department of economics
... The literature has considered several potential sources of autonomous demand, including exports, private consumption, residential investment and government consumption. I shall discuss each of these in turn. ...
... The literature has considered several potential sources of autonomous demand, including exports, private consumption, residential investment and government consumption. I shall discuss each of these in turn. ...
Monetary Growth and Business Cycles
... numerous economic variables other than money that have pervasive and systematic effects on the economy. Some of these, such as fiscal policy and interest rates, are important explanatory variables in Keynesian economic theories. Thus, nonmonetarists question whether appeal to economic theory justifi ...
... numerous economic variables other than money that have pervasive and systematic effects on the economy. Some of these, such as fiscal policy and interest rates, are important explanatory variables in Keynesian economic theories. Thus, nonmonetarists question whether appeal to economic theory justifi ...
REGIONAL MODELLING
... each sector grows at national rate in every region. Surely demand for haircuts grows faster in Central (because income grew more). Therefore, output of haircut industry grows faster in Central than elsewhere (because haircuts must be consumed where they are produced). We need local multiplier effect ...
... each sector grows at national rate in every region. Surely demand for haircuts grows faster in Central (because income grew more). Therefore, output of haircut industry grows faster in Central than elsewhere (because haircuts must be consumed where they are produced). We need local multiplier effect ...
What Caused the Build-Up of Canada`s Public Debt?
... GDP and thus to changes in the cyclical component, but these effects may be small relative to the other, non-policy sources of economic fluctuation. In addition, the government’s policies will surely have an influence on real interest rates and GDP growth rates, at least in the short run, but other ...
... GDP and thus to changes in the cyclical component, but these effects may be small relative to the other, non-policy sources of economic fluctuation. In addition, the government’s policies will surely have an influence on real interest rates and GDP growth rates, at least in the short run, but other ...
American Red: The Public Debt in US History
... borrowing authority was vital to enable the national government to undertake everything required of it, particularly with regard to defence and war. To this end, he conceived the necessity of establishing a sound public credit as an instrument of national power.5 Such thinking anticipated orthodox f ...
... borrowing authority was vital to enable the national government to undertake everything required of it, particularly with regard to defence and war. To this end, he conceived the necessity of establishing a sound public credit as an instrument of national power.5 Such thinking anticipated orthodox f ...
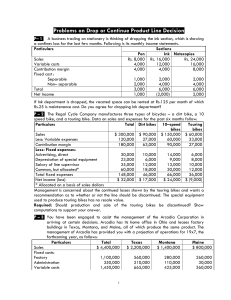
ProblemsonDropOrContinueProductLineDecision
... Under this proposal variable costs would be $8 per unit sold. b. Enter into a long–term contract with a competitor who will serve that area’s customers. This competitor would pay Arcadia a royalty of $4 per unit based upon an estimate of 30,000 units being sold. c. Close the Maine factory and not ex ...
... Under this proposal variable costs would be $8 per unit sold. b. Enter into a long–term contract with a competitor who will serve that area’s customers. This competitor would pay Arcadia a royalty of $4 per unit based upon an estimate of 30,000 units being sold. c. Close the Maine factory and not ex ...
M02_GORD0439_11_IM_C02 - Solution Manual Store
... income accounting identity of the complete four-sector economy, we see that the size of the government budget surplus (T G) is determined by the excess of investment (I NX) over saving (S). Explain that (NX) represents the amount of foreign capital inflow by saying that the U.S. dollars obtaine ...
... income accounting identity of the complete four-sector economy, we see that the size of the government budget surplus (T G) is determined by the excess of investment (I NX) over saving (S). Explain that (NX) represents the amount of foreign capital inflow by saying that the U.S. dollars obtaine ...
GDP deflator
... GDP is the best single measure of the economic well-being of a society. GDP per person tells us the income and expenditure of the average person in the economy. Higher GDP per person indicates a higher standard of living. GDP is not a perfect measure of the happiness or quality of life, however. ...
... GDP is the best single measure of the economic well-being of a society. GDP per person tells us the income and expenditure of the average person in the economy. Higher GDP per person indicates a higher standard of living. GDP is not a perfect measure of the happiness or quality of life, however. ...
כלכלת ישראל - משרד האוצר
... Israel had a very vigorous growth rate relative to the economy’s past performance and by international standards. Since October 2000, the growth rate has been declining due to the global economic slowdown, which has dampened demand for the high-tech products on which the Israeli economy relies. the ...
... Israel had a very vigorous growth rate relative to the economy’s past performance and by international standards. Since October 2000, the growth rate has been declining due to the global economic slowdown, which has dampened demand for the high-tech products on which the Israeli economy relies. the ...
Chap32
... The size and composition of the budget and the difference between outlays and revenues measure the budget’s fiscal impact When outlays exceed revenues, the budget is in deficit Stimulates aggregate demand in the short run, but reduces national saving that in the long run could ...
... The size and composition of the budget and the difference between outlays and revenues measure the budget’s fiscal impact When outlays exceed revenues, the budget is in deficit Stimulates aggregate demand in the short run, but reduces national saving that in the long run could ...
What determines fiscal balances?
... Stability and Convergence Programmes1, which states that a medium-term budgetary position “…has to take account of several elements, such as the possibility to deal with adverse cyclical developments and other unforeseen risks whilst respecting the government deficit reference value, the need to tak ...
... Stability and Convergence Programmes1, which states that a medium-term budgetary position “…has to take account of several elements, such as the possibility to deal with adverse cyclical developments and other unforeseen risks whilst respecting the government deficit reference value, the need to tak ...
How would a fiscal shock in Germany affect other European countries?
... Central, Eastern and Southeastern (CESEE) economies, these effects may be transmitted via the financial channel since financial variables such as equity prices and private sector credit significantly increase in response to the assumed fiscal shock in Germany. Upward effects on consumer prices, by c ...
... Central, Eastern and Southeastern (CESEE) economies, these effects may be transmitted via the financial channel since financial variables such as equity prices and private sector credit significantly increase in response to the assumed fiscal shock in Germany. Upward effects on consumer prices, by c ...
My lecture
... your work doesn’t count as part of GDP. If you get paid for the same work, it counts. • If you pollute during production and someone pays to clean the environment, the GDP will be higher than if the producer tried to reduce pollution during production so no clean-up was necessary. Econ 202 Dr. Ugur ...
... your work doesn’t count as part of GDP. If you get paid for the same work, it counts. • If you pollute during production and someone pays to clean the environment, the GDP will be higher than if the producer tried to reduce pollution during production so no clean-up was necessary. Econ 202 Dr. Ugur ...
Assessing the effects of military expenditure on growth.
... To interpret the results of any empirical study it is necessary to have a theory, even though this may not of itself be verifiable. For research on the economic effects of military spending this is complicated by the fact that much of economic theory does not have an explicit role for military spend ...
... To interpret the results of any empirical study it is necessary to have a theory, even though this may not of itself be verifiable. For research on the economic effects of military spending this is complicated by the fact that much of economic theory does not have an explicit role for military spend ...
經濟學講義(97
... I. The Economy’s Income and Expenditure For an economy as a whole, income must equal expenditure i.e. GDP can be measured by adding up either by the total expenditure of household or total income(wages, rent, and profit)paid by firms(p.509 figure 1) ...
... I. The Economy’s Income and Expenditure For an economy as a whole, income must equal expenditure i.e. GDP can be measured by adding up either by the total expenditure of household or total income(wages, rent, and profit)paid by firms(p.509 figure 1) ...
What are the Effects of Fiscal Policy Shocks ?
... We apply this new approach to US quarterly data, from 1955 to 2000. We use the same definitions of government expenditure and revenue as Blanchard and Perotti (2002) in order not to obscure the implications of our new methodological approach by using different data definitions. Our main results are ...
... We apply this new approach to US quarterly data, from 1955 to 2000. We use the same definitions of government expenditure and revenue as Blanchard and Perotti (2002) in order not to obscure the implications of our new methodological approach by using different data definitions. Our main results are ...
Chap 31
... 38) The government begins year 1 with $25 billion of debt. Based on the information in the above table, what is the amount of debt following year 4? A) –$20 billion (The government has net saving rather than debt). B) $35 billion. C) $5 billion. D) $320 billion. Answer: B Topic: Deficits and Debt Sk ...
... 38) The government begins year 1 with $25 billion of debt. Based on the information in the above table, what is the amount of debt following year 4? A) –$20 billion (The government has net saving rather than debt). B) $35 billion. C) $5 billion. D) $320 billion. Answer: B Topic: Deficits and Debt Sk ...
MS-WORD - Department of Economics
... (2) And that Quantity Theory of money indeed is very old, going back at least to the 16 th century when the French philosopher Jean Bodin (in 1568) attributed the contemporary Price Revolution era inflation to the influx of American treasure), opposing Malestroit’s views on the paramount role of deb ...
... (2) And that Quantity Theory of money indeed is very old, going back at least to the 16 th century when the French philosopher Jean Bodin (in 1568) attributed the contemporary Price Revolution era inflation to the influx of American treasure), opposing Malestroit’s views on the paramount role of deb ...
chapter 4 - MCNEIL ECONOMICS
... cycle. It is followed by a recession, which is a period of decline in real output that lasts six months or longer. When real output is no longer declining, it has hit its trough. This low point is followed by expansion or recovery in which the economy experiences an increase in real output. a. Busin ...
... cycle. It is followed by a recession, which is a period of decline in real output that lasts six months or longer. When real output is no longer declining, it has hit its trough. This low point is followed by expansion or recovery in which the economy experiences an increase in real output. a. Busin ...
Short-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium
... 1. In the AD–AS model, the intersection of the short-run aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve is the point of short-run macroeconomic equilibrium. It determines the short-run equilibrium aggregate price level and the level of short-run equilibrium aggregate output. 2. Economic fluct ...
... 1. In the AD–AS model, the intersection of the short-run aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve is the point of short-run macroeconomic equilibrium. It determines the short-run equilibrium aggregate price level and the level of short-run equilibrium aggregate output. 2. Economic fluct ...
Fiscal Shocks and Real Wages Agustín S. Bénétrix IIIS Trinity College Dublin
... ment variables are in real terms (log levels) and deflated with their own deflators. These are available at the OECD Economic Outlook No 82. The exception is non-wage government consumption. For this variable I use total government consumption prices. I take these deflators for the baseline estimat ...
... ment variables are in real terms (log levels) and deflated with their own deflators. These are available at the OECD Economic Outlook No 82. The exception is non-wage government consumption. For this variable I use total government consumption prices. I take these deflators for the baseline estimat ...
Chapter 11 Applications of the Ramsey model
... In this section we extend the Ramsey model of a competitive market economy by adding a government that spends on goods and services, makes transfers to the private sector, and levies taxes. Subsection 11.1.1 considers the effect of government spending on goods and services, assuming a balanced budget ...
... In this section we extend the Ramsey model of a competitive market economy by adding a government that spends on goods and services, makes transfers to the private sector, and levies taxes. Subsection 11.1.1 considers the effect of government spending on goods and services, assuming a balanced budget ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES ESTATE TAXATION, ENTREPRENEURSHIP, AND WEALTH Marco Cagetti
... positive and significant, compared to the small revenue raised by the estate and gift taxes (which is about 0.3% of GDP) when either government spending is cut, or when the tax rate on consumption is increased. Under those policies, aggregate output goes up by 1%-1.5%, while aggregate capital increa ...
... positive and significant, compared to the small revenue raised by the estate and gift taxes (which is about 0.3% of GDP) when either government spending is cut, or when the tax rate on consumption is increased. Under those policies, aggregate output goes up by 1%-1.5%, while aggregate capital increa ...