Guidelines for Antimicrobial Usage 2011 CVR(AMUG12).indd 1
... inpatient stay. It has been estimated that at least fifty percent of patients receive antimicrobials needlessly. Reasons include inappropriate prescribing for antimicrobial prophylaxis, continuation of empiric therapy despite negative cultures in a stable patient, and a lack of awareness of suscepti ...
... inpatient stay. It has been estimated that at least fifty percent of patients receive antimicrobials needlessly. Reasons include inappropriate prescribing for antimicrobial prophylaxis, continuation of empiric therapy despite negative cultures in a stable patient, and a lack of awareness of suscepti ...
- Wiley Online Library
... related bacteria and other Helicobacter spp. have been published since then. Tap and well water and ®eld soil samples were collected in a region of Japan with a high H. pylori infection rate and examined using a similar IMS-PCR technique to that 8 described in section 5.4, but with a different targe ...
... related bacteria and other Helicobacter spp. have been published since then. Tap and well water and ®eld soil samples were collected in a region of Japan with a high H. pylori infection rate and examined using a similar IMS-PCR technique to that 8 described in section 5.4, but with a different targe ...
Infection Control in the Operating Room
... wearer. These perforations allow bacteria from the surgical site to pass through to the wearer’s hands. One method for preventing this is to mandate regular glove changes in organizational policy. Changing gloves at regular intervals may decrease the incidence of glove perforation and bacterial cont ...
... wearer. These perforations allow bacteria from the surgical site to pass through to the wearer’s hands. One method for preventing this is to mandate regular glove changes in organizational policy. Changing gloves at regular intervals may decrease the incidence of glove perforation and bacterial cont ...
Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms with higher proportions of
... 1 %G+HPO42-) prevented the glucose-dependent accumulation of dormant bacteria, when compared with biofilms grown in TSB 1 %G only (data not shown). These results suggest that low culture pH, a consequence of glucose metabolism and acid lactic accumulation, was responsible for inducing cell dormancy ...
... 1 %G+HPO42-) prevented the glucose-dependent accumulation of dormant bacteria, when compared with biofilms grown in TSB 1 %G only (data not shown). These results suggest that low culture pH, a consequence of glucose metabolism and acid lactic accumulation, was responsible for inducing cell dormancy ...
Povidone – Iodine in Ophthalmology
... i.e., Staphylococcus epidermidis (95.4 %). Less frequent bacteria are Staphylococcus aureus (14.8 %), anaerobes (44 %), (Corynebacterium species), Streptococcus species (4.4%)and gram-negative rods (7.8 %). (i.e. E Coli, Pseudomonas aeuruginosa). The Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study determined that, ...
... i.e., Staphylococcus epidermidis (95.4 %). Less frequent bacteria are Staphylococcus aureus (14.8 %), anaerobes (44 %), (Corynebacterium species), Streptococcus species (4.4%)and gram-negative rods (7.8 %). (i.e. E Coli, Pseudomonas aeuruginosa). The Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study determined that, ...
IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS)
... Benzolkonium chloride, stains (Crystal violet, Methylene blue and Malachite green), lime, common salt and finally antibiotics (Ofloxacin, Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Neomycin etc.) have been used. The regular use of artificial feed supplemented with antibiotics in an effort to prevent the spread of ...
... Benzolkonium chloride, stains (Crystal violet, Methylene blue and Malachite green), lime, common salt and finally antibiotics (Ofloxacin, Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Neomycin etc.) have been used. The regular use of artificial feed supplemented with antibiotics in an effort to prevent the spread of ...
Imaging of the Infected Foot
... of the imaging literature and its clinical relevance to podiatric medicine and surgery are the issues. The anatomy of osseous tissue and the pathogenesis of osteomyelitis are key factors in new imaging theories; specifically, this concerns the skeletal location and marrow content. The central or axi ...
... of the imaging literature and its clinical relevance to podiatric medicine and surgery are the issues. The anatomy of osseous tissue and the pathogenesis of osteomyelitis are key factors in new imaging theories; specifically, this concerns the skeletal location and marrow content. The central or axi ...
Chlorhexidine: Expanding the Armamentarium for Infection Control
... chlorhexidine decreased skin and environmental contamination with VRE and reduced the incidence of VRE acquisition (risk ratio [RR], 0.4; 95% CI, 0.1–0.9) in a comparison of the intervention period with 2 periods of bathing involving baths that did not contain chlorhexidine [6]. Not only did the int ...
... chlorhexidine decreased skin and environmental contamination with VRE and reduced the incidence of VRE acquisition (risk ratio [RR], 0.4; 95% CI, 0.1–0.9) in a comparison of the intervention period with 2 periods of bathing involving baths that did not contain chlorhexidine [6]. Not only did the int ...
2 Non-typhoidal Salmonella in Children: Microbiology, Epidemiology and Treatment
... more cases of positive cultures at three weeks in the antibiotic-treated group. Adverse drug reactions, including rash, gastrointestinal upset and headache, were also more common in the antibiotic group [58]. Given the exclusion criteria, these results can not be extrapolated to patients at higher r ...
... more cases of positive cultures at three weeks in the antibiotic-treated group. Adverse drug reactions, including rash, gastrointestinal upset and headache, were also more common in the antibiotic group [58]. Given the exclusion criteria, these results can not be extrapolated to patients at higher r ...
Infectious Agents in Acute and Chronic Diarrhea of Childhood
... classical food poisoning are not mentioned or are not investigated at all. In the last 10 years, village weaning foods have been found to contain large numbers of bacteria originating in food (Bacillus cereus, Clostridium perfringens) or in man through direct or indirect contamination (Escherichia c ...
... classical food poisoning are not mentioned or are not investigated at all. In the last 10 years, village weaning foods have been found to contain large numbers of bacteria originating in food (Bacillus cereus, Clostridium perfringens) or in man through direct or indirect contamination (Escherichia c ...
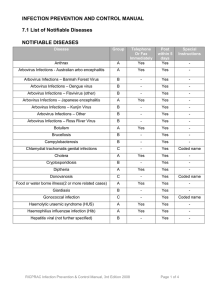
RICPRAC 7. Health (Infectious Diseases) Regulations
... diseases are listed below in Schedule 3 of the Health (Infectious Diseases) Regulations 2001. In Schedule 3 of the proposed regulations, the notifiable infectious diseases have been classified under four groups, on the basis of the method of notification and the information required. ...
... diseases are listed below in Schedule 3 of the Health (Infectious Diseases) Regulations 2001. In Schedule 3 of the proposed regulations, the notifiable infectious diseases have been classified under four groups, on the basis of the method of notification and the information required. ...
CABI_protocol_3_01082016
... Complicated intra-abdominal infection (CABI) is defined as an infection within the abdomen where there is perforation of a viscus or a collection which is believed to be infected. CABI is associated with increased morbidity and mortality (Solomkin 2010). CABI occurs across a range of clinical specia ...
... Complicated intra-abdominal infection (CABI) is defined as an infection within the abdomen where there is perforation of a viscus or a collection which is believed to be infected. CABI is associated with increased morbidity and mortality (Solomkin 2010). CABI occurs across a range of clinical specia ...
If the does not start automatically click here
... lactam antibiotics [15]. Thus, the use of vancomycin for the treatment of catheterinsertions related infections is not justified. One of the strategies to limit the spread of VRE is not to use vancomycin in the treatment of Enterococci-related infections [2]. However, this practice was still found i ...
... lactam antibiotics [15]. Thus, the use of vancomycin for the treatment of catheterinsertions related infections is not justified. One of the strategies to limit the spread of VRE is not to use vancomycin in the treatment of Enterococci-related infections [2]. However, this practice was still found i ...
UK SMI Title goes here
... immunosuppressive treatment). Molecular assays (or pp65 antigenemia) are preferred for diagnosis and monitoring of CMV infection and related disease in this patient type. CMV belongs to the Herpesviridae family and persists in the host as a life-long latent infection. After primary infection, the en ...
... immunosuppressive treatment). Molecular assays (or pp65 antigenemia) are preferred for diagnosis and monitoring of CMV infection and related disease in this patient type. CMV belongs to the Herpesviridae family and persists in the host as a life-long latent infection. After primary infection, the en ...
Report 15/2016
... Finnish Immigration Service were responsible for assessing the risks of infection among immigrants. On several occasions during the year, as the reception of asylum seekers became congested, the Ministry of Social Affairs and Health asked the National Institute for Health and Welfare (THL) for comme ...
... Finnish Immigration Service were responsible for assessing the risks of infection among immigrants. On several occasions during the year, as the reception of asylum seekers became congested, the Ministry of Social Affairs and Health asked the National Institute for Health and Welfare (THL) for comme ...
Lesson 28. Pseudomonas
... Bone and joint infections: Pseudomonas bactreamia may result in infection of bones and joints by direct inocculation. May cause chronic contiguous osteomyelitis from direct inoculation of bone. Pseudomonas also causes osteochondritis after puncture wounds of the foot. ...
... Bone and joint infections: Pseudomonas bactreamia may result in infection of bones and joints by direct inocculation. May cause chronic contiguous osteomyelitis from direct inoculation of bone. Pseudomonas also causes osteochondritis after puncture wounds of the foot. ...
Chapter 2: Natural History of Anogenital Human
... specimens in women who recently cleared HPV as measured by standard molecular techniques. As an alternative, benign hysterectomy specimens from women who have previously cleared HPV infections could be identified and studied intensively. Persistence (i.e., long-duration and detectable HPV infection) ...
... specimens in women who recently cleared HPV as measured by standard molecular techniques. As an alternative, benign hysterectomy specimens from women who have previously cleared HPV infections could be identified and studied intensively. Persistence (i.e., long-duration and detectable HPV infection) ...
Medical therapy of otitis externa and otitis media Daniel O. Morris, DVM
... Ingredients of topical antibacterials Most commercially produced topical products contain one or more active ingredients (antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory) in various combinations as well as a vehicle and various solubilizers, stabilizers, and surfactants [10]. The formulation of the ...
... Ingredients of topical antibacterials Most commercially produced topical products contain one or more active ingredients (antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory) in various combinations as well as a vehicle and various solubilizers, stabilizers, and surfactants [10]. The formulation of the ...
Bacterial and fungal infections
... the sample volume , the time from sampling to incubation , and the use of antibiotics or antifungal therapy can decrease the sensitivity of cultures 10-13. On the other hand, the specificity of cultures can be hampered by the occurrence of false-positives due to contamination 14. The rapid and accur ...
... the sample volume , the time from sampling to incubation , and the use of antibiotics or antifungal therapy can decrease the sensitivity of cultures 10-13. On the other hand, the specificity of cultures can be hampered by the occurrence of false-positives due to contamination 14. The rapid and accur ...
Alexander Fleming - Nobel Lecture
... which are normally found in the respiratory tract in association with large numbers of cocci which are sensitive to penicillin. In those early days also I used penicillin to show up bacterial antagonisms in a dramatic manner and I combined this with the use of a method which I had developed for grow ...
... which are normally found in the respiratory tract in association with large numbers of cocci which are sensitive to penicillin. In those early days also I used penicillin to show up bacterial antagonisms in a dramatic manner and I combined this with the use of a method which I had developed for grow ...
Guide to Infection Control in the Hospital 4th Edition
... term “healthcare associated” infections. Such nosocomial or hospital acquired infections lead to significant morbidity, mortality and economic burden beyond those expected from the patients’ underlying diseases alone. In the Western world the nosocomial infection rate is 5–10% or 5–10 infections per ...
... term “healthcare associated” infections. Such nosocomial or hospital acquired infections lead to significant morbidity, mortality and economic burden beyond those expected from the patients’ underlying diseases alone. In the Western world the nosocomial infection rate is 5–10% or 5–10 infections per ...
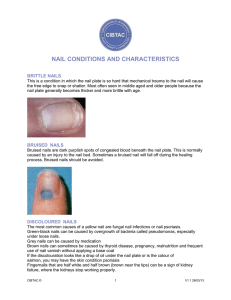
NAIL CONDITIONS AND CHARACTERISTICS BRITTLE NAILS This
... Can affect either the fingers or the toes. In this condition, the nail cuts into one or both sides of the nail bed, resulting in inflammation and possibly infection. The relative rarity of this condition in the fingers suggests that pressure from the ground or shoe against the toe is a prime factor. ...
... Can affect either the fingers or the toes. In this condition, the nail cuts into one or both sides of the nail bed, resulting in inflammation and possibly infection. The relative rarity of this condition in the fingers suggests that pressure from the ground or shoe against the toe is a prime factor. ...
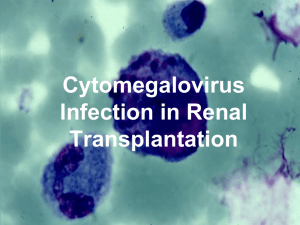
CMV infections
... CMV and SOT • CMV is the most common and single most important viral infection in solid organ transplant recipients. • CMV infection usually develops during the first few months after transplantation • Associated with clinical infectious disease (eg, fever, pneumonia, GI ulcers, hepatitis) and acut ...
... CMV and SOT • CMV is the most common and single most important viral infection in solid organ transplant recipients. • CMV infection usually develops during the first few months after transplantation • Associated with clinical infectious disease (eg, fever, pneumonia, GI ulcers, hepatitis) and acut ...
Bacteria - Calf Scours Treatment
... can be grown in the laboratory.[4] The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology. There are approximately ten times as many bacterial cells in the human flora of bacteria as there are human cells in the body, with large numbers of bacteria on the skin and as gut flora.[5] ...
... can be grown in the laboratory.[4] The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology. There are approximately ten times as many bacterial cells in the human flora of bacteria as there are human cells in the body, with large numbers of bacteria on the skin and as gut flora.[5] ...
Sepsis
... Sepsis • Sepsis: 2 or more– Tachycardia >90bpm – Rectal temp>38°C or <36°C – Tachypnea(>20bpm) • With 1 or more – Alteration in mental status – Hypoxemia (PaO2<72mmHG at FiO20.21) – Elevated plasma lactate – Oligouria ...
... Sepsis • Sepsis: 2 or more– Tachycardia >90bpm – Rectal temp>38°C or <36°C – Tachypnea(>20bpm) • With 1 or more – Alteration in mental status – Hypoxemia (PaO2<72mmHG at FiO20.21) – Elevated plasma lactate – Oligouria ...