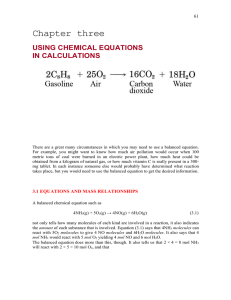
File
... G = RTlnK = H TS; HX(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + X(aq) Ka reaction; The value of Ka for HF is less than one while the other hydrogen halide acids have K a > 1. In terms of G, HF must have a positive G orxn value while the other H-X acids have Grxn < 0. The reason for the sign change in the Ka value ...
... G = RTlnK = H TS; HX(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + X(aq) Ka reaction; The value of Ka for HF is less than one while the other hydrogen halide acids have K a > 1. In terms of G, HF must have a positive G orxn value while the other H-X acids have Grxn < 0. The reason for the sign change in the Ka value ...
The science of chemistry is concerned
... human populations. Similarly, the growth of algae in natural bodies of water such as Lake Erie can be inhibited by reducing the supply of nutrients such as phosphorus in the form of phosphates. It is for this reason that many states have regulated or banned the use of phosphates in detergents and ar ...
... human populations. Similarly, the growth of algae in natural bodies of water such as Lake Erie can be inhibited by reducing the supply of nutrients such as phosphorus in the form of phosphates. It is for this reason that many states have regulated or banned the use of phosphates in detergents and ar ...
Physics of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
... angle with and also precesses around The precession frequency is usually quite high so that only the component of along is observed, while the other component averages out to zero. The magnetic properties are therefore determined by the quantity ...
... angle with and also precesses around The precession frequency is usually quite high so that only the component of along is observed, while the other component averages out to zero. The magnetic properties are therefore determined by the quantity ...
“The Language of the Permanent Magnet Industry”
... Often the air gap is just air, but may also include other materials such as paint, aluminum, epoxy etc. Alnico Magnets - Developed in the 1930s. Alnico magnets are an iron-based alloy system and named from their main alloying elements – aluminum, nickel and cobalt. Alnico magnets have the widest ran ...
... Often the air gap is just air, but may also include other materials such as paint, aluminum, epoxy etc. Alnico Magnets - Developed in the 1930s. Alnico magnets are an iron-based alloy system and named from their main alloying elements – aluminum, nickel and cobalt. Alnico magnets have the widest ran ...
Choi_uta_2502M_13250
... the dielectric material is an insulator, defects are easily formed at grain boundary with atomic vacancies which allows free electrons to flow into the material between the electrodes. This defect will give rise to a current path. ...
... the dielectric material is an insulator, defects are easily formed at grain boundary with atomic vacancies which allows free electrons to flow into the material between the electrodes. This defect will give rise to a current path. ...
Geometrical frustration
In condensed matter physics, the term geometrical frustration (or in short: frustration) refers to a phenomenon, where atoms tend to stick to non-trivial positions or where, on a regular crystal lattice, conflicting inter-atomic forces (each one favoring rather simple, but different structures) lead to quite complex structures. As a consequence of the frustration in the geometry or in the forces, a plenitude of distinct ground states may result at zero temperature, and usual thermal ordering may be suppressed at higher temperatures. Much studied examples are amorphous materials, glasses, or dilute magnets.The term frustration, in the context of magnetic systems, has been introduced by Gerard Toulouse (1977). Indeed, frustrated magnetic systems had been studied even before. Early work includes a study of the Ising model on a triangular lattice with nearest-neighbor spins coupled antiferromagnetically, by G. H. Wannier, published in 1950. Related features occur in magnets with competing interactions, where both ferro- as well as antiferromagnetic couplings between pairs of spins or magnetic moments are present, with the type of interaction depending on the separation distance of the spins. In that case commensurability, such as helical spin arrangements may result, as had been discussed originally, especially, by A. Yoshimori, T. A. Kaplan, R. J. Elliott, and others, starting in 1959, to describe experimental findings on rare-earth metals. A renewed interest in such spin systems with frustrated or competing interactions arose about two decades later, beginning in the 70s of the 20th century, in the context of spin glasses and spatially modulated magnetic superstructures. In spin glasses, frustration is augmented by stochastic disorder in the interactions, as may occur, experimentally, in non-stoichiometric magnetic alloys. Carefully analyzed spin models with frustration include the Sherrington-Kirkpatrick model, describing spin glasses, and the ANNNI model, describing commensurability magnetic superstructures.