The sensitivity of carbon fluxes to spring warming and summer
... Low moisture conditions during drought (created by either anomalously low precipitation or anomalously high temperature that increases evapotranspiration) cause both GPP and Re to decline (Ciais et al., 2005; Kljun et al., 2006). There is still debate about whether GPP or Re is most adversely affect ...
... Low moisture conditions during drought (created by either anomalously low precipitation or anomalously high temperature that increases evapotranspiration) cause both GPP and Re to decline (Ciais et al., 2005; Kljun et al., 2006). There is still debate about whether GPP or Re is most adversely affect ...
Combating Global Climate Change - University of Michigan Law
... to address if Congress fails to enact limits on greenhouse gas emissions early in the Obama Administration.' Part I of this Article reviews the global climate change crisis and the inadequacy of historical efforts to combat global warming. This overview demonstrates the need for strong and immediate ...
... to address if Congress fails to enact limits on greenhouse gas emissions early in the Obama Administration.' Part I of this Article reviews the global climate change crisis and the inadequacy of historical efforts to combat global warming. This overview demonstrates the need for strong and immediate ...
i1880e12
... Soils represent the Earth’s largest terrestrial C sink that can be controlled and improved, and grassland management has been cited as the second most important agricultural technology available for climate change mitigation. This chapter argues that livestock and pastoral systems have a major role ...
... Soils represent the Earth’s largest terrestrial C sink that can be controlled and improved, and grassland management has been cited as the second most important agricultural technology available for climate change mitigation. This chapter argues that livestock and pastoral systems have a major role ...
mb_ch03
... • Carbon atoms can readily form four covalent bonds with other atoms including other carbon atoms. The carbon bonds allow the carbon atoms to form a wide variety of simple and complex organic compounds. ...
... • Carbon atoms can readily form four covalent bonds with other atoms including other carbon atoms. The carbon bonds allow the carbon atoms to form a wide variety of simple and complex organic compounds. ...
Climate Change and Australia`s Tree Clearing Crisis
... function of taking carbon out of the atmosphere. Vast quantities of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases are released, exacerbating climate change. Australia has historically had one of the highest rates of tree clearing of any developed country.2 However, between 2006–2012, legislative reform ...
... function of taking carbon out of the atmosphere. Vast quantities of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases are released, exacerbating climate change. Australia has historically had one of the highest rates of tree clearing of any developed country.2 However, between 2006–2012, legislative reform ...
Ch 3 Notes
... • Carbon atoms can readily form four covalent bonds with other atoms including other carbon atoms. The carbon bonds allow the carbon atoms to form a wide variety of simple and complex organic compounds. ...
... • Carbon atoms can readily form four covalent bonds with other atoms including other carbon atoms. The carbon bonds allow the carbon atoms to form a wide variety of simple and complex organic compounds. ...
CSPR Briefing C SP R B
... Land use and land uses changes are not only a source of emission, but certain land use activities can help sequester carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Forestry, for example, can be a cost effective method for achieving a large effect on global mitigation of GHG, while at the same time increa ...
... Land use and land uses changes are not only a source of emission, but certain land use activities can help sequester carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Forestry, for example, can be a cost effective method for achieving a large effect on global mitigation of GHG, while at the same time increa ...
Chapter 6-Photosynthesis
... the stroma to combine with NADP and make NADPH. (2) Increasing the carbon dioxide concentration makes more of it available to enter the Calvin Cycle, thus accelerating photosynthesis. As the carbon dioxide levels rise still higher, the rate of photosynthesis begins to become limited by other compone ...
... the stroma to combine with NADP and make NADPH. (2) Increasing the carbon dioxide concentration makes more of it available to enter the Calvin Cycle, thus accelerating photosynthesis. As the carbon dioxide levels rise still higher, the rate of photosynthesis begins to become limited by other compone ...
BURNERS AND FLAMES:
... in its normal state has its electrons occupying the orbitals of lowest possible energy. This is called the ground (energy) state of the atom. If energy is added to an atom, some of the electrons in the atom absorb that energy and jump into an orbital of high energy and an excited (energy) state is f ...
... in its normal state has its electrons occupying the orbitals of lowest possible energy. This is called the ground (energy) state of the atom. If energy is added to an atom, some of the electrons in the atom absorb that energy and jump into an orbital of high energy and an excited (energy) state is f ...
Towards the atomic level protein sequence analysis
... Two genomes namely – viruses and plants were targeted for their atomic content analysis. The entire work was been divided into two phases. During the first phase, the analysis of the plant genome for aquaporin proteins, a special class of channel protein that controls the precise transport of water ...
... Two genomes namely – viruses and plants were targeted for their atomic content analysis. The entire work was been divided into two phases. During the first phase, the analysis of the plant genome for aquaporin proteins, a special class of channel protein that controls the precise transport of water ...
Name Biology Chemistry of Life What can reduce the effect of a
... Discuss which of the molecules are most similar in structure. ...
... Discuss which of the molecules are most similar in structure. ...
biodiversity and ground-level ozone
... while a long-term field release study in the northern US showed that an initial reduction in aspen growth was lost after 12 years, because relatively tolerant clones benefit at the expense of more sensitive clones. There is evidence of a shift in forest species composition in regions subject to high ...
... while a long-term field release study in the northern US showed that an initial reduction in aspen growth was lost after 12 years, because relatively tolerant clones benefit at the expense of more sensitive clones. There is evidence of a shift in forest species composition in regions subject to high ...
Cellular Energetics Review
... 36. What is a photon? 37. Why are leaves green? 38. Which organisms are responsible for carrying out the most photosynthesis on the earth? 39. The energy conversion in photosynthesis occurs in three stages. What are they? 40. State the four factors that must be present to begin the process of photo ...
... 36. What is a photon? 37. Why are leaves green? 38. Which organisms are responsible for carrying out the most photosynthesis on the earth? 39. The energy conversion in photosynthesis occurs in three stages. What are they? 40. State the four factors that must be present to begin the process of photo ...
carbohydrates
... Configura=onal: Diastereomers-‐ Stereoisomers that are not mirror images; may have same D-‐ or L-‐ configura=on (or not). Configura=onal: Anomers-‐ Stereoisomers that differ in configura=on at the anomeric carbon ( ...
... Configura=onal: Diastereomers-‐ Stereoisomers that are not mirror images; may have same D-‐ or L-‐ configura=on (or not). Configura=onal: Anomers-‐ Stereoisomers that differ in configura=on at the anomeric carbon ( ...
PowerPoint presentation (PPT file)
... emissions from wetlands have gone through various processes and improvements The needs for capacity building and research on tropical wetlands are huge, especially in relation to Chapters 2, 3 and 4 Estimating emission factors and tallying activity data in a systematic way is key to reducing ...
... emissions from wetlands have gone through various processes and improvements The needs for capacity building and research on tropical wetlands are huge, especially in relation to Chapters 2, 3 and 4 Estimating emission factors and tallying activity data in a systematic way is key to reducing ...
Characterization of AtAAP1 function in amino acid uptake by the root
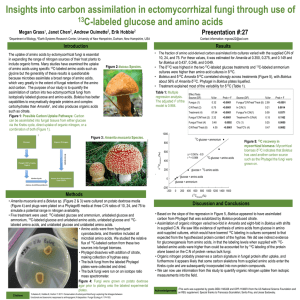
... for gluconeogenesis from amino acids, in that the labeling levels when supplied with 13Clabeled amino acids were higher than could be accounted for by 13C labeling of the protein alone based on the C:N of protein versus bulk fungi. • Organic nitrogen probably preserves a carbon signature in fungal p ...
... for gluconeogenesis from amino acids, in that the labeling levels when supplied with 13Clabeled amino acids were higher than could be accounted for by 13C labeling of the protein alone based on the C:N of protein versus bulk fungi. • Organic nitrogen probably preserves a carbon signature in fungal p ...
Wildfires threaten mercury stocks in northern soils
... [1] With climate change rapidly affecting northern forests and wetlands, mercury reserves once protected in cold, wet soils are being exposed to burning, likely triggering large releases of mercury to the atmosphere. We quantify organic soil mercury stocks and burn areas across western, boreal Canad ...
... [1] With climate change rapidly affecting northern forests and wetlands, mercury reserves once protected in cold, wet soils are being exposed to burning, likely triggering large releases of mercury to the atmosphere. We quantify organic soil mercury stocks and burn areas across western, boreal Canad ...
Researches on Agricultural Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and
... contribution to the global warming; Greenpeace (2006) estimated the indirect agricultural emissions (converted into CO2) account for 17% -32% of the global total emissions; researches form IPCC Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change , LING Er-da (2001) and ZHAO Qi-guo(2009) confirmed that agricul ...
... contribution to the global warming; Greenpeace (2006) estimated the indirect agricultural emissions (converted into CO2) account for 17% -32% of the global total emissions; researches form IPCC Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change , LING Er-da (2001) and ZHAO Qi-guo(2009) confirmed that agricul ...
8373863306
... Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each correct answer will score one mark. A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer. Any rough working should be done in this booklet. Electronic calculators may be used. ...
... Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each correct answer will score one mark. A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer. Any rough working should be done in this booklet. Electronic calculators may be used. ...
Global Warming and Stomatal Complex Types
... the ozone layer and consequently causes global warming. Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are often called greenhouse gases. That the Earth has warmed by 0.74o C over the last hundred years and that around 0.4o C of this warming has occurred since the 1970s is unequivocal fact that leaves littl ...
... the ozone layer and consequently causes global warming. Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are often called greenhouse gases. That the Earth has warmed by 0.74o C over the last hundred years and that around 0.4o C of this warming has occurred since the 1970s is unequivocal fact that leaves littl ...
Chapter 6 Energy and Nutrient Relations
... CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism) both C3 and C4 both C4 and CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism) ...
... CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism) both C3 and C4 both C4 and CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism) ...
Saturation of the terrestrial carbon sink
... processes are CO2 fertilization of photosynthesis, N fertilization of net primary production, woody vegetation thickening and encroachment, forest regrowth in abandoned cropland, and afforestation/resforestation. Key C emission Box 6.1. Description of GPP, NPP, NEP and NBP Plants take up carbon diox ...
... processes are CO2 fertilization of photosynthesis, N fertilization of net primary production, woody vegetation thickening and encroachment, forest regrowth in abandoned cropland, and afforestation/resforestation. Key C emission Box 6.1. Description of GPP, NPP, NEP and NBP Plants take up carbon diox ...
Reversible and irreversible impacts of greenhouse gas
... inorganic carbon, alkalinity, oxygen and dissolved organic phosphorus. The marine iron cycle is parametrized and a constant rain-ratio of CaCO3 to organic carbon of 0.07 and constant Redfield ratios are used. The model does not include marine sediments, which only need to be considered on longer tim ...
... inorganic carbon, alkalinity, oxygen and dissolved organic phosphorus. The marine iron cycle is parametrized and a constant rain-ratio of CaCO3 to organic carbon of 0.07 and constant Redfield ratios are used. The model does not include marine sediments, which only need to be considered on longer tim ...
Conference - Carbon Expo
... Climate Policy Initiative (CPI) The panelists will present and discuss a suite of fiscal policy responses to climate change, based on concrete examples from various countries, that play a crucial role in accelerating the transition towards low carbon and resilient development. Fiscal reforms can hel ...
... Climate Policy Initiative (CPI) The panelists will present and discuss a suite of fiscal policy responses to climate change, based on concrete examples from various countries, that play a crucial role in accelerating the transition towards low carbon and resilient development. Fiscal reforms can hel ...
Biosequestration

Biosequestration is the capture and storage of the atmospheric greenhouse gas carbon dioxide by biological processes.This may be by increased photosynthesis (through practices such as reforestation / preventing deforestation and genetic engineering); by enhanced soil carbon trapping in agriculture; or by the use of algal bio sequestration (see algae bioreactor) to absorb the carbon dioxide emissions from coal, petroleum (oil) or natural gas-fired electricity generation.Biosequestration as a natural process has occurred in the past, and was responsible for the formation of the extensive coal and oil deposits which are now being burned. It is a key policy concept in the climate change mitigation debate. It does not generally refer to the sequestering of carbon dioxide in oceans (see carbon sequestration and ocean acidification) or rock formations, depleted oil or gas reservoirs (see oil depletion and peak oil), deep saline aquifers, or deep coal seams (see coal mining) (for all see geosequestration) or through the use of industrial chemical carbon dioxide scrubbing.