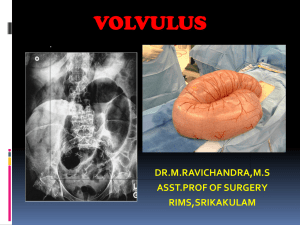
C H A P T E R 6 3
... Propulsive Movements—Peristalsis A contractile ring appears around the gut and then moves forward, any material in front of the contractile ring is moved forward. Peristalsis is an inherent property of many syncytial smooth muscle tubes; stimulation at any point in the gut can cause a contractile ri ...
... Propulsive Movements—Peristalsis A contractile ring appears around the gut and then moves forward, any material in front of the contractile ring is moved forward. Peristalsis is an inherent property of many syncytial smooth muscle tubes; stimulation at any point in the gut can cause a contractile ri ...
ANOPHELES GUT MICROBIOTA PROVIDE POSSIBILITIES
... Some transgenic mosquitoes have been shown to prevent pathogen development by expression of molecules that impair the survival of the pathogens (Coutinho-Abreu et al. 2010). To begin with, proof-of-principle laboratory experiments showing anti-Plasmodium resistance in transgenic Anopheles were perfo ...
... Some transgenic mosquitoes have been shown to prevent pathogen development by expression of molecules that impair the survival of the pathogens (Coutinho-Abreu et al. 2010). To begin with, proof-of-principle laboratory experiments showing anti-Plasmodium resistance in transgenic Anopheles were perfo ...
Recurrent Clostridium difficile infections: The importance of the
... methods able to stabilize and study C. difficile taken out of the gut[20]. Gut microbiota and its imbalance, called dysbiosis, has a crucial role in the pathophysiology of CDI recurrence. Over the last decade, an emerging consensus has formed about the importance of the intestinal microbiota, which ...
... methods able to stabilize and study C. difficile taken out of the gut[20]. Gut microbiota and its imbalance, called dysbiosis, has a crucial role in the pathophysiology of CDI recurrence. Over the last decade, an emerging consensus has formed about the importance of the intestinal microbiota, which ...
Negative Regulation by Amidase PGRPs Shapes the
... has been proposed that this systemic reaction to a local infection is mediated by translocation of peptidoglycan fragments across the gut epithelium (Gendrin et al., 2009; Zaidman-Rémy et al., 2006). This was supported by the observation that PGRP-LB RNAi flies with reduced amidase activity showed ...
... has been proposed that this systemic reaction to a local infection is mediated by translocation of peptidoglycan fragments across the gut epithelium (Gendrin et al., 2009; Zaidman-Rémy et al., 2006). This was supported by the observation that PGRP-LB RNAi flies with reduced amidase activity showed ...
Diarrhea - ISpatula
... Beneficial microbes such as bifidobacteria live in the intestinal ecosystem with potentially pathogenic bacteria. Beneficial microbes prevent the overgrowth of “bad bacteria” by producing antimicrobial agents. Additionally, beneficial microbes competitively limit pathogenic bacterial overgrowth by o ...
... Beneficial microbes such as bifidobacteria live in the intestinal ecosystem with potentially pathogenic bacteria. Beneficial microbes prevent the overgrowth of “bad bacteria” by producing antimicrobial agents. Additionally, beneficial microbes competitively limit pathogenic bacterial overgrowth by o ...
pdf - Open Assembly
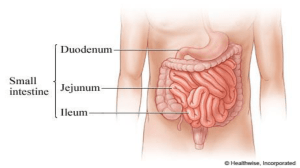
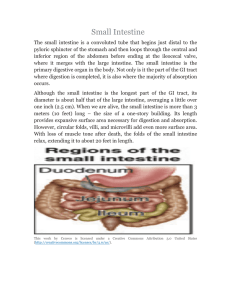
... part of the small intestine; it is less than 1 foot of the 10 foot intestine (30 cm of the 3 m). The duodenum receives the stomach contents, pancreatic juice and bile. Chemical digestion continues in the duodenum. The jejunum is the next portion (3.5 - 5.5 ft or 110-170 cm) of the small intestine an ...
... part of the small intestine; it is less than 1 foot of the 10 foot intestine (30 cm of the 3 m). The duodenum receives the stomach contents, pancreatic juice and bile. Chemical digestion continues in the duodenum. The jejunum is the next portion (3.5 - 5.5 ft or 110-170 cm) of the small intestine an ...
1. Bacteria without cell Wall a. Chlamydia b. Rickettsia c
... a. Adaptation phase b. Exponential phase . c. Stationary phase. d. Decline Phase ...
... a. Adaptation phase b. Exponential phase . c. Stationary phase. d. Decline Phase ...
Gut flora

Gut flora or, more appropriately, gut microbiota, consists of a complex community of microorganism species that live in the digestive tracts of animals and is the largest reservoir of microorganisms mutual to humans. In this context gut is synonymous with intestinal, and flora with microbiota and microflora. The gut microbiome refer to the genomes of the gut microbiota.Gut microorganisms benefit the host by gleaning the energy from the fermentation of undigested carbohydrates and the subsequent absorption of short-chain fatty acids. The most important of these fatty acids are butyrates, metabolised by the colonic epithelium; propionates by the liver; and acetates by the muscle tissue. Intestinal bacteria also play a role in synthesizing vitamin B and vitamin K as well as metabolizing bile acids, sterols and xenobiotics.The human body carries about 100 trillion microorganisms in its intestines, a number ten times greater than the total number of human cells in the body. The metabolic activities performed by these bacteria resemble those of an organ, leading some to liken gut bacteria to a ""forgotten"" organ. It is estimated that these gut flora have around a hundred times as many genes in aggregate as there are in the human genome.