13-2 Manipulating DNA
... • Transgenic bacteria produce important substances useful for health and industry. ...
... • Transgenic bacteria produce important substances useful for health and industry. ...
Unit 2 summary notes
... o If there is a low concentration of these nutrients, these organisms struggle to grow and survive. amount of light: o Plants require light as an energy source for photosynthesis. o In low light intensities plants grow very slowly. availability of water: o All organisms require water. o It is es ...
... o If there is a low concentration of these nutrients, these organisms struggle to grow and survive. amount of light: o Plants require light as an energy source for photosynthesis. o In low light intensities plants grow very slowly. availability of water: o All organisms require water. o It is es ...
The Biology Staff Handbook
... o If there is a low concentration of these nutrients, these organisms struggle to grow and survive. amount of light: o Plants require light as an energy source for photosynthesis. o In low light intensities plants grow very slowly. availability of water: o All organisms require water. o It is es ...
... o If there is a low concentration of these nutrients, these organisms struggle to grow and survive. amount of light: o Plants require light as an energy source for photosynthesis. o In low light intensities plants grow very slowly. availability of water: o All organisms require water. o It is es ...
File - Westpine Biology EOC
... It may seem obvious to people living in the modern world that disease is caused by germs or pathogens, but germ theory took centuries to be developed and accepted. Germ theory proposes that microorganisms are the cause of many diseases. This theory was highly controversial when it was first proposed ...
... It may seem obvious to people living in the modern world that disease is caused by germs or pathogens, but germ theory took centuries to be developed and accepted. Germ theory proposes that microorganisms are the cause of many diseases. This theory was highly controversial when it was first proposed ...
Hinsdale High School - Hinsdale School District
... I enjoy teaching as much hands on activities and lab experiments as I possibly can. These require that the students follow directions and use the materials provided for what they are intended for. There cannot be ANY horsing around during labs. Students that cannot behave appropriately will be asked ...
... I enjoy teaching as much hands on activities and lab experiments as I possibly can. These require that the students follow directions and use the materials provided for what they are intended for. There cannot be ANY horsing around during labs. Students that cannot behave appropriately will be asked ...
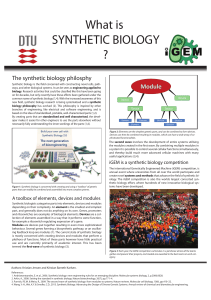
What is SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY
... Synthetic biology is the field concerned with constructing novel cells, pathways, and other biological systems. It can be seen as engineering applied to biology. Research activities that could be classified like this have been going on for decades, but only recently have these efforts been gathered ...
... Synthetic biology is the field concerned with constructing novel cells, pathways, and other biological systems. It can be seen as engineering applied to biology. Research activities that could be classified like this have been going on for decades, but only recently have these efforts been gathered ...
File
... acid, acid (carboxyl) group, adenine, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), alpha helix, amine group, amino acid, base, beta pleated sheet, bonding, buffer, carbohydrate, cellulose, complementary base pairing, cytosine, dehydration synthesis, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), deoxyribose, dipeptide, disaccharide ...
... acid, acid (carboxyl) group, adenine, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), alpha helix, amine group, amino acid, base, beta pleated sheet, bonding, buffer, carbohydrate, cellulose, complementary base pairing, cytosine, dehydration synthesis, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), deoxyribose, dipeptide, disaccharide ...
Chemistry in Biology
... The number and the order in which the amino acids are joined define the protein’s primary structure. After an amino acid chain is formed, it folds into a unique three-dimensional shape. Enzymes are proteins and when conditions are unfavorable to the enzyme they change shape. ...
... The number and the order in which the amino acids are joined define the protein’s primary structure. After an amino acid chain is formed, it folds into a unique three-dimensional shape. Enzymes are proteins and when conditions are unfavorable to the enzyme they change shape. ...
... disulfide bond and glycosylation, which simplifies processing of the downstream of gene engineering and assures bioactivity and quality of the protein products. • D.salina is, because of being nontoxic and abundant in natural vitamins and polyunsaturated fatty acids, valuable edible alga. Oral vacci ...
Sickle Cell Workshop
... In HbA HbS individuals, half their hemoglobin will sickle when the oxygen tension becomes very low. These sickled cells are removed from the body by the spleen, along with the merozoites inside of them. Thus, heterozygotes remove the infected cells from their body before the protozoans can produce a ...
... In HbA HbS individuals, half their hemoglobin will sickle when the oxygen tension becomes very low. These sickled cells are removed from the body by the spleen, along with the merozoites inside of them. Thus, heterozygotes remove the infected cells from their body before the protozoans can produce a ...
A) How Chewing Helps Digestion?
... There are three mechanisms involved in stimulating the flow of gastric juice: 1. The _______________, or _____ of food stimulates the ____ to send messages via nerve impulses to the __________________. 2. Food ___________ the ___________ of the stomach. 3. Secretion of the hormone _______ caused by ...
... There are three mechanisms involved in stimulating the flow of gastric juice: 1. The _______________, or _____ of food stimulates the ____ to send messages via nerve impulses to the __________________. 2. Food ___________ the ___________ of the stomach. 3. Secretion of the hormone _______ caused by ...
The Biology Staff Handbook - St. Mary`s Independent School
... AQA GCSE Biology – Unit 2 summary notes ...
... AQA GCSE Biology – Unit 2 summary notes ...
Anaerobic respiration - Pukekohe High School
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. This simply means that they are substances that speed up the rate of reaction that occur in the cells of living organisms. Without enzymes these reactions would occur so slowly that the cell could not survive. Hundred of chemical reactions can occur in a single livi ...
... Enzymes are biological catalysts. This simply means that they are substances that speed up the rate of reaction that occur in the cells of living organisms. Without enzymes these reactions would occur so slowly that the cell could not survive. Hundred of chemical reactions can occur in a single livi ...
Ch. 7 Nutrition
... Carbohydrates Carbohydrates • Structure and function: Carbohydrates are sugars and starches that the body uses for ENERGY! • PLANTS are the major source of carbohydrates in the food we eat. • Source of Fiber Simple Carbohydrates • Sugars that are quickly digested and provide a BOOST of energy for t ...
... Carbohydrates Carbohydrates • Structure and function: Carbohydrates are sugars and starches that the body uses for ENERGY! • PLANTS are the major source of carbohydrates in the food we eat. • Source of Fiber Simple Carbohydrates • Sugars that are quickly digested and provide a BOOST of energy for t ...
File
... 53. What is the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion, and what are some examples of each? 54. Describe the structure of the villi in the small intestines. Explain the function of the villi. 55. Be able to compare intracellular vs. extracellular digestion. UNIT 2: THE DYNAMIC CELL (Ch ...
... 53. What is the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion, and what are some examples of each? 54. Describe the structure of the villi in the small intestines. Explain the function of the villi. 55. Be able to compare intracellular vs. extracellular digestion. UNIT 2: THE DYNAMIC CELL (Ch ...
Nutrients WS
... Proteins contain (a) carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (b) carbon dioxide, oxygen, sulfur (c) carbon, calcium, oxygen, fluorine (d) chlorine, sulfur, hydrogen, oxygen. Most proteins also contain (a) fluorine (b) iron (c) calcium (d) sulfur. Some proteins also contain (a) potassium (b) phosphorus (c ...
... Proteins contain (a) carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (b) carbon dioxide, oxygen, sulfur (c) carbon, calcium, oxygen, fluorine (d) chlorine, sulfur, hydrogen, oxygen. Most proteins also contain (a) fluorine (b) iron (c) calcium (d) sulfur. Some proteins also contain (a) potassium (b) phosphorus (c ...
01st lecture
... (Gels: some macromolecules in solutions – like proteins or carbohydrates – form a crosslinked structure holding the liquid in form. This shows a quasi-solid properties – like jelly or jam.) ...
... (Gels: some macromolecules in solutions – like proteins or carbohydrates – form a crosslinked structure holding the liquid in form. This shows a quasi-solid properties – like jelly or jam.) ...
Human Body Poetry Booklet
... With teeth for mechanical munching, And enzymes for chemical cutting, Peristalsis keeps squeezing the food along Which mechanically mushes it too! I know a change in surface area From the biting and slicing of food; Pieces getting smaller and smaller, While the surface area grows. ...
... With teeth for mechanical munching, And enzymes for chemical cutting, Peristalsis keeps squeezing the food along Which mechanically mushes it too! I know a change in surface area From the biting and slicing of food; Pieces getting smaller and smaller, While the surface area grows. ...
Presentation
... Carbohydrates Complex Carbohydrates • Starches that are composed of many sugars linked together • They provide the body with long-term energy since they are digested more slowly than sugars. • Foods with LOTS of starch: rice, beans, potatoes © 2005 JupiterImages Corporation ...
... Carbohydrates Complex Carbohydrates • Starches that are composed of many sugars linked together • They provide the body with long-term energy since they are digested more slowly than sugars. • Foods with LOTS of starch: rice, beans, potatoes © 2005 JupiterImages Corporation ...
Document
... Carbohydrates Complex Carbohydrates • Starches that are composed of many sugars linked together • They provide the body with long-term energy since they are digested more slowly than sugars. • Foods with LOTS of starch: rice, beans, potatoes © 2005 JupiterImages Corporation ...
... Carbohydrates Complex Carbohydrates • Starches that are composed of many sugars linked together • They provide the body with long-term energy since they are digested more slowly than sugars. • Foods with LOTS of starch: rice, beans, potatoes © 2005 JupiterImages Corporation ...
M.Sc. (Prev.) ZOOLOGY Exam. –2014 Distribution of Marks Paper
... Section-B : 10 questions, 2 questions from each unit, 5 questions to be attempted, taking one from each unit, answer approximately in 250 words. Total marks : 50 Section-C : 04 questions (question may have sub division) covering all units but not more than one question from each unit, descriptive ty ...
... Section-B : 10 questions, 2 questions from each unit, 5 questions to be attempted, taking one from each unit, answer approximately in 250 words. Total marks : 50 Section-C : 04 questions (question may have sub division) covering all units but not more than one question from each unit, descriptive ty ...
AP Biology
... energies EA, EB, EC, ED, respectively. The distance marked "Z" represents (A) The activation energy for A(g) + B(g) * C(g) + D(g) (B) The heat of reaction energy for A(g) + B(g) * C(g) + D(g) (C) The activation energy for C(g) + D(g) * A(g) + B(g) (D) The heat of reaction for C(g) + D(g) * A(g) + B( ...
... energies EA, EB, EC, ED, respectively. The distance marked "Z" represents (A) The activation energy for A(g) + B(g) * C(g) + D(g) (B) The heat of reaction energy for A(g) + B(g) * C(g) + D(g) (C) The activation energy for C(g) + D(g) * A(g) + B(g) (D) The heat of reaction for C(g) + D(g) * A(g) + B( ...
Protocol Application
... Experiments using restricted agents (See Select Agents Registry) or microorganism(s) classified as risk group 2, 3, or 4 as host-vector systems (see Appendix B) OR experiments in which DNA from risk group 2, 3, 4, or restricted agents is cloned into nonpathogenic prokaryotic or lower eukaryotic ho ...
... Experiments using restricted agents (See Select Agents Registry) or microorganism(s) classified as risk group 2, 3, or 4 as host-vector systems (see Appendix B) OR experiments in which DNA from risk group 2, 3, 4, or restricted agents is cloned into nonpathogenic prokaryotic or lower eukaryotic ho ...
Bio 105 Env
... whether plants or animals use the following polysaccharides and 2) what each polysaccharide is used for (function) by the plant or animal. Also state which polysaccharide is the most abundant on earth. 1. Starch ...
... whether plants or animals use the following polysaccharides and 2) what each polysaccharide is used for (function) by the plant or animal. Also state which polysaccharide is the most abundant on earth. 1. Starch ...
17_Learning_Objectives
... initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Describe the functional and evolutionary significance of introns. 18. Explain why, due to alternative RNA splicing, the number of different protein products an organism can produce i ...
... initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Describe the functional and evolutionary significance of introns. 18. Explain why, due to alternative RNA splicing, the number of different protein products an organism can produce i ...