Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... food webs, and providing habitats for animals, fungi, and other organisms. Their decomposing tissues provide nutrients for organisms that live in leaf litter and enrich watery habitats like lakes and streams. Plants also changed the atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide and O2. Plants are vital to li ...
... food webs, and providing habitats for animals, fungi, and other organisms. Their decomposing tissues provide nutrients for organisms that live in leaf litter and enrich watery habitats like lakes and streams. Plants also changed the atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide and O2. Plants are vital to li ...
Biology 3B Laboratory Vascular Seed Plants – Gymnosperm
... The phylum Coniferophyta has the most numerous (550 species), widespread and ecologically important gymnosperms. Coniferophyta also has the oldest living individual organism, a 5,000 year old bristlecone pine and the tallest vascular plant, the redwoods with heights up to 117 meters. This group incl ...
... The phylum Coniferophyta has the most numerous (550 species), widespread and ecologically important gymnosperms. Coniferophyta also has the oldest living individual organism, a 5,000 year old bristlecone pine and the tallest vascular plant, the redwoods with heights up to 117 meters. This group incl ...
Biology Plant Classification
... – whisk ferns and horsetails are close relatives of ferns – ferns have large leaves called fronds ...
... – whisk ferns and horsetails are close relatives of ferns – ferns have large leaves called fronds ...
word
... Lycopodium (genus) - also called club moss and ground pine a) Resemble pine seedlings - microphylls spirally arranged b) Upright stems have sporophylls with sporangia in leaf axils c) True roots, stems, and leaves (as will be hereafter unless specified) d) Vascular complex - xylem and phloem mixed a ...
... Lycopodium (genus) - also called club moss and ground pine a) Resemble pine seedlings - microphylls spirally arranged b) Upright stems have sporophylls with sporangia in leaf axils c) True roots, stems, and leaves (as will be hereafter unless specified) d) Vascular complex - xylem and phloem mixed a ...
Powerpoint
... lives in the shade with underground stems and roots. Everything above ground is leaves. Life cycle includes a tiny gametophyte stage and a large sporophyte stage ...
... lives in the shade with underground stems and roots. Everything above ground is leaves. Life cycle includes a tiny gametophyte stage and a large sporophyte stage ...
answers - Parkway C-2
... gametophyte, one sperm nucleus disintegrates and the other fertilizes the egg within the female gametophyte. 14. Male pollen cones produce male gametophytes called pollen grains. Later, one of the nuclei in the pollen grain divides to produce two sperm nuclei. 15. Check students’ diagrams against Fi ...
... gametophyte, one sperm nucleus disintegrates and the other fertilizes the egg within the female gametophyte. 14. Male pollen cones produce male gametophytes called pollen grains. Later, one of the nuclei in the pollen grain divides to produce two sperm nuclei. 15. Check students’ diagrams against Fi ...
Plant Anatomy: Intro to Plant Reproduction
... • Molecular data support this group as having a single common ancestor • No obvious defining character (see characters for Lignophytes & Spermatophytes) ...
... • Molecular data support this group as having a single common ancestor • No obvious defining character (see characters for Lignophytes & Spermatophytes) ...
Green plant diversity
... • Molecular data support this group as having a single common ancestor • No obvious defining character (see characters for Lignophytes & Spermatophytes) ...
... • Molecular data support this group as having a single common ancestor • No obvious defining character (see characters for Lignophytes & Spermatophytes) ...
Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
... thickening meristems form the trunk. The pollen from the rst angiosperms was monosulcate, containing a single furrow or pore through the outer layer. This feature is still seen in the modern monocots. Vascular tissue of the stem is not arranged in any particular pattern. The root system is mostly a ...
... thickening meristems form the trunk. The pollen from the rst angiosperms was monosulcate, containing a single furrow or pore through the outer layer. This feature is still seen in the modern monocots. Vascular tissue of the stem is not arranged in any particular pattern. The root system is mostly a ...
Section 6.2 Notes
... plant by itself, without fertilization? Explain. Because a gamete is either a sperm or egg cell, it cannot develop into a complete plant by itself without being fertilized. ...
... plant by itself, without fertilization? Explain. Because a gamete is either a sperm or egg cell, it cannot develop into a complete plant by itself without being fertilized. ...
Section 6.2 Notes – pdf
... plant by itself, without fertilization? Explain. Because a gamete is either a sperm or egg cell, it cannot develop into a complete plant by itself without being fertilized. ...
... plant by itself, without fertilization? Explain. Because a gamete is either a sperm or egg cell, it cannot develop into a complete plant by itself without being fertilized. ...
Plant Classification
... 2) Through water, sperm from the male gametophyte will swim to the female gametophyte to create a diploid ...
... 2) Through water, sperm from the male gametophyte will swim to the female gametophyte to create a diploid ...
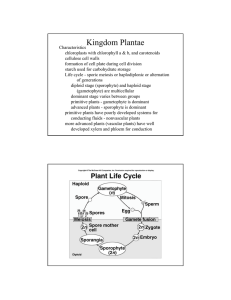
Kingdom Plantae
... integument, opening called micropyle One integument layer becomes seed coat Single megaspore mother cells undergoes meiosis, forms row of four megaspores Three break down, one develops into female gametophyte Each gametophyte produces two to six archegonia, each contains an egg ...
... integument, opening called micropyle One integument layer becomes seed coat Single megaspore mother cells undergoes meiosis, forms row of four megaspores Three break down, one develops into female gametophyte Each gametophyte produces two to six archegonia, each contains an egg ...
Plant Diversity
... integument, opening called micropyle One integument layer becomes seed coat Single megaspore mother cells undergoes meiosis, forms row of four megaspores Three break down, one develops into female gametophyte Each gametophyte produces two to six archegonia, each contains an egg ...
... integument, opening called micropyle One integument layer becomes seed coat Single megaspore mother cells undergoes meiosis, forms row of four megaspores Three break down, one develops into female gametophyte Each gametophyte produces two to six archegonia, each contains an egg ...
Plant ID
... *Native to eastern North America. *Monoecious. *An individual that has both male and female reproductive units (flowers, conifer cones). *The bark was used by some Native American tribes to make a drink for treatment of intestinal pain. *One of the most popular ornamental trees in the United States. ...
... *Native to eastern North America. *Monoecious. *An individual that has both male and female reproductive units (flowers, conifer cones). *The bark was used by some Native American tribes to make a drink for treatment of intestinal pain. *One of the most popular ornamental trees in the United States. ...
Life cycles and reproductive structures
... pollen cones and ovulate cones. 2. A pollen cone contains hundreds of microsporangia held on small sporophylls. • Cell in the microsporangia undergo meiosis to form haploid microspores that develop into pollen grains. ...
... pollen cones and ovulate cones. 2. A pollen cone contains hundreds of microsporangia held on small sporophylls. • Cell in the microsporangia undergo meiosis to form haploid microspores that develop into pollen grains. ...
Plant Divisions ppt basic
... 2. Flowers: where egg and sperm are produced 3. Flowers provide direct and efficient pollen ...
... 2. Flowers: where egg and sperm are produced 3. Flowers provide direct and efficient pollen ...
Alternation of generations: a review
... Megasporocyte in sporangium of each ovule grows and goes through meiosis to form four haploid megaspores (only one usually survives) Remaining megaspore grows and its nucleus undergoes three mitotic divisions, forming one large cell with eight haploid nucleii Membranes partition this into a multicel ...
... Megasporocyte in sporangium of each ovule grows and goes through meiosis to form four haploid megaspores (only one usually survives) Remaining megaspore grows and its nucleus undergoes three mitotic divisions, forming one large cell with eight haploid nucleii Membranes partition this into a multicel ...
Section 24–1 Reproduction With Cones and - Parkway C-2
... a. They produce pollen grains. b. They produce female gametophytes. c. They have two ovules at the base of each scale. d. They are generally much larger than pollen cones. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Each mature female gametophyte contains hundreds of egg cells ready for fertilizatio ...
... a. They produce pollen grains. b. They produce female gametophytes. c. They have two ovules at the base of each scale. d. They are generally much larger than pollen cones. 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Each mature female gametophyte contains hundreds of egg cells ready for fertilizatio ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... The better-known gymnosperms are evergreen, cone-bearing trees called conifers. Adaptations and Uses of Conifers Conifers are adapted to cold, dry weather. Conifers supply much of the wood used to construct buildings and to manufacture paper. Other Gymnosperms Cycads have large, finely divided leave ...
... The better-known gymnosperms are evergreen, cone-bearing trees called conifers. Adaptations and Uses of Conifers Conifers are adapted to cold, dry weather. Conifers supply much of the wood used to construct buildings and to manufacture paper. Other Gymnosperms Cycads have large, finely divided leave ...
Part I: Dichotomous Key for Identifying Pine Trees A dichotomous
... 1a. Plant has seeds in flowers/ fruits and has broad leaves……………….Flowering plant b. Plant has seeds in cones and has needle-like leaves ….……………………………………………Conifer (cone bearing plant): go to 2 2a. Needles grow individually (not in a bundle) and directly from the branch ………………..……...…………………………Sequoi ...
... 1a. Plant has seeds in flowers/ fruits and has broad leaves……………….Flowering plant b. Plant has seeds in cones and has needle-like leaves ….……………………………………………Conifer (cone bearing plant): go to 2 2a. Needles grow individually (not in a bundle) and directly from the branch ………………..……...…………………………Sequoi ...
Gymnosperms
... Key to Native and Commonly Cultivated Wisconsin Gymnosperms 1a. Leaves fan-shaped with many fine forking veins radiating from petiole, deciduous; seeds solitary, fleshy, plum like, about 3 cm in diameter .................................................. Ginkgo biloba GINKGO 1b. Leaves needle-like, ...
... Key to Native and Commonly Cultivated Wisconsin Gymnosperms 1a. Leaves fan-shaped with many fine forking veins radiating from petiole, deciduous; seeds solitary, fleshy, plum like, about 3 cm in diameter .................................................. Ginkgo biloba GINKGO 1b. Leaves needle-like, ...
Document
... is called the gametophyte is larger and more conspicuous than the haploid stage develops from a spore produces eggs and sperm 13. The eggs of seed plants are fertilized within ovules, and the ovules then develop into _____. seeds spores gametophytes 14. The cells within pollen grains are _____ and t ...
... is called the gametophyte is larger and more conspicuous than the haploid stage develops from a spore produces eggs and sperm 13. The eggs of seed plants are fertilized within ovules, and the ovules then develop into _____. seeds spores gametophytes 14. The cells within pollen grains are _____ and t ...
Pinophyta
The conifers, division Pinophyta, also known as division Coniferophyta or Coniferae, are one of 12 extant division-level taxa within the Kingdom Plantae (Viridiplantae) and 10 within the extant land plants. Pinophytes are gymnosperms, cone-bearing seed plants with vascular tissue. All extant conifers are woody plants with secondary growth, the great majority being trees with just a few being shrubs. Typical examples of conifers include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews. The division contains approximately eight families, 68 genera, and 630 living species.Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are of immense ecological importance. They are the dominant plants over huge areas of land, most notably the boreal forests of the northern hemisphere, but also in similar cool climates in mountains further south. Boreal conifers have many wintertime adaptations. The narrow conical shape of northern conifers, and their downward-drooping limbs, help them shed snow. Many of them seasonally alter their biochemistry to make them more resistant to freezing, called ""hardening"". While tropical rainforests have more biodiversity and turnover, the immense conifer forests of the world represent the largest terrestrial carbon sink, i.e. where carbon from atmospheric CO2 is bound as organic compounds.They are also of great economic value, primarily for timber and paper production; the wood of conifers is known as softwood.Conifer is a Latin word, a compound of conus (cone) and ferre (to bear), meaning ""the one that bears (a) cone(s)"".