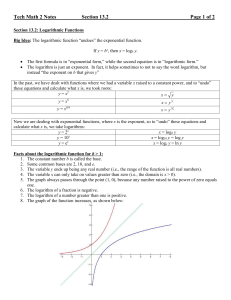
Lecture notes for Section 13.2
... 1. The constant number b is called the base. 2. Some common bases are 2, 10, and e. 3. The variable y ends up being any real number (i.e., the range of the function is all real numbers). 4. The variable x can only take on values greater than zero (i.e., the domain is x > 0). 5. The graph always pass ...
... 1. The constant number b is called the base. 2. Some common bases are 2, 10, and e. 3. The variable y ends up being any real number (i.e., the range of the function is all real numbers). 4. The variable x can only take on values greater than zero (i.e., the domain is x > 0). 5. The graph always pass ...
CLASSWORK REVIEW WARM-UP TODAY’S OBJECTIVE
... 1. Is the point (0,3) a solution for this system of inequalities? ...
... 1. Is the point (0,3) a solution for this system of inequalities? ...
CHAPTE 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction I have performed
... Frequency Modulation (FM) is the method of varying a carrier wave's frequency proportionally to the frequency of another signal, in our case the human voice. This compares to the other most common transmission method, Amplitude Modulation (AM). AM broadcasts vary the amplitude of the carrier wave ac ...
... Frequency Modulation (FM) is the method of varying a carrier wave's frequency proportionally to the frequency of another signal, in our case the human voice. This compares to the other most common transmission method, Amplitude Modulation (AM). AM broadcasts vary the amplitude of the carrier wave ac ...
Wireless Media
... Wireless Propagation: Line-Of-Sight (LOS) LOS propagation is found in frequencies above 30MHz the transmitting and receiving antennas must be within a line of sight of each other ...
... Wireless Propagation: Line-Of-Sight (LOS) LOS propagation is found in frequencies above 30MHz the transmitting and receiving antennas must be within a line of sight of each other ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.