the annual population sample survey reported in China Statistical Yearbooks. All three control variables are expected to be positively cor ...