Sociological Perspectives on Sports
... integration, reinforcing social norms, provides athletes and spectators with socially acceptable aggression. ...
... integration, reinforcing social norms, provides athletes and spectators with socially acceptable aggression. ...
Sociological Perspective
... Recap…Sociological Imagination Allows us to understand the individual’s relationship with society Our view of the world changes once we begin to explore the ways in which our lives are influenced by social forces that surround us all Significant events in a person’s life often leads to change ...
... Recap…Sociological Imagination Allows us to understand the individual’s relationship with society Our view of the world changes once we begin to explore the ways in which our lives are influenced by social forces that surround us all Significant events in a person’s life often leads to change ...
Chapter 4: Socialization:
... different socializing agents support one another --> social harmony --> social order The Conflict perspective - different socializing agents have conflicting goals --> social conflict --> social change – Those who have power use socialization to manipulate others into supporting the power structur ...
... different socializing agents support one another --> social harmony --> social order The Conflict perspective - different socializing agents have conflicting goals --> social conflict --> social change – Those who have power use socialization to manipulate others into supporting the power structur ...
Social Structure I
... 1. Disregard for the rights of others. At least three of the following: behaves in a way that is grounds for arrest, deceitful and manipulative, impulsive, aggressive, irresponsible, lack of remorse ...
... 1. Disregard for the rights of others. At least three of the following: behaves in a way that is grounds for arrest, deceitful and manipulative, impulsive, aggressive, irresponsible, lack of remorse ...
Homeless and Mentally ill In our Public Libraries
... “Only human beings can look directly at something, have all the information they need to make an accurate prediction, perhaps even momentarily make the accurate prediction and then say it isn’t so.” ...
... “Only human beings can look directly at something, have all the information they need to make an accurate prediction, perhaps even momentarily make the accurate prediction and then say it isn’t so.” ...
Sociology 314: 03/04 Contemporary Sociological Theory Fall 2014
... singular truth. Rather, the tools approach allows us to treat theories as dense analytical concepts that are more or less appropriate for studying social life from a specific point of view. In other words, we will be operating with the assumption that there is no single theoretical perspective that ...
... singular truth. Rather, the tools approach allows us to treat theories as dense analytical concepts that are more or less appropriate for studying social life from a specific point of view. In other words, we will be operating with the assumption that there is no single theoretical perspective that ...
Sociology
... Social-Conflict Too broad, ignores how shared values and mutual interdependence unify society, pursues political goals Symbolic-Interaction Ignores larger social structures, effects of culture, factors such as class, gender & race ...
... Social-Conflict Too broad, ignores how shared values and mutual interdependence unify society, pursues political goals Symbolic-Interaction Ignores larger social structures, effects of culture, factors such as class, gender & race ...
Sociology
... Social Class ~ Students will examine the characteristics of people in various social classes and understand the role that social class plays to influence human behavior. ...
... Social Class ~ Students will examine the characteristics of people in various social classes and understand the role that social class plays to influence human behavior. ...
FREE INQUIRY IN CREATIVE SOCIOLOGY Volume 40, Number 1
... engaging in some form of social deviance if the norms and the acts are strictly defined as being opposites. With only a few notable exceptions such as the terms suburban, urban, and exurban discussed in relation to a rural-urban division, there are no interstitial typologies between oppositional cat ...
... engaging in some form of social deviance if the norms and the acts are strictly defined as being opposites. With only a few notable exceptions such as the terms suburban, urban, and exurban discussed in relation to a rural-urban division, there are no interstitial typologies between oppositional cat ...
Aim: What is deviance?
... reach them, you’re an innovator. You’re a retreatist if you reject all means and goals of society. You’re a rebel, like Che Guevara, if you not only reject social means and goals but also want to destroy society itself and replace it with a new paradigm. ...
... reach them, you’re an innovator. You’re a retreatist if you reject all means and goals of society. You’re a rebel, like Che Guevara, if you not only reject social means and goals but also want to destroy society itself and replace it with a new paradigm. ...
Human social behavior
... N of 1 and Critical Thinking (1) • “N” or sometimes “n” refers to the number of observations a scientist made – In a survey, the number who completed it – In medical research, n of people/animals studied • Old phrase: “One mouse equals no mouse” means conclusions drawn from studying one mouse are n ...
... N of 1 and Critical Thinking (1) • “N” or sometimes “n” refers to the number of observations a scientist made – In a survey, the number who completed it – In medical research, n of people/animals studied • Old phrase: “One mouse equals no mouse” means conclusions drawn from studying one mouse are n ...
teori-teori belajar
... as favorable or unfavorable. In some societies an individual is surrounded by persons who invariably define the legal codes as rules to be observed, while in others he is surrounded by persons whose definitions are favorable to the violation of the legal codes A person becomes delinquent because of ...
... as favorable or unfavorable. In some societies an individual is surrounded by persons who invariably define the legal codes as rules to be observed, while in others he is surrounded by persons whose definitions are favorable to the violation of the legal codes A person becomes delinquent because of ...
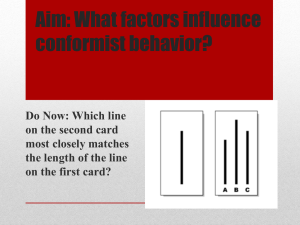
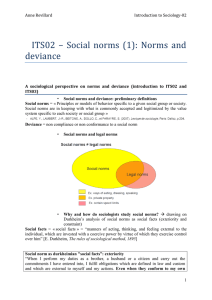
ITS02 – Social norms (1): Norms and deviance
... Deviance as process: the interactionist perspective (Becker, Goffman) The Chicago tradition in American sociology • First generation : R.Park, H. Blumer, E. Burgess, N. Anderson, G.H. Mead… • Second generation (50s-60s) : E. Hughes, H. Becker, E. Goffman, A. Strauss… Deviance as process: H.Becker « ...
... Deviance as process: the interactionist perspective (Becker, Goffman) The Chicago tradition in American sociology • First generation : R.Park, H. Blumer, E. Burgess, N. Anderson, G.H. Mead… • Second generation (50s-60s) : E. Hughes, H. Becker, E. Goffman, A. Strauss… Deviance as process: H.Becker « ...
Sociological Theories A Sociological theory is a
... and social institutions. He wrote about the ways societies could maintain their integrity and coherence in the modern diversified era, following the fragmentation of the religious, racial, and ethnic solidarity of the past. His sociological perspective was to see society as comparable to a living or ...
... and social institutions. He wrote about the ways societies could maintain their integrity and coherence in the modern diversified era, following the fragmentation of the religious, racial, and ethnic solidarity of the past. His sociological perspective was to see society as comparable to a living or ...
File - New Richmond High School Behavioral Sciences
... a. Where we live makes a great difference in shaping our lives. b. Societies the world over are increasingly interconnected, making traditional distinctions between “us” and “them” less and less valid. c. Many human problems faced in the United States are far more serious elsewhere. d. Thinking glob ...
... a. Where we live makes a great difference in shaping our lives. b. Societies the world over are increasingly interconnected, making traditional distinctions between “us” and “them” less and less valid. c. Many human problems faced in the United States are far more serious elsewhere. d. Thinking glob ...
Social Structure Theories
... The Work of Shaw and McKay Linked transitional slum areas to the inclination to commit crime Transitional neighborhoods are incapable of inducing residents to defend against criminal groups Concentric zone mapping identified the inner-city transitional zones as having the heaviest concentratio ...
... The Work of Shaw and McKay Linked transitional slum areas to the inclination to commit crime Transitional neighborhoods are incapable of inducing residents to defend against criminal groups Concentric zone mapping identified the inner-city transitional zones as having the heaviest concentratio ...
Courses Sheets x17 sorts_Layout 1
... Read, read and read some more! Use the Webb text book regularly Access past exam papers and mark schemes to help develop your understanding of how to structure your answers. This will help you see what the examiners are looking for in your answer • Discuss and debate in class, this is a very interes ...
... Read, read and read some more! Use the Webb text book regularly Access past exam papers and mark schemes to help develop your understanding of how to structure your answers. This will help you see what the examiners are looking for in your answer • Discuss and debate in class, this is a very interes ...
What are the root causes of antisocial behavior and juvenile
... develop the same problems. Moreover, because so many more boys than girls develop the disorder, some think male hormones may play a role. Still other biological researchers think a problem in the central nervous system could contribute to the erratic and antisocial behavior. ...
... develop the same problems. Moreover, because so many more boys than girls develop the disorder, some think male hormones may play a role. Still other biological researchers think a problem in the central nervous system could contribute to the erratic and antisocial behavior. ...
What is a Theory?
... Founders of Sociology • Capitalism created social inequality • Between the bourgeoisie, who owned the means of production (money, factories, natural resources, land), and the proletariat, who were the workers • According to Marx, this inequality leads to ...
... Founders of Sociology • Capitalism created social inequality • Between the bourgeoisie, who owned the means of production (money, factories, natural resources, land), and the proletariat, who were the workers • According to Marx, this inequality leads to ...
here - Sociology Class
... 73. One of the main findings of the sociologist Kohn was that socialization depends on a family’s social class. 74. The process of learning new norms, values, attitudes, and behaviors to match new life situations is re-socialization. 75. An attempt to remake the self by stripping away the individual ...
... 73. One of the main findings of the sociologist Kohn was that socialization depends on a family’s social class. 74. The process of learning new norms, values, attitudes, and behaviors to match new life situations is re-socialization. 75. An attempt to remake the self by stripping away the individual ...
Mental Illness: Know The Signs and Symptoms!
... Counselor, with 16 years of experience in Community Mental Health) provided the program. The Topics: What Is Mental Illness? Who has it? What are the Most Common Disorders? Mental Illness is a Disorder of the Brain that changes a person’s thinking, feelings, and behavior and causes the person distre ...
... Counselor, with 16 years of experience in Community Mental Health) provided the program. The Topics: What Is Mental Illness? Who has it? What are the Most Common Disorders? Mental Illness is a Disorder of the Brain that changes a person’s thinking, feelings, and behavior and causes the person distre ...
File
... explain how society works. These are structuralist theories such as Functionalism, Marxism and Feminism which say all of society behaves in this way, e.g. for Marxism culture, identity and socialisation are all to do with capitalism and class inequality. Postmodernists believe that the norms and val ...
... explain how society works. These are structuralist theories such as Functionalism, Marxism and Feminism which say all of society behaves in this way, e.g. for Marxism culture, identity and socialisation are all to do with capitalism and class inequality. Postmodernists believe that the norms and val ...
Chapter One
... What is the difference between counterconditioning and extinction? Which of these experimental procedures is most directly linked to response prevention? Which one is linked to systematic desensitization? ...
... What is the difference between counterconditioning and extinction? Which of these experimental procedures is most directly linked to response prevention? Which one is linked to systematic desensitization? ...
Chapter 1 PPT.1
... • Sociologists are interested in studying social interaction. • Social Interaction is how people relate to one another and influence each other’s behavior. • Sociologists focus on the group rather than on the individual. ...
... • Sociologists are interested in studying social interaction. • Social Interaction is how people relate to one another and influence each other’s behavior. • Sociologists focus on the group rather than on the individual. ...