Marine macroalgae and associated flowering plants from the Keret
... substrata and the inflow of freshwater along the extensive northern coast. The White Sea is an exception to this generalization, and a long history of floristic studies show lush populations of macroalgae. The principal algal monographs including Zinova (1929, 1950, 1953, 1955), Vozzhinskaya (1986), ...
... substrata and the inflow of freshwater along the extensive northern coast. The White Sea is an exception to this generalization, and a long history of floristic studies show lush populations of macroalgae. The principal algal monographs including Zinova (1929, 1950, 1953, 1955), Vozzhinskaya (1986), ...
Document
... is the importance of their apparently fastsinking fecal material in oceanic export flux? Can we relate this material directly to new production as the biological pump concept requires (e.g. Michaels and Silver 1988), since mesoplankton fecal pellets will usually not represent more than a small fract ...
... is the importance of their apparently fastsinking fecal material in oceanic export flux? Can we relate this material directly to new production as the biological pump concept requires (e.g. Michaels and Silver 1988), since mesoplankton fecal pellets will usually not represent more than a small fract ...
Deep-Sea Mining
... off the coast of Papua New Guinea, may begin in 2018. For the UK, current deep-sea mining focus is on international waters, regulations for which are under development. Three different types of deposit are being considered, each associated with a distinct geology and ecosystem. However, the extrem ...
... off the coast of Papua New Guinea, may begin in 2018. For the UK, current deep-sea mining focus is on international waters, regulations for which are under development. Three different types of deposit are being considered, each associated with a distinct geology and ecosystem. However, the extrem ...
Coastal Upwelling Feat From ROMS eatures over Arabian Sea From
... More important for light wind situation For mid-latitude, the stability effect is usually small but in tropical and subtropical regions, it should be included. ...
... More important for light wind situation For mid-latitude, the stability effect is usually small but in tropical and subtropical regions, it should be included. ...
Ocean Boundary Currents - Student Climate Data
... of the ocean and in the heat balance of the Earth. Surface currents are governed by winds and the rotation of the Earth. Atmospheric trade winds lead to the formation of surface currents, which are driven from east to west along the equator. When these currents encounter land, they divide to the nor ...
... of the ocean and in the heat balance of the Earth. Surface currents are governed by winds and the rotation of the Earth. Atmospheric trade winds lead to the formation of surface currents, which are driven from east to west along the equator. When these currents encounter land, they divide to the nor ...
consequences and acclimatization strategies
... organizers to the great success of the first two meetings, which made this third one possible. We observe an increasing awareness in the media, politics and the public mind, of the importance of the world’s oceans in climate dynamics and protein resources, but also of the threats from the sea. For a ...
... organizers to the great success of the first two meetings, which made this third one possible. We observe an increasing awareness in the media, politics and the public mind, of the importance of the world’s oceans in climate dynamics and protein resources, but also of the threats from the sea. For a ...
Marine Habitat Protection in Sea Areas under the
... harvest coral for commercial purposes but adversely impact upon the structural integrity of the coral reefs by utilising bottom trawls and other ground gear to catch deep-water species in reef areas. There is also a danger to the biodiversity associated with the reefs as a result of ``ghost fishing' ...
... harvest coral for commercial purposes but adversely impact upon the structural integrity of the coral reefs by utilising bottom trawls and other ground gear to catch deep-water species in reef areas. There is also a danger to the biodiversity associated with the reefs as a result of ``ghost fishing' ...
Marine science and technology
... stock levels, and to set maximum allowable catches, aimed at conserving remaining stocks and creating sustainable fisheries. Similarly, sand and gravel have been extracted from the sea-bed for centuries, with the UK offshore aggregates industry now the largest and most technically advanced in the wo ...
... stock levels, and to set maximum allowable catches, aimed at conserving remaining stocks and creating sustainable fisheries. Similarly, sand and gravel have been extracted from the sea-bed for centuries, with the UK offshore aggregates industry now the largest and most technically advanced in the wo ...
FROM: The Antarctic Coastal Current
... southernmost current in the world. This current is the counter-current of the largest ocean current in the world, Antarctic Circumpolar Current. On the average, it flows westward and parallel to the Antarctic coastline. Although it is circumpolar, the Antarctic Peninsula partially impedes its flow ( ...
... southernmost current in the world. This current is the counter-current of the largest ocean current in the world, Antarctic Circumpolar Current. On the average, it flows westward and parallel to the Antarctic coastline. Although it is circumpolar, the Antarctic Peninsula partially impedes its flow ( ...
7.1-7.2 Bay of Biscay and Iberian ecosystem overview
... The continental shelf in the northern Bay of Biscay is about 140 km wide; it becomes narrower to the south (about 50 km off southern France). From coast to offshore, the depth increases almost regularly down to 200 m, the shelf is mainly flat. On the southern border of the Bay of Biscay, the contine ...
... The continental shelf in the northern Bay of Biscay is about 140 km wide; it becomes narrower to the south (about 50 km off southern France). From coast to offshore, the depth increases almost regularly down to 200 m, the shelf is mainly flat. On the southern border of the Bay of Biscay, the contine ...
Richard Thomas / Plymouth
... Data on sea birds showing the ingestion of plastic waste as being a cause of death first began to appear in the 1950s. 95% of dead fulmars (a common sea bird) washed ashore in Scotland will have some plastic debris in their gut. Worldwide, 260 species bird and mammal are known to ingest or become en ...
... Data on sea birds showing the ingestion of plastic waste as being a cause of death first began to appear in the 1950s. 95% of dead fulmars (a common sea bird) washed ashore in Scotland will have some plastic debris in their gut. Worldwide, 260 species bird and mammal are known to ingest or become en ...
Activities of JSPS-Asian CORE Project: Establishment of Research
... located in front of a large mangrove area seriously affected by human activities, while the latter are located in an open, fore-reef area isolated from human activities. These areas also represent two major types of seagrass ecosystems in Southeast Asia. This research will provide detailed and preci ...
... located in front of a large mangrove area seriously affected by human activities, while the latter are located in an open, fore-reef area isolated from human activities. These areas also represent two major types of seagrass ecosystems in Southeast Asia. This research will provide detailed and preci ...
Chapter 51. Biological Communities on Seamounts and Other
... Trenches are defined as “long, narrow, characteristically very deep and asymmetrical depressions(s) of the seafloor, with relatively steep sides” (IHO, 2008). In addition to featuring steep terrain with typically hard substrates, often narrow terraces and the deepest ocean depths, the trenches have ...
... Trenches are defined as “long, narrow, characteristically very deep and asymmetrical depressions(s) of the seafloor, with relatively steep sides” (IHO, 2008). In addition to featuring steep terrain with typically hard substrates, often narrow terraces and the deepest ocean depths, the trenches have ...
Mining Industry - Cluster Maritime Français
... Regarding Seafloor Mineral resources, France decided to prepare for the medium-term development of Deep Sea mining projects by immediately beginning to organize the development and industrial management of offshore mineral extraction processes on the basis of improvements in the knowledge of the oce ...
... Regarding Seafloor Mineral resources, France decided to prepare for the medium-term development of Deep Sea mining projects by immediately beginning to organize the development and industrial management of offshore mineral extraction processes on the basis of improvements in the knowledge of the oce ...
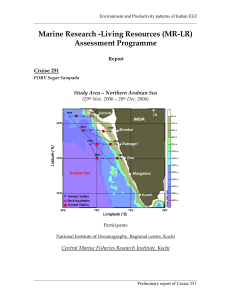
Cruise 251
... sightings were done and 94% of the sighted cetaceans could be unmistakably “identified”, while the remaining was “unidentified”. Photos have been taken wherever possible and would certainly lead to identification up to genus or species level once other expertise are sought for ratification based on ...
... sightings were done and 94% of the sighted cetaceans could be unmistakably “identified”, while the remaining was “unidentified”. Photos have been taken wherever possible and would certainly lead to identification up to genus or species level once other expertise are sought for ratification based on ...
Coral Reef Ecology Coral Reef Conservation
... generations of polyps build on top of previous generations’ "skeletons" leading to reef formation. As such, reef-building (hermatypic) corals are the basis of life in reef communities. Where are coral reefs found? Coral reefs are present in the waters of over 100 countries. These are warm (18-29°C), ...
... generations of polyps build on top of previous generations’ "skeletons" leading to reef formation. As such, reef-building (hermatypic) corals are the basis of life in reef communities. Where are coral reefs found? Coral reefs are present in the waters of over 100 countries. These are warm (18-29°C), ...
Directed Reading
... support b. a piloted, self-propelled, free-moving submarine c. remotely piloted submersible that allows oceanographers to study the ocean depths for long periods of time ...
... support b. a piloted, self-propelled, free-moving submarine c. remotely piloted submersible that allows oceanographers to study the ocean depths for long periods of time ...
Research paper : Anatomy of a new international instrument
... mining; offshore energy exploration and production operations; shipping; pollution, especially from plastic and acoustic sources; the spread of alien and invasive species; cable-laying; tourism; marine scientific research, including bio-discovery and bioprospecting research activities; ocean acidifi ...
... mining; offshore energy exploration and production operations; shipping; pollution, especially from plastic and acoustic sources; the spread of alien and invasive species; cable-laying; tourism; marine scientific research, including bio-discovery and bioprospecting research activities; ocean acidifi ...
The National Centre for Marine Research (NCMR) is the leading
... Institutes that is the Institute of Oceanography, the Institute of Fisheries and the Institute of Inland Waters. The NCMR operates an oceanographic vessel (AEGAIO R/V) 65m long, a small submersible (THETIS S/B) and other large-scale marine facilities. From the three Institutes, the Institute of Ocea ...
... Institutes that is the Institute of Oceanography, the Institute of Fisheries and the Institute of Inland Waters. The NCMR operates an oceanographic vessel (AEGAIO R/V) 65m long, a small submersible (THETIS S/B) and other large-scale marine facilities. From the three Institutes, the Institute of Ocea ...
Modelling in Coastal and Shelf Seas
... requirements by developers of these ocean models is essential. To deliver the full range of benefits from our models over the diverse scope of habitats in Europe, interfaces with socio-economic-political concerns must be established. This may require simplification of our complex models, or aggregat ...
... requirements by developers of these ocean models is essential. To deliver the full range of benefits from our models over the diverse scope of habitats in Europe, interfaces with socio-economic-political concerns must be established. This may require simplification of our complex models, or aggregat ...
The Impacts of Marine Debris: A Review and Synthesis of Existing
... 170,000 hectare, deep water bay located on the Pacific coast. The bay is incredibly rich in biodiversity. It is critical breeding and calving habitat for eastern Pacific grey whales, and also home to the largest stretches of mangrove forest in the Baja. We dropped anchor at a small, uninhabited isla ...
... 170,000 hectare, deep water bay located on the Pacific coast. The bay is incredibly rich in biodiversity. It is critical breeding and calving habitat for eastern Pacific grey whales, and also home to the largest stretches of mangrove forest in the Baja. We dropped anchor at a small, uninhabited isla ...
Plastic photodegradation in the ocean
... Some plastics decompose within a year of entering the water, leaching potentially toxic chemicals such as bisphenol A, PCBs, and derivatives of polystyrene.[21] Mass of plastics through water column Charles Moore has estimated the mass of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch at 100 million tons[22], whic ...
... Some plastics decompose within a year of entering the water, leaching potentially toxic chemicals such as bisphenol A, PCBs, and derivatives of polystyrene.[21] Mass of plastics through water column Charles Moore has estimated the mass of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch at 100 million tons[22], whic ...
Uncertainty in fisheries management
... Ocean ecosystems in a nutshell: Almost all ocean ecosystems depend (directly or indirectly) on the energy of sunlight, which enables phytoplankton, algae and other plants to synthesize carbohydrates, using dissolved carbon dioxide and nutrients. Carbohydrates provide the energy source for resulting ...
... Ocean ecosystems in a nutshell: Almost all ocean ecosystems depend (directly or indirectly) on the energy of sunlight, which enables phytoplankton, algae and other plants to synthesize carbohydrates, using dissolved carbon dioxide and nutrients. Carbohydrates provide the energy source for resulting ...
Full Article
... ordered and serene environment. 7 It was from this period that “development” started. The oceans and seas cover about 71.4 percent of the earth surface. 8 They comprise nine-tenths (9/10) of our water resources and are home to over 97 percent of life in our planet. They are an essential part of our ...
... ordered and serene environment. 7 It was from this period that “development” started. The oceans and seas cover about 71.4 percent of the earth surface. 8 They comprise nine-tenths (9/10) of our water resources and are home to over 97 percent of life in our planet. They are an essential part of our ...
Marine biology

Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the ocean or other marine or brackish bodies of water. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Marine biology differs from marine ecology as marine ecology is focused on how organisms interact with each other and the environment, while biology is the study of the organisms themselves.A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. Exactly how large the proportion is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world covering about 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habitats include coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and thermal vents, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky bottoms, and the open ocean (pelagic) zone, where solid objects are rare and the surface of the water is the only visible boundary. The organisms studied range from microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton to huge cetaceans (whales) 30 meters (98 feet) in length.Marine life is a vast resource, providing food, medicine, and raw materials, in addition to helping to support recreation and tourism all over the world. At a fundamental level, marine life helps determine the very nature of our planet. Marine organisms contribute significantly to the oxygen cycle, and are involved in the regulation of the Earth's climate. Shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life, and some marine organisms even help create new land.Many species are economically important to humans, including food fish (both finfish and shellfish). It is also becoming understood that the well-being of marine organisms and other organisms are linked in very fundamental ways. The human body of knowledge regarding the relationship between life in the sea and important cycles is rapidly growing, with new discoveries being made nearly every day. These cycles include those of matter (such as the carbon cycle) and of air (such as Earth's respiration, and movement of energy through ecosystems including the ocean). Large areas beneath the ocean surface still remain effectively unexplored.