Institute for Microbiology, Medical Faculty of Masaryk
... Brain abscess (both acute and chronic): punctate or excission for bacteriology (incl. tbc), mycology (cryptococci) & histology (cysticerci) ...
... Brain abscess (both acute and chronic): punctate or excission for bacteriology (incl. tbc), mycology (cryptococci) & histology (cysticerci) ...
Pathology Resident Microbiology Lecture Series
... Presence can indicate contamination Seeing an increase due to prosthetic devices, catheters and immunocompromised Abbreviated CNS or CoNS ...
... Presence can indicate contamination Seeing an increase due to prosthetic devices, catheters and immunocompromised Abbreviated CNS or CoNS ...
Vibrio vulnificus FACT SHEET - Seafood Network Information Center
... patients also develop painful skin lesions. The skin initially appears red. Blisters develop quickly and erode into necrotic ulcers. Gastroenteritis occurs after ingestion of food containing V. vulnificus. Patients with gastroenteritis have a relatively milder syndrome consisting of vomiting, diarrh ...
... patients also develop painful skin lesions. The skin initially appears red. Blisters develop quickly and erode into necrotic ulcers. Gastroenteritis occurs after ingestion of food containing V. vulnificus. Patients with gastroenteritis have a relatively milder syndrome consisting of vomiting, diarrh ...
A Case of Septic Portal Vein Thrombosis
... these criteria. Infections such as appendicitis and diverticulitis are the most frequent predisposing conditions to pylephlebitis, though other intra-abdominal infections have also been implicated 1,7 Blood cultures are positive in 23-88% of patients. 1-4 When positive, organisms are usually bowel f ...
... these criteria. Infections such as appendicitis and diverticulitis are the most frequent predisposing conditions to pylephlebitis, though other intra-abdominal infections have also been implicated 1,7 Blood cultures are positive in 23-88% of patients. 1-4 When positive, organisms are usually bowel f ...
Investigation and Analysis on Pathogen Distribution of HIV/AIDS
... PSM strains is preponderant. It may be connected with fixed value bacteria and pathogens of syndrome differentiation, quality and quantity of regional samples and so on. The constituent ratio of Mycobacterium reported authoritatively by Liu Jiao, etc. was 14.44% [5], which was relatively lower than ...
... PSM strains is preponderant. It may be connected with fixed value bacteria and pathogens of syndrome differentiation, quality and quantity of regional samples and so on. The constituent ratio of Mycobacterium reported authoritatively by Liu Jiao, etc. was 14.44% [5], which was relatively lower than ...
CLINICAL ASPECTS OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS IN DIABETES
... (15). At the present time, only few studies show evidence that diabetes mellitus is a risk factor for intestinal Candida colonization (9, 16). It has been demonstrated that the frequent of colonization by moulds and yeast-like fungi in the intestine of children with diabetes mellitus is higher than ...
... (15). At the present time, only few studies show evidence that diabetes mellitus is a risk factor for intestinal Candida colonization (9, 16). It has been demonstrated that the frequent of colonization by moulds and yeast-like fungi in the intestine of children with diabetes mellitus is higher than ...
Hospital-Onset Infections
... monitor the incidence of nosocomial infections in health care settings in an attempt to minimize their occurrence. Rates of hospital-onset infection have been measured for more than 30 years. The NNIS System and similar infection monitoring systems compare the observed infection rate in a given hosp ...
... monitor the incidence of nosocomial infections in health care settings in an attempt to minimize their occurrence. Rates of hospital-onset infection have been measured for more than 30 years. The NNIS System and similar infection monitoring systems compare the observed infection rate in a given hosp ...
GI infections, bacteria
... Gastrointestinal Infections 1: BACTERIAL – 22/09/03 INFECTIOUS DIARRHOEA (Lecture notes) Diarrhoea due to an infectious cause is a very common syndrome experienced in a GP setting. It has a very high infant mortality rate, and is characterised by distinct symptoms such as: nausea, vomiting, abdomina ...
... Gastrointestinal Infections 1: BACTERIAL – 22/09/03 INFECTIOUS DIARRHOEA (Lecture notes) Diarrhoea due to an infectious cause is a very common syndrome experienced in a GP setting. It has a very high infant mortality rate, and is characterised by distinct symptoms such as: nausea, vomiting, abdomina ...
Hand Washing, Routine Practices and Disease Specifics
... aerosols and small particle droplets Also discourages you from touching your ...
... aerosols and small particle droplets Also discourages you from touching your ...
A Non-Mammalian System to Study Bacterial Infections
... Dictyostelium discoideum is a powerful genetic system to analyse the complex relationship between bacteria and phagocytic cells. Our initial work was focused on the mechanisms controlling phagocytosis of bacteria by amoebae (Cornillon et al., 2000). We have more recently focused on the interaction o ...
... Dictyostelium discoideum is a powerful genetic system to analyse the complex relationship between bacteria and phagocytic cells. Our initial work was focused on the mechanisms controlling phagocytosis of bacteria by amoebae (Cornillon et al., 2000). We have more recently focused on the interaction o ...
Urinary Tract Infections
... In young women, on the other hand, several factors predispose to infection, and these include: 1) short urethra; 2) sexual intercourse and lack of post-coital voiding; 3) diaphragm use (manipulation involved in placing it on the cervix may promote bacterial colonization); and 4) spermicide use (rais ...
... In young women, on the other hand, several factors predispose to infection, and these include: 1) short urethra; 2) sexual intercourse and lack of post-coital voiding; 3) diaphragm use (manipulation involved in placing it on the cervix may promote bacterial colonization); and 4) spermicide use (rais ...
have been linked to acute bronchitis. People at - Home Planet
... Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the part of the respiratory system that leads into the lungs. Acute bronchitis has a sudden onset and usually appears after a respiratory infection, such as a cold, and can be caused by either a virus bacteria. The infection inflames the bronchi ...
... Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the part of the respiratory system that leads into the lungs. Acute bronchitis has a sudden onset and usually appears after a respiratory infection, such as a cold, and can be caused by either a virus bacteria. The infection inflames the bronchi ...
Infection Control: IV Drug Administration
... to IV therapy. • Discuss the actions required to prevent/minimise the risk of infection in a patient receiving IV drug/fluid therapy. • Describe how vascular access device related infections can be detected. ...
... to IV therapy. • Discuss the actions required to prevent/minimise the risk of infection in a patient receiving IV drug/fluid therapy. • Describe how vascular access device related infections can be detected. ...
Administration of IV Therapy
... to IV therapy. • Discuss the actions required to prevent/minimise the risk of infection in a patient receiving IV drug/fluid therapy. • Describe how vascular access device related infections can be detected. ...
... to IV therapy. • Discuss the actions required to prevent/minimise the risk of infection in a patient receiving IV drug/fluid therapy. • Describe how vascular access device related infections can be detected. ...
View Full Text-PDF
... significant risk factor was artificial respiration (OR=9.81). Gram negative bacilli (38.5%) were the first cause followed by Gram positive cocci (35.5%) then fungi (26.0%). The mortality rate was 15%. The incidence of noscomial respiratory tract infection in cirrhotic patients was not low. Artificia ...
... significant risk factor was artificial respiration (OR=9.81). Gram negative bacilli (38.5%) were the first cause followed by Gram positive cocci (35.5%) then fungi (26.0%). The mortality rate was 15%. The incidence of noscomial respiratory tract infection in cirrhotic patients was not low. Artificia ...
PDF - Nexus Academic Publishers
... collected. Bacterial skin infections common in animal veterinary practice, are most frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus apart from other common causative agents like Escherichia coli as evident from the results. Gram negative bacteria are generally secondary invaders which establishes under c ...
... collected. Bacterial skin infections common in animal veterinary practice, are most frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus apart from other common causative agents like Escherichia coli as evident from the results. Gram negative bacteria are generally secondary invaders which establishes under c ...
No Slide Title
... 2. muscle edema 3. fluid collections and/or gas within the muscle. 4. avid enhancement of the muscles and fascia (not shown) ...
... 2. muscle edema 3. fluid collections and/or gas within the muscle. 4. avid enhancement of the muscles and fascia (not shown) ...
MSc/PGD/PGC in Infection (part
... The MSc/PGD/PGC in Infection is aimed at health care professionals across the globe with an interest in infection prevention and infectious diseases. This course creates a pathway into clinical research for pharmacists, doctors, biomedical scientists, nurses and health care managers so that they can ...
... The MSc/PGD/PGC in Infection is aimed at health care professionals across the globe with an interest in infection prevention and infectious diseases. This course creates a pathway into clinical research for pharmacists, doctors, biomedical scientists, nurses and health care managers so that they can ...
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update
... related risk factors (33% v. 72%, p = 0.097) and more likely to report community related risk factors (56% v. 6%, p = 0.008) than patients with other MRSA strains. The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) has issued treatment guidelines for MRSA in order to help clinicians choose the best t ...
... related risk factors (33% v. 72%, p = 0.097) and more likely to report community related risk factors (56% v. 6%, p = 0.008) than patients with other MRSA strains. The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) has issued treatment guidelines for MRSA in order to help clinicians choose the best t ...
No Slide Title
... cells/mm3 (normal 2,500-7,000 cells/mm3), but at this stage the patient is often already medicated with antibiotics due to frequent bacterial infections and as prophylaxis against opportunistic infections. ...
... cells/mm3 (normal 2,500-7,000 cells/mm3), but at this stage the patient is often already medicated with antibiotics due to frequent bacterial infections and as prophylaxis against opportunistic infections. ...
Chapter 11
... • Know characteristics of 2 groups of grampositive bacteria and some of the examples listed in the chapter review • Know characteristics of Arhaea, and its 3 major groups (characteristics and where they are found) given in the chapter review • Know why many bacteria have not been classified and iden ...
... • Know characteristics of 2 groups of grampositive bacteria and some of the examples listed in the chapter review • Know characteristics of Arhaea, and its 3 major groups (characteristics and where they are found) given in the chapter review • Know why many bacteria have not been classified and iden ...
Tuberculosis
... Tuberculosis bacteria are transmitted from person to person via the airways. When they cough, people suffering from TB release minute droplets containing tuberculosis bacteria into the surrounding air. These can then be breathed in by another person. You are at risk of being infected if you come int ...
... Tuberculosis bacteria are transmitted from person to person via the airways. When they cough, people suffering from TB release minute droplets containing tuberculosis bacteria into the surrounding air. These can then be breathed in by another person. You are at risk of being infected if you come int ...
Skin and Soft tissue infections
... Severe or Linezolid 600mg PO BID (formulary restriction; ID approval) Recurrent MRSA Outpatient ID consultation if patient has frequent MRSA soft tissue abscesses >2 infections. Call 425-261-4905 to schedule. episodes Mild ...
... Severe or Linezolid 600mg PO BID (formulary restriction; ID approval) Recurrent MRSA Outpatient ID consultation if patient has frequent MRSA soft tissue abscesses >2 infections. Call 425-261-4905 to schedule. episodes Mild ...
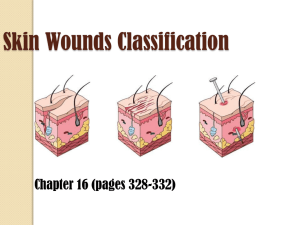
Skin Wounds Classification
... o Risk of infections increases if: o wound was exposed to soil (may contain tetanus or other bacteria) o went through sole of shoe (↑ risk of bacterial infection that is difficult to treat) o injected into skin under high pressure o i.e. nail from nail gun, paint from highpressure paint sprayer o Ph ...
... o Risk of infections increases if: o wound was exposed to soil (may contain tetanus or other bacteria) o went through sole of shoe (↑ risk of bacterial infection that is difficult to treat) o injected into skin under high pressure o i.e. nail from nail gun, paint from highpressure paint sprayer o Ph ...
staphylococcus -study material-2012
... Skin and soft tissue: Folliculitis, furuncle (boil), abscess (particularly breast abscess), wound infection, carbuncle, impetigo, paronychia, less often cellulitis. Musculoskeletal: Osteomyelitis, arthritis, bursitis, pyomyositis Respiratory: Tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, otitis, bronchopneum ...
... Skin and soft tissue: Folliculitis, furuncle (boil), abscess (particularly breast abscess), wound infection, carbuncle, impetigo, paronychia, less often cellulitis. Musculoskeletal: Osteomyelitis, arthritis, bursitis, pyomyositis Respiratory: Tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, otitis, bronchopneum ...