Aztec diamond
... over all groves with this projection, then we will find the total probability is equal to the infinite sum of (1/3)^k, k=1 to infinity. What is this sum? ½. ...
... over all groves with this projection, then we will find the total probability is equal to the infinite sum of (1/3)^k, k=1 to infinity. What is this sum? ½. ...
states and empires in ancient mesoamerica
... core of provinces that made regular tribute payments (as listed in documents such as part 2 of the Codex Mendoza [Berdan and Anawalt 1992]); and (2) a group of outer client states that maintained imperial frontiers and provided “gifts,” but not “tribute,” to the capitals. Pedro Carrasco (1999) analy ...
... core of provinces that made regular tribute payments (as listed in documents such as part 2 of the Codex Mendoza [Berdan and Anawalt 1992]); and (2) a group of outer client states that maintained imperial frontiers and provided “gifts,” but not “tribute,” to the capitals. Pedro Carrasco (1999) analy ...
states and empires in ancient mesoamerica
... core of provinces that made regular tribute payments (as listed in documents such as part 2 of the Codex Mendoza [Berdan and Anawalt 1992]); and (2) a group of outer client states that maintained imperial frontiers and provided “gifts,” but not “tribute,” to the capitals. Pedro Carrasco (1999) analy ...
... core of provinces that made regular tribute payments (as listed in documents such as part 2 of the Codex Mendoza [Berdan and Anawalt 1992]); and (2) a group of outer client states that maintained imperial frontiers and provided “gifts,” but not “tribute,” to the capitals. Pedro Carrasco (1999) analy ...
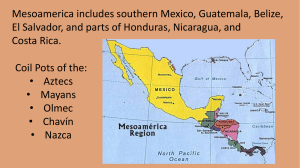
Nazca pottery is known for
... Nazca Culture is known by many, thanks to the colorful ceramics that were found at the many cemeteries located along the banks of the Nazca River. The curiousness of these vessels is that they show in a very realistic way the ancient world of the Nazca men, showing mainly their everyday life, animal ...
... Nazca Culture is known by many, thanks to the colorful ceramics that were found at the many cemeteries located along the banks of the Nazca River. The curiousness of these vessels is that they show in a very realistic way the ancient world of the Nazca men, showing mainly their everyday life, animal ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... Puerto Rico is a ________ of the United States. The Mexican state of ________ was the focus of a recent Indian/peasant uprising. The Aztec language and people today are known as ________. The name Mexico comes from "Mexica," the original name of the ________. Was the country of Mexico called "New Sp ...
... Puerto Rico is a ________ of the United States. The Mexican state of ________ was the focus of a recent Indian/peasant uprising. The Aztec language and people today are known as ________. The name Mexico comes from "Mexica," the original name of the ________. Was the country of Mexico called "New Sp ...
File
... The Maya never formed an empire, but they had many powerful city-states. Tikal and Calakmul were the strongest. ...
... The Maya never formed an empire, but they had many powerful city-states. Tikal and Calakmul were the strongest. ...
The Maya - iMiddle7thgradeWorldHistory
... Severe droughts, deforestation, a decline in large game animals and malnutrition; that began around 800 A.D., coincided with a sharp drop in new construction. By the time the Spanish Conquistadors arrived, most of the Mayan sites had been abandoned for hundreds of years. They were in ruins and were ...
... Severe droughts, deforestation, a decline in large game animals and malnutrition; that began around 800 A.D., coincided with a sharp drop in new construction. By the time the Spanish Conquistadors arrived, most of the Mayan sites had been abandoned for hundreds of years. They were in ruins and were ...
Chapter 15: The Americas
... emerged in the areas of present-day Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, and Belize. Amid volcanic mountains, cool valleys, dense rain forests, and dry forested plains, early farmers developed methods that produced plentiful harvests and supported large populations. Maize was their basic crop. ...
... emerged in the areas of present-day Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, and Belize. Amid volcanic mountains, cool valleys, dense rain forests, and dry forested plains, early farmers developed methods that produced plentiful harvests and supported large populations. Maize was their basic crop. ...
Explain why you think tribute may have been essential to the
... Two continents—North America and South America—make up the region we call the Americas. These two continents have a wide range of landforms and climates. The northern continent, North America, has high mountains, desert plateaus, grassy plains, and forests. Look at the map to find the location of so ...
... Two continents—North America and South America—make up the region we call the Americas. These two continents have a wide range of landforms and climates. The northern continent, North America, has high mountains, desert plateaus, grassy plains, and forests. Look at the map to find the location of so ...
Lesson # 2 - Native Populations & Columbian Exchange
... The neophytes were given morning and evening meals of atole and a mid day meal of pozole. They were allowed to gather wild foods, as was their custom before the Spanish came. On Sundays and special feast days everyone received almost a half peck of wheat. Neophyte men were given a woolen blanket, a ...
... The neophytes were given morning and evening meals of atole and a mid day meal of pozole. They were allowed to gather wild foods, as was their custom before the Spanish came. On Sundays and special feast days everyone received almost a half peck of wheat. Neophyte men were given a woolen blanket, a ...
Spanish conquistador primary sources
... Close to the city there is a wooden bridge ten paces wide across a breach in the causeway to allow the water to flow, as it rises and falls. After we had crossed this bridge, Moctezuma came to greet us and with him some two hundred lords, all barefoot and dressed in a different costume, but also ver ...
... Close to the city there is a wooden bridge ten paces wide across a breach in the causeway to allow the water to flow, as it rises and falls. After we had crossed this bridge, Moctezuma came to greet us and with him some two hundred lords, all barefoot and dressed in a different costume, but also ver ...
aztec human sacrifice
... expelJed gods could not avoid death, through which they descended to the cold place of darkness, where they acquired-like ...
... expelJed gods could not avoid death, through which they descended to the cold place of darkness, where they acquired-like ...
Priests
... plaza. Witnessing the gruesome deaths of not only enemy soldiers but also local slaves, infants, and the occasional free commoner must have made most people think twice before engaging in any form of resistance against their king or local noble. Just as commoners paid tribute in goods and services t ...
... plaza. Witnessing the gruesome deaths of not only enemy soldiers but also local slaves, infants, and the occasional free commoner must have made most people think twice before engaging in any form of resistance against their king or local noble. Just as commoners paid tribute in goods and services t ...
THE MIGRATION TO AMERICA
... This horrified Cortez and he ordered his Spanish troops to attack Montezuma and the Aztecs. Cortez killed over 6000 people in this attack as he marched towards the Aztec capital Tencochitlan. Once Cortez got to Tenochitlan, his troops got surrounded by Aztec warriors. Cortez takes Montezuma hostage ...
... This horrified Cortez and he ordered his Spanish troops to attack Montezuma and the Aztecs. Cortez killed over 6000 people in this attack as he marched towards the Aztec capital Tencochitlan. Once Cortez got to Tenochitlan, his troops got surrounded by Aztec warriors. Cortez takes Montezuma hostage ...
Chapter 11 The Americas on the Eve of Invasion
... They built enormous fortresses on top of steep mountains that enabled them to see their enemies and defend themselves. One of the most famous Inca fortresses is Sacasahuman, located in Cuzco. Even though the Inca never had access to the wheel, they built a sophisticated road system to connect the vi ...
... They built enormous fortresses on top of steep mountains that enabled them to see their enemies and defend themselves. One of the most famous Inca fortresses is Sacasahuman, located in Cuzco. Even though the Inca never had access to the wheel, they built a sophisticated road system to connect the vi ...
The Earliest Americans - Washougal School District
... In time, many of the larger animals began to disappear. Deprived of their main source of food, hunters had to change their ways of life. In many places, hunters became gatherers. They traveled from place to place, searching for wild plants and small game. Some 8,000 years ago, gatherers in Mexico be ...
... In time, many of the larger animals began to disappear. Deprived of their main source of food, hunters had to change their ways of life. In many places, hunters became gatherers. They traveled from place to place, searching for wild plants and small game. Some 8,000 years ago, gatherers in Mexico be ...
Ancient Americans: The Mayas and Aztecs
... languages. The characters were little pictures of common things from the lives of the Indian peoples. Writing was carved into wood and stone. They also wrote in folding books, called "codices," which were often made from the bark of the fig tree. The bark was flattened and coated with a thin layer o ...
... languages. The characters were little pictures of common things from the lives of the Indian peoples. Writing was carved into wood and stone. They also wrote in folding books, called "codices," which were often made from the bark of the fig tree. The bark was flattened and coated with a thin layer o ...
Montezuma II - Social Studies E
... actions, ruling style, and general life. During his reign, the Aztec Empire grew to its maximum size. It is believed that he was very superstitious, and so many of his actions which might make little sense to today’s scholars, were done because of deeply entrenched beliefs and fears. Because his cou ...
... actions, ruling style, and general life. During his reign, the Aztec Empire grew to its maximum size. It is believed that he was very superstitious, and so many of his actions which might make little sense to today’s scholars, were done because of deeply entrenched beliefs and fears. Because his cou ...
Chapter 15 - Aztec and Inca Empires
... The king was the most important person in Aztec society. He lived in a great palace that had gardens, a zoo, and an aviary full of beautiful birds. Some 3,000 servants attended to his every need. Of these servants, 300 did nothing but tend to the animals in the zoo, and 300 more tended to the birds ...
... The king was the most important person in Aztec society. He lived in a great palace that had gardens, a zoo, and an aviary full of beautiful birds. Some 3,000 servants attended to his every need. Of these servants, 300 did nothing but tend to the animals in the zoo, and 300 more tended to the birds ...
ch1 sec1 - sakidsmoody
... In time, many of the larger animals began to disappear. Deprived of their main source of food, hunters had to change their ways of life. In many places, hunters became gatherers. They traveled from place to place, searching for wild plants and small game. Some 8,000 years ago, gatherers in Mexico be ...
... In time, many of the larger animals began to disappear. Deprived of their main source of food, hunters had to change their ways of life. In many places, hunters became gatherers. They traveled from place to place, searching for wild plants and small game. Some 8,000 years ago, gatherers in Mexico be ...
Mesoamerican Civilizations
... Aztecs Grow Stronger: Over the years, the Aztecs gradually increased in strength and number. In 1428, they joined with two other city-states—Texcoco and Tlacopan— to form the Triple Alliance. This alliance became the leading power in the Valley of Mexico and soon gained control over neighboring regi ...
... Aztecs Grow Stronger: Over the years, the Aztecs gradually increased in strength and number. In 1428, they joined with two other city-states—Texcoco and Tlacopan— to form the Triple Alliance. This alliance became the leading power in the Valley of Mexico and soon gained control over neighboring regi ...
Radiometric Dating
... 1. Radiometric dating is the comparison of the % of parent material to the % of ________________ material. 2. (T/F) Rubidium/Strontium would be perfect to date Aztec cook fire sites. 3. This is the time it takes for ½ of a radioactive material to decay to a more stable product. 4. (T/F) Radiocarbon ...
... 1. Radiometric dating is the comparison of the % of parent material to the % of ________________ material. 2. (T/F) Rubidium/Strontium would be perfect to date Aztec cook fire sites. 3. This is the time it takes for ½ of a radioactive material to decay to a more stable product. 4. (T/F) Radiocarbon ...
Lesson Documents
... Hernán Cortés writes to King Charles V of Spain about his march to Tenochtitlán and subsequent takeover of the city. 1. “(The area around Vera Cruz) includes as many as fifty thousand warriors and fifty villages and strongholds, all…loyal subjects of your Majesty…for they became subjects of (Moctezu ...
... Hernán Cortés writes to King Charles V of Spain about his march to Tenochtitlán and subsequent takeover of the city. 1. “(The area around Vera Cruz) includes as many as fifty thousand warriors and fifty villages and strongholds, all…loyal subjects of your Majesty…for they became subjects of (Moctezu ...
Mysteries of the Ancient Indian Tribes of the Americas
... and his sister. The god told them to go establish a city and teach other Indians. Manco Capac and his sister found the city of Cuzco, which became the capital of the Incan empire. http://library.thinkquest.org/C005121/citetemp.html ...
... and his sister. The god told them to go establish a city and teach other Indians. Manco Capac and his sister found the city of Cuzco, which became the capital of the Incan empire. http://library.thinkquest.org/C005121/citetemp.html ...