Swedish efforts concerning sustainable blue growth
... human well-being and social equity, while significantly reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities”. The concept of the blue economy has developed alongside the green economy to consider the economic benefits generated by coasts and oceans in all aspects of economic activity (UNCSD, 2012 ...
... human well-being and social equity, while significantly reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities”. The concept of the blue economy has developed alongside the green economy to consider the economic benefits generated by coasts and oceans in all aspects of economic activity (UNCSD, 2012 ...
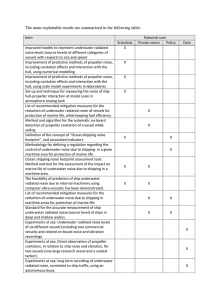
The main exploitable results are summarized in the following table:
... control of underwater noise due to shipping in a given maritime area for protection of marine life. Ocean shipping noise footprint assessment tool: Method and tool for the assessment of the impact on marine life of underwater noise due to shipping in a maritime area. The feasibility of prediction of ...
... control of underwater noise due to shipping in a given maritime area for protection of marine life. Ocean shipping noise footprint assessment tool: Method and tool for the assessment of the impact on marine life of underwater noise due to shipping in a maritime area. The feasibility of prediction of ...
Oceanography
... The most important feature of the ancient environment was an absence of free oxygen About 3 billion years ago cyanobacteria began to photosynthesis creating oxygen and as this oxygen increased, the carbon dioxide decreased In the upper atmosphere, some oxygen molecules absorbed energy from UV rays a ...
... The most important feature of the ancient environment was an absence of free oxygen About 3 billion years ago cyanobacteria began to photosynthesis creating oxygen and as this oxygen increased, the carbon dioxide decreased In the upper atmosphere, some oxygen molecules absorbed energy from UV rays a ...
AMS Ocean Studies
... Classification of Marine Sediments by Size – More energy is required to transport larger sediment particles than smaller ones. – Hence, as a river enters the ocean, larger particles settle out of suspension almost immediately whereas finer particles are carried farther away from the coast before se ...
... Classification of Marine Sediments by Size – More energy is required to transport larger sediment particles than smaller ones. – Hence, as a river enters the ocean, larger particles settle out of suspension almost immediately whereas finer particles are carried farther away from the coast before se ...
Chapter 7 - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Special Attributes of Penguins Penguins, order Sphenisciformes, all live in the Southern hemisphere. Penguins make up about 80% of all Antarctic birds and by far outnumber even the massive marine mammal populations. Not all species live in cold places. Penguins are found on the coasts of Sou ...
... Special Attributes of Penguins Penguins, order Sphenisciformes, all live in the Southern hemisphere. Penguins make up about 80% of all Antarctic birds and by far outnumber even the massive marine mammal populations. Not all species live in cold places. Penguins are found on the coasts of Sou ...
Spatial Pattern of Bathymetry in Wangi
... right for the implementation of archipelagic Wakatobi does have its own charm. These sea lanes based on the international law of the islands are also known as the blacksmith sea convention. It isintended to combine two Islands which have 25 coral reefs with variuos free waters, the Indian Ocean and ...
... right for the implementation of archipelagic Wakatobi does have its own charm. These sea lanes based on the international law of the islands are also known as the blacksmith sea convention. It isintended to combine two Islands which have 25 coral reefs with variuos free waters, the Indian Ocean and ...
Key Concept Review (Answers to in-text “Concept Checks”) Chapter
... 11. Most sediment deposits are a mixture of biogenous and terrigenous particles, with an occasional hydrogenous or cosmogenous supplement. The dominant type gives its name to the mixture. 12. Neritic sediments consist primarily of terrigenous material. Deep-ocean floors are covered by finer sediment ...
... 11. Most sediment deposits are a mixture of biogenous and terrigenous particles, with an occasional hydrogenous or cosmogenous supplement. The dominant type gives its name to the mixture. 12. Neritic sediments consist primarily of terrigenous material. Deep-ocean floors are covered by finer sediment ...
Research on Solid Waste Pollution along the Israeli Mediterranean
... The effect of currents on the distribution floating debris was examined by distributing a 'message in a bottle' along the Israeli coast. 300 used plastic bottles were filled with sand to allow them to sink to eliminate wind effect. In each bottle, a letter made of waterproof paper was inserted, expl ...
... The effect of currents on the distribution floating debris was examined by distributing a 'message in a bottle' along the Israeli coast. 300 used plastic bottles were filled with sand to allow them to sink to eliminate wind effect. In each bottle, a letter made of waterproof paper was inserted, expl ...
The UN Ocean Conference - June 2017, Guidance to the ENVI
... to targets outlined in SDG 14 4 on setting sustainable fishing quotas and establishing marine protected areas, among others. Fully implementing the individual SDGs means considering both the positive and negative effects they will have on achieving other SDGs 5 . In particular, the objectives of SDG ...
... to targets outlined in SDG 14 4 on setting sustainable fishing quotas and establishing marine protected areas, among others. Fully implementing the individual SDGs means considering both the positive and negative effects they will have on achieving other SDGs 5 . In particular, the objectives of SDG ...
The Changing Ocean Carbon Cycle - Assets
... matter to the deep ocean at Station ‘P’ in the North Pacific. The concept of seasonal and annual variability in vertical flux to great depth is now so well established that we tend to forget how recent these findings are. ...
... matter to the deep ocean at Station ‘P’ in the North Pacific. The concept of seasonal and annual variability in vertical flux to great depth is now so well established that we tend to forget how recent these findings are. ...
Land-based pollution
... environmental features are: low depth, high productivity, organic matter enrichment and low hydrodynamic forces. In the Baltic Sea hypoxia is widespread in large areas both in the open deeper parts and at coastal sites. A side effect is increased release of phosphorous from sediments, causing furt ...
... environmental features are: low depth, high productivity, organic matter enrichment and low hydrodynamic forces. In the Baltic Sea hypoxia is widespread in large areas both in the open deeper parts and at coastal sites. A side effect is increased release of phosphorous from sediments, causing furt ...
The deep sea is a major sink for microplastic debris
... in its production, monitoring data show limited evidence of concomitant increasing concentrations in marine habitats. There appears to be a considerable proportion of the manufactured plastic that is unaccounted for in surveys tracking the fate of environmental plastics. Even the discovery of widesp ...
... in its production, monitoring data show limited evidence of concomitant increasing concentrations in marine habitats. There appears to be a considerable proportion of the manufactured plastic that is unaccounted for in surveys tracking the fate of environmental plastics. Even the discovery of widesp ...
D O E I
... including developing innovative temperature and chemical sensors for on site measurements at ...
... including developing innovative temperature and chemical sensors for on site measurements at ...
Reefs_DIve_Wkst.v3
... All three of these types of coral colonies form massive rigid structures. How would this benefit the coral? ...
... All three of these types of coral colonies form massive rigid structures. How would this benefit the coral? ...
17TH MEETING OF THE - Convention on Migratory Species
... Biological Diversity Beyond Areas of National Jurisdiction, including its deliberations with respect to area-based conservation measures and environmental impact assessment in marine areas beyond the limits of national jurisdiction; Recalling Resolution 10.3 acknowledging the processes, workshop and ...
... Biological Diversity Beyond Areas of National Jurisdiction, including its deliberations with respect to area-based conservation measures and environmental impact assessment in marine areas beyond the limits of national jurisdiction; Recalling Resolution 10.3 acknowledging the processes, workshop and ...
Ocean Bottom Relief
... convergence, descent, and upwelling. This period is estimated at about 700 years for water of the Atlantic and 1,500 years for that of the Pacific. Slow as it is, this vast vertical circulation system is crucial to sea life. The descent of surface water in areas of convergence carries dissolved carb ...
... convergence, descent, and upwelling. This period is estimated at about 700 years for water of the Atlantic and 1,500 years for that of the Pacific. Slow as it is, this vast vertical circulation system is crucial to sea life. The descent of surface water in areas of convergence carries dissolved carb ...
Krasting PowerPoint on Circulation
... = RTOA - Ñ· Fao ¶t Time rate of change of energy in the atmosphere and oceans ...
... = RTOA - Ñ· Fao ¶t Time rate of change of energy in the atmosphere and oceans ...
Real time ocean data in the classroom.
... Objective: Students determine where marine organisms live, based on ocean temperatures. Visit NOAA’s NDBC website (www.ndbc.noaa.gov) to locate water temperatures at several offshore sites from Maine to Florida on the east coast and from Oregon to southern California on the west coast. Record temper ...
... Objective: Students determine where marine organisms live, based on ocean temperatures. Visit NOAA’s NDBC website (www.ndbc.noaa.gov) to locate water temperatures at several offshore sites from Maine to Florida on the east coast and from Oregon to southern California on the west coast. Record temper ...
Issue 2 - INDEEP
... of the sediment) on the New Zealand continental slope. Nematode diversity at our study sites was relatively high [ES(51) = 30–42], and there was no relationship between species/functional diversity and ecosystem function/efficiency after accounting for the effects of water depth and food availabilit ...
... of the sediment) on the New Zealand continental slope. Nematode diversity at our study sites was relatively high [ES(51) = 30–42], and there was no relationship between species/functional diversity and ecosystem function/efficiency after accounting for the effects of water depth and food availabilit ...
R/V Aranda – a moving platform for integrated
... for weather forecast and sea models. There is also increased pressure to do multidisciplinary, multiinvestigator research to better understand the complicated interactions between physical, chemical and ecological state of the sea and the climate conditions (e.g. ocean acidification, carbon and biog ...
... for weather forecast and sea models. There is also increased pressure to do multidisciplinary, multiinvestigator research to better understand the complicated interactions between physical, chemical and ecological state of the sea and the climate conditions (e.g. ocean acidification, carbon and biog ...
The Geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef
... explaining patterns of reef morphology throughout the GBR region. This chapter goes into some detail, supplying reef and reef-island statistics, and descriptions of classification and distribution of reefs by type (e.g., crescentic or ribbon reefs). The chapter demonstrates the nonrandomness of reef ...
... explaining patterns of reef morphology throughout the GBR region. This chapter goes into some detail, supplying reef and reef-island statistics, and descriptions of classification and distribution of reefs by type (e.g., crescentic or ribbon reefs). The chapter demonstrates the nonrandomness of reef ...
Cross-Curricular Discussion
... 2c. Corals live underwater, so they are dealing with the effects of increased absorption of carbon dioxide in seawater. How does carbon dioxide, a common greenhouse gas, react with water? [In a water (aqueous) state, carbon dioxide forms carbonic acid (H2CO3), which loses a proton (H+) to form bicar ...
... 2c. Corals live underwater, so they are dealing with the effects of increased absorption of carbon dioxide in seawater. How does carbon dioxide, a common greenhouse gas, react with water? [In a water (aqueous) state, carbon dioxide forms carbonic acid (H2CO3), which loses a proton (H+) to form bicar ...
Plankton biodiversity of the North Atlantic: changing patterns
... groups in terrestrial European ecosystems. The shifts are related to both the increasing trend in Northern Hemisphere temperature and the North Atlantic Oscillation (Figure 2). 2.3) New biological coupling of Pacific and Atlantic Oceans In 1999, the CPR survey revealed large numbers of the Pacific ...
... groups in terrestrial European ecosystems. The shifts are related to both the increasing trend in Northern Hemisphere temperature and the North Atlantic Oscillation (Figure 2). 2.3) New biological coupling of Pacific and Atlantic Oceans In 1999, the CPR survey revealed large numbers of the Pacific ...
Ocean Acidification - Joint Nature Conservation Committee
... compare the results of experiments due to the various methods to generate lower pH (CO2 bubbling or acid addition) being used. As experiments using more realistic conditions are conducted, our knowledge on more chronic effects will grow. Initial in situ experiments have been undertaken by the Monter ...
... compare the results of experiments due to the various methods to generate lower pH (CO2 bubbling or acid addition) being used. As experiments using more realistic conditions are conducted, our knowledge on more chronic effects will grow. Initial in situ experiments have been undertaken by the Monter ...
Marine biology

Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the ocean or other marine or brackish bodies of water. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Marine biology differs from marine ecology as marine ecology is focused on how organisms interact with each other and the environment, while biology is the study of the organisms themselves.A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. Exactly how large the proportion is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world covering about 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habitats include coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and thermal vents, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky bottoms, and the open ocean (pelagic) zone, where solid objects are rare and the surface of the water is the only visible boundary. The organisms studied range from microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton to huge cetaceans (whales) 30 meters (98 feet) in length.Marine life is a vast resource, providing food, medicine, and raw materials, in addition to helping to support recreation and tourism all over the world. At a fundamental level, marine life helps determine the very nature of our planet. Marine organisms contribute significantly to the oxygen cycle, and are involved in the regulation of the Earth's climate. Shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life, and some marine organisms even help create new land.Many species are economically important to humans, including food fish (both finfish and shellfish). It is also becoming understood that the well-being of marine organisms and other organisms are linked in very fundamental ways. The human body of knowledge regarding the relationship between life in the sea and important cycles is rapidly growing, with new discoveries being made nearly every day. These cycles include those of matter (such as the carbon cycle) and of air (such as Earth's respiration, and movement of energy through ecosystems including the ocean). Large areas beneath the ocean surface still remain effectively unexplored.