M392 Lecture April 6th
... However, other systems behave differently The system below has NO SOLUTIONS. The equations contradict each other! 2x + 3y = 5 -------> times 2------>4x + 6y = 10 …….10 doesn’t equal 7!! 4x + 6y = 7------------------------->4x + 6y = 7 The system below has MANY SOLUTIONS. The equations repeat each ot ...
... However, other systems behave differently The system below has NO SOLUTIONS. The equations contradict each other! 2x + 3y = 5 -------> times 2------>4x + 6y = 10 …….10 doesn’t equal 7!! 4x + 6y = 7------------------------->4x + 6y = 7 The system below has MANY SOLUTIONS. The equations repeat each ot ...
NJDOE MODEL CURRICULUM PROJECT CONTENT AREA
... Solve systems of linear equations in two variables graphically and algebraically. Include solutions that have been found by replacing one equation by the sum of that equation and a multiple of the other. Find approximate solutions of linear equations by making a table of values, using technology to ...
... Solve systems of linear equations in two variables graphically and algebraically. Include solutions that have been found by replacing one equation by the sum of that equation and a multiple of the other. Find approximate solutions of linear equations by making a table of values, using technology to ...
21. Frequency Response
... Lecture 21. Frequency Response • Frequency Response • Frequency Response of R, L and C • Resonance circuit • Examples ...
... Lecture 21. Frequency Response • Frequency Response • Frequency Response of R, L and C • Resonance circuit • Examples ...
Algebra II Level 2 Curriculum
... equation. Students can visualize the solutions of quadratic equations through graphing (e.g., min, max, transformations, complex roots). Completing the squares is used as an introduction to the equation of circles to further understanding of transformations. Students will demonstrate their efficienc ...
... equation. Students can visualize the solutions of quadratic equations through graphing (e.g., min, max, transformations, complex roots). Completing the squares is used as an introduction to the equation of circles to further understanding of transformations. Students will demonstrate their efficienc ...
Chapter 1
... We write the variables on one side of the equation and the constants on the other. In the matrix separate the variables from the constants with a line (sometimes dashed). The entries of the matrix are the coefficients of the variables. It is important that if a variable does not show up in an equati ...
... We write the variables on one side of the equation and the constants on the other. In the matrix separate the variables from the constants with a line (sometimes dashed). The entries of the matrix are the coefficients of the variables. It is important that if a variable does not show up in an equati ...
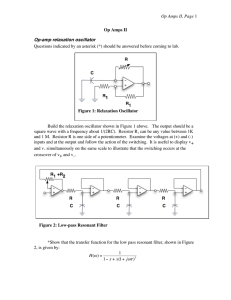
Op Amps II, Page
... When you understand the equation for the transfer function, build the circuit. It is convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit nearly oscillates. See how close you can get. Notice how oscillations ...
... When you understand the equation for the transfer function, build the circuit. It is convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit nearly oscillates. See how close you can get. Notice how oscillations ...
HERE
... This situation addresses several key concepts that occur frequently in school mathematics: opposites, negative numbers, domains and ranges of functions. These concepts are represented symbolically, graphically and numerically. Mathematical focus 1 contrasts the terms “opposite” and “negative” and hi ...
... This situation addresses several key concepts that occur frequently in school mathematics: opposites, negative numbers, domains and ranges of functions. These concepts are represented symbolically, graphically and numerically. Mathematical focus 1 contrasts the terms “opposite” and “negative” and hi ...
Revised Version 070427
... This situation addresses several key concepts that occur frequently in school mathematics: opposites, negative numbers, domains and ranges of functions. These concepts are represented symbolically, graphically and numerically. Mathematical focus 1 contrasts the terms “opposite” and “negative” and hi ...
... This situation addresses several key concepts that occur frequently in school mathematics: opposites, negative numbers, domains and ranges of functions. These concepts are represented symbolically, graphically and numerically. Mathematical focus 1 contrasts the terms “opposite” and “negative” and hi ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.