7-1 Momentum and Its Relation to Force
... •Inelastic Collisions •Collisions in Two or Three Dimensions •Center of Mass (CM) •CM for the Human Body •Center of Mass and Translational Motion ...
... •Inelastic Collisions •Collisions in Two or Three Dimensions •Center of Mass (CM) •CM for the Human Body •Center of Mass and Translational Motion ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy conclusion
... Energy can neither be created not destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of molecules. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat. Examples of heat generation: sliding ...
... Energy can neither be created not destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of molecules. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat. Examples of heat generation: sliding ...
Chapter 1 - asmasaid
... Why is the recoil less if a person holds a gun tightly against the shoulder? A) The recoil is not less. Since momentum is conserved, the recoil is the same whether or not the gun is held tightly B) Your mass becomes part of the system, and since momentum is conserved, the velocity of the gun/person ...
... Why is the recoil less if a person holds a gun tightly against the shoulder? A) The recoil is not less. Since momentum is conserved, the recoil is the same whether or not the gun is held tightly B) Your mass becomes part of the system, and since momentum is conserved, the velocity of the gun/person ...
Thursday, Oct. 30, 2014
... Since the individual angular momentum can change, the total angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system ...
... Since the individual angular momentum can change, the total angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system ...
The Vector Product Defined Ch 11: Question 3
... The concept of angular momentum is also valid on a submicroscopic scale Angular momentum has been used in the development of modern theories of atomic, molecular and nuclear physics In these systems, the angular momentum has been found to be a fundamental quantity ...
... The concept of angular momentum is also valid on a submicroscopic scale Angular momentum has been used in the development of modern theories of atomic, molecular and nuclear physics In these systems, the angular momentum has been found to be a fundamental quantity ...
Variational Principles and Lagrangian Mechanics
... is a satisfying state of affairs given the fact that classical mechanics can be viewed as a macroscopic approximation to quantum mechanics. Of course, the variational principles of mechanics (19th century) came much earlier than quantum mechanics (1920’s), let alone Feynman’s path integral approach ...
... is a satisfying state of affairs given the fact that classical mechanics can be viewed as a macroscopic approximation to quantum mechanics. Of course, the variational principles of mechanics (19th century) came much earlier than quantum mechanics (1920’s), let alone Feynman’s path integral approach ...
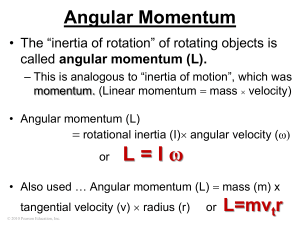
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum
... • From the previous, the relations among the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation ...
... • From the previous, the relations among the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation ...
Chapter 7
... and the length of the wire is 1.20 m. Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the ball (a) just before the collision, and (b) just after the collision. ...
... and the length of the wire is 1.20 m. Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the ball (a) just before the collision, and (b) just after the collision. ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... Simple Bayesian Reasoning • If we assume there are n possible disjoint diagnoses, d1 … dn P(di | e) = P(e | di) P(di) P(e) • P(e) may not be known but the total probability of all diagnoses must always be 1, so all must sum to 1 • Thus, we can determine the most probable without knowing P(e). ...
... Simple Bayesian Reasoning • If we assume there are n possible disjoint diagnoses, d1 … dn P(di | e) = P(e | di) P(di) P(e) • P(e) may not be known but the total probability of all diagnoses must always be 1, so all must sum to 1 • Thus, we can determine the most probable without knowing P(e). ...
PH212Chapter11_15
... • From the previous, the relations among the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation ...
... • From the previous, the relations among the external torque along the rotation axis, the angular momentum along the rotation axis, the moment of inertia about the rotation axis, the angular velocity about the rotation axis, and the angular acceleration about the rotation axis • Examples of rotation ...
Center of Mass and Momentum
... zero, then (even if the velocity of individual objects changes), there is a point associated with the distribution of objects that moves with zero acceleration (constant velocity). •This point is called the “center of mass” of the system. It is the balancing point for the mass distribution. ...
... zero, then (even if the velocity of individual objects changes), there is a point associated with the distribution of objects that moves with zero acceleration (constant velocity). •This point is called the “center of mass” of the system. It is the balancing point for the mass distribution. ...
PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
... concepts give us new useful ways of analyzing motion. In life, some quantities stay the same while other things around them change. For example, when a bomb explodes, if you add up the mass of all the products, it will be the same as the mass of the original bomb. This is “Conservation of Mass”: Mf ...
... concepts give us new useful ways of analyzing motion. In life, some quantities stay the same while other things around them change. For example, when a bomb explodes, if you add up the mass of all the products, it will be the same as the mass of the original bomb. This is “Conservation of Mass”: Mf ...
Momentum and Impulse
... Conservation of Kinetic Energy Kinetic energy is the energy due to the motion of an object. KE = ½mv2 where m is the mass in kg, v is the velocity in m/s, and KE is the kinetic energy in J (joules). ...
... Conservation of Kinetic Energy Kinetic energy is the energy due to the motion of an object. KE = ½mv2 where m is the mass in kg, v is the velocity in m/s, and KE is the kinetic energy in J (joules). ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued
... PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM The total linear momentum of an isolated system is constant (conserved). An isolated system is one for which the sum of the average external forces acting on the system is zero. In the picture, the net external force on the system is zero. ...
... PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM The total linear momentum of an isolated system is constant (conserved). An isolated system is one for which the sum of the average external forces acting on the system is zero. In the picture, the net external force on the system is zero. ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy conclusion
... Energy can neither be created not destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of molecules. Examples of heat generation: sliding ...
... Energy can neither be created not destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of molecules. Examples of heat generation: sliding ...