storing, retrieving, and processing optical information by raman
... propagating Langmuir wave. Recording is provided by nonlinear interaction of the information pulse with a counterpropagating short laser pulse producing a beating wave resonant to electrostatic plasma oscillations. Langmuir wave can sustain its structure on time scales large compared to the duration ...
... propagating Langmuir wave. Recording is provided by nonlinear interaction of the information pulse with a counterpropagating short laser pulse producing a beating wave resonant to electrostatic plasma oscillations. Langmuir wave can sustain its structure on time scales large compared to the duration ...
apparatus for teaching physics Litiholo holography – So easy even a
... shutter is placed in front of the laser. The laser is then turned tireless efforts have made it possible to engage students in the on and allowed to stabilize for five minutes. Once an object, study of optics through the exciting field of holography. Now such as the toy car shown in Fig. 1, has been ...
... shutter is placed in front of the laser. The laser is then turned tireless efforts have made it possible to engage students in the on and allowed to stabilize for five minutes. Once an object, study of optics through the exciting field of holography. Now such as the toy car shown in Fig. 1, has been ...
Single Longitudinal Mode Blue-Violet Laser Diode for Data Storage
... longitudinal modes and have thus a sub-millimeter coherence length. Optical data storage technologies requiring coherent interference, such as holographic e.g., will benefit from having a compact blue-violet laser diode source with a long coherence length and some level of wavelength tuning. Prior a ...
... longitudinal modes and have thus a sub-millimeter coherence length. Optical data storage technologies requiring coherent interference, such as holographic e.g., will benefit from having a compact blue-violet laser diode source with a long coherence length and some level of wavelength tuning. Prior a ...
The Interaction of Radiation and Matter: Semiclassical
... occurs. Other types of laser operate on a four level system and , in general, the mechanism of amplification differs for different lasing materials. However, in all cases, it is necessary to set up a population inversion so that stimulated emission occurs more often than absorption." The following i ...
... occurs. Other types of laser operate on a four level system and , in general, the mechanism of amplification differs for different lasing materials. However, in all cases, it is necessary to set up a population inversion so that stimulated emission occurs more often than absorption." The following i ...
Report on T tasks
... We have theoretically studied the stability of Fabry-Perot cavities in presence of radiation pressure and photo-thermal effects. The analysis provides important indications that should be taken into account in the development of quantum optics experiments and gravitational-wave detectors. We have sh ...
... We have theoretically studied the stability of Fabry-Perot cavities in presence of radiation pressure and photo-thermal effects. The analysis provides important indications that should be taken into account in the development of quantum optics experiments and gravitational-wave detectors. We have sh ...
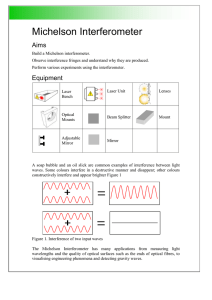
Michelson Interferometer - Research School of Physics and
... Explain how the lenses might change the interference pattern given the speed of light in air and these media is different. Tap the laser bench or table with your hand. Note how sensitive the pattern is to vibrations. This isn’t surprising as the interference pattern is generated from light waves 650 ...
... Explain how the lenses might change the interference pattern given the speed of light in air and these media is different. Tap the laser bench or table with your hand. Note how sensitive the pattern is to vibrations. This isn’t surprising as the interference pattern is generated from light waves 650 ...
1. Which of the following statement are true about "LED life" term?
... Emitted light directly supply from a electric current In fotovoltaic mode, an external reverse bias is applied to the photodiode and in fotoconductive mode is un-biased Has a fastest switching speed when operates in photoconductive mode 9. An optical amplifiers is a device that: Amplifies the optica ...
... Emitted light directly supply from a electric current In fotovoltaic mode, an external reverse bias is applied to the photodiode and in fotoconductive mode is un-biased Has a fastest switching speed when operates in photoconductive mode 9. An optical amplifiers is a device that: Amplifies the optica ...
What is total internal reflection?
... some of the basic concepts and principles. The groups will be assigned (three to four students per group). Hand out the assignments. Day 3: Laser safety test will be administered. Group 1 – Design a set-up that shows total internal reflection. This group will have one or two laser pointers (differen ...
... some of the basic concepts and principles. The groups will be assigned (three to four students per group). Hand out the assignments. Day 3: Laser safety test will be administered. Group 1 – Design a set-up that shows total internal reflection. This group will have one or two laser pointers (differen ...
( NONLINEAR OPTICS PHYC/ECE 568) Homework #4, Due Thu Sept. 24
... a. Calculate the type-I phase matching angle for SHG in KDP using 1.06 m output of a Nd:YAG laser. b. For a beam radius w0=500 m, calculate the aperture length defined as la= w0 / where is the Poynting vector walk-off angle. Obtain the aperture length for w0=15 m and discuss the role of addi ...
... a. Calculate the type-I phase matching angle for SHG in KDP using 1.06 m output of a Nd:YAG laser. b. For a beam radius w0=500 m, calculate the aperture length defined as la= w0 / where is the Poynting vector walk-off angle. Obtain the aperture length for w0=15 m and discuss the role of addi ...
Synchronized ti scattering microscopy
... must fulfill the following requirements: (1) It must provide for two-color excitation, with at least one color tunable so that the difference frequency matches a molecular vibrational frequency. (2) The two colors must be temporally overlapped, with relative timing jitter much less than the pulse wi ...
... must fulfill the following requirements: (1) It must provide for two-color excitation, with at least one color tunable so that the difference frequency matches a molecular vibrational frequency. (2) The two colors must be temporally overlapped, with relative timing jitter much less than the pulse wi ...
Slide 1
... In a slow-light medium we can dynamically control the propagation speed and polarisation state of light. Consequently slow light is a useful tool for quantum information processing and interferometry. Here in Durham we are mainly interested in the propagation of light through atomic media with a lin ...
... In a slow-light medium we can dynamically control the propagation speed and polarisation state of light. Consequently slow light is a useful tool for quantum information processing and interferometry. Here in Durham we are mainly interested in the propagation of light through atomic media with a lin ...
Microsoft Word Format - McMaster University > ECE
... refractive index change due to the material gain change. In reality, an extra LPF has to be cascaded to the above frequency response in considering the thermal effect, since the material refractive index of the laser diode also changes significantly as a function of the temperature. 5. Large-signal ...
... refractive index change due to the material gain change. In reality, an extra LPF has to be cascaded to the above frequency response in considering the thermal effect, since the material refractive index of the laser diode also changes significantly as a function of the temperature. 5. Large-signal ...
Mode-locking

Mode-locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s).The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed-phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. The laser is then said to be 'phase-locked' or 'mode-locked'. Interference between these modes causes the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. Depending on the properties of the laser, these pulses may be of extremely brief duration, as short as a few femtoseconds.