A1979HZ30700001
... beams were to be confined into a cross section with dimensions on the order of 10 um or less, giving relatively high fields at low absolute power levels This facilitated getting desirable nonlinear effects at low power levels, and because the wave was guided, it would be feasible to have long intera ...
... beams were to be confined into a cross section with dimensions on the order of 10 um or less, giving relatively high fields at low absolute power levels This facilitated getting desirable nonlinear effects at low power levels, and because the wave was guided, it would be feasible to have long intera ...
At what intensity is the laser set?
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
femtosecond laser ablation of dielectrics
... processes: multiphoton excitation, heating of free carriers, multiplication of carriers due to impact ionisation- i.e. the avalanche mechanism which is very often invoked but has never been directly observed, de-trapping of self-trapped exciton- in the case of SiO2. Our results show that different b ...
... processes: multiphoton excitation, heating of free carriers, multiplication of carriers due to impact ionisation- i.e. the avalanche mechanism which is very often invoked but has never been directly observed, de-trapping of self-trapped exciton- in the case of SiO2. Our results show that different b ...
Optically-Pumped SESAM for Fast Switching between Continuous Wave and
... • Actively mode locked lasers have demonstrated this type of regime change, but the electronic modulators required for this complicate the system and add cost to the overall setup. Mechanical methods have been implemented to switch between cw and femtosecond operation of passively mode locked system ...
... • Actively mode locked lasers have demonstrated this type of regime change, but the electronic modulators required for this complicate the system and add cost to the overall setup. Mechanical methods have been implemented to switch between cw and femtosecond operation of passively mode locked system ...
Modern Optics PHY485F/1485F www.physics.utoronto.ca/~phy485
... http://cord.org/step_online/st1-5/st15ttl.htm ...
... http://cord.org/step_online/st1-5/st15ttl.htm ...
Mode-locking of a CW laser 1 Introduction
... Short pulses are useful in a number of applications in optics, e.g., time resolved spectroscopy, sampling of fast electronics, and communications. This has led to a number of mode-locking techniques to obtain such pulses, for example acousto-optic, injection, synchronous-pump, collidingpulse mode-lo ...
... Short pulses are useful in a number of applications in optics, e.g., time resolved spectroscopy, sampling of fast electronics, and communications. This has led to a number of mode-locking techniques to obtain such pulses, for example acousto-optic, injection, synchronous-pump, collidingpulse mode-lo ...
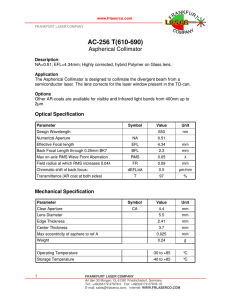
AC-256 T(610-690) - Frankfurt Laser Company
... The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrared light bands from 400nm up to 2µm ...
... The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrared light bands from 400nm up to 2µm ...
科目名 Course Title Extreme Laser Physics [極限レーザー物理E] 講義
... 受講条件 Pre-requisite: classical electromagnetism, classical optics, quantum mechanics ...
... 受講条件 Pre-requisite: classical electromagnetism, classical optics, quantum mechanics ...
PHYS4014 - Lasers and Nonlinear Optics
... absorption and gain coefficients in lasing media, population inversions, optical pumping and the principles of optical cavities. Different types of lasers: The design and operation of different types of lasers with particular reference to solid-state lasers excimer lasers tunable dye lasers and semi ...
... absorption and gain coefficients in lasing media, population inversions, optical pumping and the principles of optical cavities. Different types of lasers: The design and operation of different types of lasers with particular reference to solid-state lasers excimer lasers tunable dye lasers and semi ...
optical cavity
... 7. Optical cavity( optical resonator) An optical cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors that forms a standing wave cavity resonator for light waves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light 7.1 Resonator ...
... 7. Optical cavity( optical resonator) An optical cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors that forms a standing wave cavity resonator for light waves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light 7.1 Resonator ...
Click To
... Background: A high-average-power solid-state laser is typically pumped by injecting light from high-power two-dimensional semiconductor laser arrays. The laser arrays are frequently fitted with lenses that separately collimate the output of the bars so that the pump light is collimated well enough f ...
... Background: A high-average-power solid-state laser is typically pumped by injecting light from high-power two-dimensional semiconductor laser arrays. The laser arrays are frequently fitted with lenses that separately collimate the output of the bars so that the pump light is collimated well enough f ...
direct electron acceleration by chirped laser pulse in the regime of
... In our paper we carried out the numerical simulation of chirped relativistically strong laser pulse with free electrons interaction in optic scheme diffraction grating – focusing lens or mirror. In such system, in focal plane the dynamic focusing may be observed. For EM field calculation the diffrac ...
... In our paper we carried out the numerical simulation of chirped relativistically strong laser pulse with free electrons interaction in optic scheme diffraction grating – focusing lens or mirror. In such system, in focal plane the dynamic focusing may be observed. For EM field calculation the diffrac ...
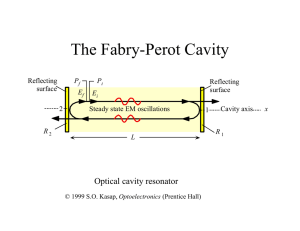
The Fabry-Perot Cavity
... In the steady-state, the light (plane wave assumption) should remain unchanged after one round trip (2L). In other words, the gain = loss at threshold. An energy pumped in above threshold is converted into photons. R1 and R2 are the power reflectivities of mirrors 1 and 2, respectively. g is the (in ...
... In the steady-state, the light (plane wave assumption) should remain unchanged after one round trip (2L). In other words, the gain = loss at threshold. An energy pumped in above threshold is converted into photons. R1 and R2 are the power reflectivities of mirrors 1 and 2, respectively. g is the (in ...
Frequency Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (FDOCT)
... Faculty mentor: Prof. Zhongping Chen Lab mentor: Jun Zhang ...
... Faculty mentor: Prof. Zhongping Chen Lab mentor: Jun Zhang ...
Midterm Exam
... b. Pick one of these stable resonators (choose numbers that satisfy the condition for part a) and solve for the mode of this cavity. Specifically, plot the spotsize, w(z), and the radius of curvature, R(z), of the mode everywhere in the cavity. c. Put a focusing lens immediately after the output cou ...
... b. Pick one of these stable resonators (choose numbers that satisfy the condition for part a) and solve for the mode of this cavity. Specifically, plot the spotsize, w(z), and the radius of curvature, R(z), of the mode everywhere in the cavity. c. Put a focusing lens immediately after the output cou ...
Mode-locking

Mode-locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s).The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed-phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. The laser is then said to be 'phase-locked' or 'mode-locked'. Interference between these modes causes the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. Depending on the properties of the laser, these pulses may be of extremely brief duration, as short as a few femtoseconds.











![科目名 Course Title Extreme Laser Physics [極限レーザー物理E] 講義](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003538965_1-4c9ae3641327c1116053c260a01760fe-300x300.png)