Two – wires method: Circuit 1. Two-wire resistance measurement, R
... voltage between the two midpoints (B and D) will be zero and no current will flow through the galvanometer . If the bridge is unbalanced, the direction of the current indicates whether is too high or too low. is varied until there is no current through the galvanometer, which then reads zero. Detect ...
... voltage between the two midpoints (B and D) will be zero and no current will flow through the galvanometer . If the bridge is unbalanced, the direction of the current indicates whether is too high or too low. is varied until there is no current through the galvanometer, which then reads zero. Detect ...
IntegraPower is the third type of energy saving device
... area (shown in yellow above) can be met in less time. If this time period still includes the peak voltage of the AC sine wave then the motor speed is maintained. The power factor can be improved for the AC motor and the utility provider will deliver less energy resulting in a reduced energy bill. Wh ...
... area (shown in yellow above) can be met in less time. If this time period still includes the peak voltage of the AC sine wave then the motor speed is maintained. The power factor can be improved for the AC motor and the utility provider will deliver less energy resulting in a reduced energy bill. Wh ...
LED770x LED drivers New monolithic step-up family driving LEDs
... converter and six integrated PWM-dimmable current generators. The boost section is based on a constant switchingfrequency, peak current-mode architecture. The devices keep the lowest row’s voltage regulated at the internal reference voltage, and adapt the boost output voltage to reduce power losses ...
... converter and six integrated PWM-dimmable current generators. The boost section is based on a constant switchingfrequency, peak current-mode architecture. The devices keep the lowest row’s voltage regulated at the internal reference voltage, and adapt the boost output voltage to reduce power losses ...
79L05 pdf - Soemtron.org
... applications. These include on-card regulation for elimination of noise and distribution problems associated with single-point regulation. In addition, they can be used to control series pass elements to make high-current voltage-regulator circuits. One of these regulators can deliver up to 100 mA o ...
... applications. These include on-card regulation for elimination of noise and distribution problems associated with single-point regulation. In addition, they can be used to control series pass elements to make high-current voltage-regulator circuits. One of these regulators can deliver up to 100 mA o ...
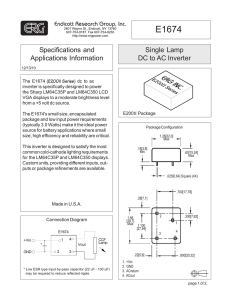
E1674 - Endicott Research Group, Inc.
... Endicott Research Group, Inc. (ERG) reserves the right to make changes in circuit design and/ or specifications at any time without notice. Accordingly, the reader is cautioned to verify that data sheets are current before placing orders. Information furnished by ERG is believed to be accurate and r ...
... Endicott Research Group, Inc. (ERG) reserves the right to make changes in circuit design and/ or specifications at any time without notice. Accordingly, the reader is cautioned to verify that data sheets are current before placing orders. Information furnished by ERG is believed to be accurate and r ...
Negative Input (–4.5V to –80V) Synchronous
... respect to system ground, without the need of complicated level shifting circuitry. The device’s synchronous operation means that the output diode is replaced with a high efficiency P-channel MOSFET, thereby increasing efficiency, allowing for higher output currents (up to 20A), and eliminating the ...
... respect to system ground, without the need of complicated level shifting circuitry. The device’s synchronous operation means that the output diode is replaced with a high efficiency P-channel MOSFET, thereby increasing efficiency, allowing for higher output currents (up to 20A), and eliminating the ...
View Poster
... crosses zero volts twice per Hz, two arcs are required per Hz to create the tone. Arcs are created by switching a large power supply on and off at a musical frequency. The musical frequencies we are targeting exist between 20Hz and 1.2kHz, so up to 2,400 switches per second are required. To accompli ...
... crosses zero volts twice per Hz, two arcs are required per Hz to create the tone. Arcs are created by switching a large power supply on and off at a musical frequency. The musical frequencies we are targeting exist between 20Hz and 1.2kHz, so up to 2,400 switches per second are required. To accompli ...
AN9601: Using the HI7190 with Single +5V Supply
... All Intersil semiconductor products are manufactured, assembled and tested under ISO9000 quality systems certification. Intersil semiconductor products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes in circuit design and/or specifications at any time without no ...
... All Intersil semiconductor products are manufactured, assembled and tested under ISO9000 quality systems certification. Intersil semiconductor products are sold by description only. Intersil Corporation reserves the right to make changes in circuit design and/or specifications at any time without no ...
GSR - switching regulator modules High-efficiency step-down switching regulator modules
... GS-R12F and 500 kHz for GS-R12FP. The GSR modules include all the components required to drive the ST embedded regulator, providing a plug and play-like point of regulation. The main features common to the GSR family are: pulse-by-pulse and frequency foldback current protection, overvoltage protecti ...
... GS-R12F and 500 kHz for GS-R12FP. The GSR modules include all the components required to drive the ST embedded regulator, providing a plug and play-like point of regulation. The main features common to the GSR family are: pulse-by-pulse and frequency foldback current protection, overvoltage protecti ...
Science 9 Unit 4: Electricity Name - Science 9 Portfolio
... ground to prevent buildup of electricity ...
... ground to prevent buildup of electricity ...
Voltage in Electrical Systems
... • Two types of current in electrical systems: • Direct current (DC) – current flows in one ...
... • Two types of current in electrical systems: • Direct current (DC) – current flows in one ...
SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
... What happens if the duty cycle of the converter is decreased from 20µsec on time to 5µsec on time in V2 set up? Is the converter operating in the continuous conduction mode? What is the average output voltage now? Did the output voltage ripple increase? What observations can be made from increasing ...
... What happens if the duty cycle of the converter is decreased from 20µsec on time to 5µsec on time in V2 set up? Is the converter operating in the continuous conduction mode? What is the average output voltage now? Did the output voltage ripple increase? What observations can be made from increasing ...
Buck converter
A buck converter is a voltage step down and current step up converter.The simplest way to reduce the voltage of a DC supply is to use a linear regulator (such as a 7805), but linear regulators waste energy as they operate by dissipating excess power as heat. Buck converters, on the other hand, can be remarkably efficient (95% or higher for integrated circuits), making them useful for tasks such as converting the main voltage in a computer (12V in a desktop, 12-24V in a laptop) down to the 0.8-1.8V needed by the processor.