Plant Reproduction - Doral Academy Preparatory
... from spores. The life cycle of a fern is very different from the life cycle of many other plants. While many plants grow a mature adult form straight out of the seed, ferns have an intermediate stage, called a gametophyte, which then grows into a mature fern. ...
... from spores. The life cycle of a fern is very different from the life cycle of many other plants. While many plants grow a mature adult form straight out of the seed, ferns have an intermediate stage, called a gametophyte, which then grows into a mature fern. ...
Seeds - Del Mar College
... migrate and cell walls form. The resulting female gametophyte includes the egg and a cell with two nuclei that will form endosperm. ...
... migrate and cell walls form. The resulting female gametophyte includes the egg and a cell with two nuclei that will form endosperm. ...
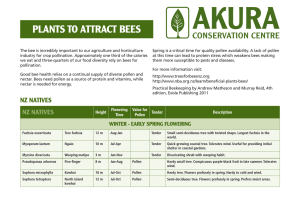
PLANTS TO ATTRACT BEES
... PLANTS TO ATTRACT BEES The bee is incredibly important to our agriculture and horticulture industry for crop pollination. Approximately one third of the calories we eat and three-quarters of our food diversity rely on bees for pollination. ...
... PLANTS TO ATTRACT BEES The bee is incredibly important to our agriculture and horticulture industry for crop pollination. Approximately one third of the calories we eat and three-quarters of our food diversity rely on bees for pollination. ...
Chapter 11/12 PLANT REPRODUCTION
... 2) Pistil - the female part of the flower. Stigma - covered with a sticky substance to capture pollen. Style - the thin ‘neck’ to support the stigma. Ovary - holds the ovules which turn into seeds after fertilization. ...
... 2) Pistil - the female part of the flower. Stigma - covered with a sticky substance to capture pollen. Style - the thin ‘neck’ to support the stigma. Ovary - holds the ovules which turn into seeds after fertilization. ...
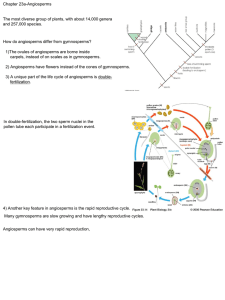
Chapter 23a-Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from
... Each microsprocyte undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid microspores. ...
... Each microsprocyte undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid microspores. ...
Plant reproduction
... pollen grains and seeds. • Pollen grains are the male gametophyte packaged in a hard coat that allows it to reach the female without having to swim through water. This is a large advantage on dry land. • Seeds are diploid sporophyte embryos, packaged to survive a period of dormancy and bad environme ...
... pollen grains and seeds. • Pollen grains are the male gametophyte packaged in a hard coat that allows it to reach the female without having to swim through water. This is a large advantage on dry land. • Seeds are diploid sporophyte embryos, packaged to survive a period of dormancy and bad environme ...
May12
... Petals- The petals (which are usually bright or bold in color) are the part of the flower that usually catch our eye when we first look at it. They catch bees' eyes, too! They are what attract the bees to the flower. Sepals- Parts that look like little green leaves that cover the outside of a flower ...
... Petals- The petals (which are usually bright or bold in color) are the part of the flower that usually catch our eye when we first look at it. They catch bees' eyes, too! They are what attract the bees to the flower. Sepals- Parts that look like little green leaves that cover the outside of a flower ...
Power Point 1 - G. Holmes Braddock
... Assists in pollination in order for flowers to reproduce Attracts pollinators by the colors and scent to get nectar Protects the female and male reproductive parts of the plant ...
... Assists in pollination in order for flowers to reproduce Attracts pollinators by the colors and scent to get nectar Protects the female and male reproductive parts of the plant ...
Plant Reproduction
... pollen from the stigma or one flower to the anther of a flower of another plant of the same species. ...
... pollen from the stigma or one flower to the anther of a flower of another plant of the same species. ...
Formation of Angiosperm Gametes
... reproductive organs of angiosperms are different from those of animals in two ways. First, in angiosperms, both male and female structures usually occur together in the same individual flower with some exceptions. Second, angiosperm reproductive structures are not permanent parts of the adult indivi ...
... reproductive organs of angiosperms are different from those of animals in two ways. First, in angiosperms, both male and female structures usually occur together in the same individual flower with some exceptions. Second, angiosperm reproductive structures are not permanent parts of the adult indivi ...
Pollinators PowerPoint
... • Do their foraging at night and are attracted to white or light colored flowers • Pollen clings to their forhead as they readh into flowers with their long snout and bristly tongue to reach the nectar • Responsible for pollinating cactus, bananas, cashews, peaches, avocados, mangos and other tropic ...
... • Do their foraging at night and are attracted to white or light colored flowers • Pollen clings to their forhead as they readh into flowers with their long snout and bristly tongue to reach the nectar • Responsible for pollinating cactus, bananas, cashews, peaches, avocados, mangos and other tropic ...
Name: Period: Date: Lesson 1-6 Study Guide Lesson 1: What are
... 6. What do you think will develop as the flowers wither? - A fruit develops as the flower withers. 7. Why do you think some flowers have so many pollen grains and ovules? - An abundance of pollen and ovules helps ensure that fertilization takes place and that a sufficient number of seeds is produced ...
... 6. What do you think will develop as the flowers wither? - A fruit develops as the flower withers. 7. Why do you think some flowers have so many pollen grains and ovules? - An abundance of pollen and ovules helps ensure that fertilization takes place and that a sufficient number of seeds is produced ...
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
... Pollen grain has landed on stigma. It germinates and a pollen tube grows down through the stigma and style to the embryo sac. The two male gamete nuclei are inside the pollen tube. Pollen tube enters micropyle – tip of tube bursts open – ...
... Pollen grain has landed on stigma. It germinates and a pollen tube grows down through the stigma and style to the embryo sac. The two male gamete nuclei are inside the pollen tube. Pollen tube enters micropyle – tip of tube bursts open – ...
plant parts - Horace Mann Webmail
... They: 1.) support the plant. 2.) hold leaves up to the light. 3.) contain xylem and phloem. 4.) may store water and starch. Herbaceous stems are green, soft and flexible, like a flower stem. Woody stems are brown and rigid, like a tree trunk. ...
... They: 1.) support the plant. 2.) hold leaves up to the light. 3.) contain xylem and phloem. 4.) may store water and starch. Herbaceous stems are green, soft and flexible, like a flower stem. Woody stems are brown and rigid, like a tree trunk. ...
1) Pollen sticks to animal or released into wind
... • Seed grows and stores food – 2nd year: • grows more… • makes flowers & seeds… • dies ...
... • Seed grows and stores food – 2nd year: • grows more… • makes flowers & seeds… • dies ...
Vascular plants
... Pollen: Sperm cells (that will eventually fertilize the egg cells) Seed: The zygote! Seed contains the young plant and PROTECTS it. Roots: Anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients Stem: Carries substances from roots up to plant. Also, holds the plant and leaves up so they can be expos ...
... Pollen: Sperm cells (that will eventually fertilize the egg cells) Seed: The zygote! Seed contains the young plant and PROTECTS it. Roots: Anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients Stem: Carries substances from roots up to plant. Also, holds the plant and leaves up so they can be expos ...
ANGIOSPERMS - E
... aquatic plants). The pollen is released and floats on top of the water. The stigmas of another plant must be close to the surface of the water so that they can catch the pollen as it floats by. Why is pollination important for us? Most of our food comes from plants or from animals that eat plants. P ...
... aquatic plants). The pollen is released and floats on top of the water. The stigmas of another plant must be close to the surface of the water so that they can catch the pollen as it floats by. Why is pollination important for us? Most of our food comes from plants or from animals that eat plants. P ...
Plant Anatomy and Life Processes Study Guide
... pollen goes down into the ovary where it fertilizes the ovule (egg). The ovule then becomes a SEED. When the seed falls on the ground it may germinate into a new plant. ...
... pollen goes down into the ovary where it fertilizes the ovule (egg). The ovule then becomes a SEED. When the seed falls on the ground it may germinate into a new plant. ...
Ncumisa_Mnotoza
... The male cone releases pollen to fertilise the ovum. The pollen is transported by wind to the female cone. When the female gamete is fertilized it is called a zygote that grows into an embryo.The embyro has integument cells that surround it and altogether can be found in the seed. When the seed is m ...
... The male cone releases pollen to fertilise the ovum. The pollen is transported by wind to the female cone. When the female gamete is fertilized it is called a zygote that grows into an embryo.The embyro has integument cells that surround it and altogether can be found in the seed. When the seed is m ...
Flowering plants
... Ovary – Where the pollen goes down. It becomes the fruit Ovule – Where the seed develops ...
... Ovary – Where the pollen goes down. It becomes the fruit Ovule – Where the seed develops ...
From ferns to Gymnosperms : from sporangia to seeds
... F : the functional macrospore is growing into a female gametophyte (= macroprothallium) on top of the micropyle a pollination drop is formed (in many Gymnosperms) G : several pollen grains were captured in the pollination drop, and have sunken into the micropyle, on top of the nucellus in the pollen ...
... F : the functional macrospore is growing into a female gametophyte (= macroprothallium) on top of the micropyle a pollination drop is formed (in many Gymnosperms) G : several pollen grains were captured in the pollination drop, and have sunken into the micropyle, on top of the nucellus in the pollen ...
General Plant Life Cycle
... • sticks to archegonium • Pollen tube grows from pollen • Sperm travels down pollen tube (zygote/seed created) • Sporophyte stage restarts ...
... • sticks to archegonium • Pollen tube grows from pollen • Sperm travels down pollen tube (zygote/seed created) • Sporophyte stage restarts ...
Pollen

Pollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the female cone of coniferous plants. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics.Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower.