Student Activity DOC
... i 1. That is, it constructs a sequence of the form i, i 2 , i 3 ,, i end . The variable end is the largest value the sequence variable will assume, in this case the last power of i. . a. Change the value of the variable end as necessary to complete the following tables. Note: the variable end is ...
... i 1. That is, it constructs a sequence of the form i, i 2 , i 3 ,, i end . The variable end is the largest value the sequence variable will assume, in this case the last power of i. . a. Change the value of the variable end as necessary to complete the following tables. Note: the variable end is ...
PHYS219 Fall semester 2014 - Purdue Physics
... equations will be provided) • All cell phones/smart phones are to be deactivated ...
... equations will be provided) • All cell phones/smart phones are to be deactivated ...
1 INTRODUCTION
... 4.5.7 Digital Sinusoidal Oscilatators. 4.6 Inverse Systems and Deconvolution 4.6.1 Invertibility of Linear Time-Invariant systems. 4.6.2 Minimum-Phase. Maximum-Phase, and Mixed-Phase Systems. 4.6.3 System Identification and Deconvolution, 4.6.4 Homomorphic Deconvolution. 5 THE DISCRETE FOURIER TRANS ...
... 4.5.7 Digital Sinusoidal Oscilatators. 4.6 Inverse Systems and Deconvolution 4.6.1 Invertibility of Linear Time-Invariant systems. 4.6.2 Minimum-Phase. Maximum-Phase, and Mixed-Phase Systems. 4.6.3 System Identification and Deconvolution, 4.6.4 Homomorphic Deconvolution. 5 THE DISCRETE FOURIER TRANS ...
Graphs of Functions Instructions (Word Format)
... How are the graphs similar and how are they different? What general statement can be made for the graph of y = kx, for any whole number k? 2. What happens if the value of k in y = kx is a fraction? Graph the following equations and make a generalization about what happens as the fractions decrease. ...
... How are the graphs similar and how are they different? What general statement can be made for the graph of y = kx, for any whole number k? 2. What happens if the value of k in y = kx is a fraction? Graph the following equations and make a generalization about what happens as the fractions decrease. ...
0091_hsm11a1_te_01tr.indd
... Write an algebraic expression for each phrase. 1. a number p minus 19 2. 12 more than 5 times c 3. 1 less than the quotient of a number n and 6 4. 9 times the sum of a number t and 3 5. 12 times the quantity 15 minus a number d ...
... Write an algebraic expression for each phrase. 1. a number p minus 19 2. 12 more than 5 times c 3. 1 less than the quotient of a number n and 6 4. 9 times the sum of a number t and 3 5. 12 times the quantity 15 minus a number d ...
Coach Stalder
... Learning these guidelines has been directly linked to greater Algebra success!! ...
... Learning these guidelines has been directly linked to greater Algebra success!! ...
Name:
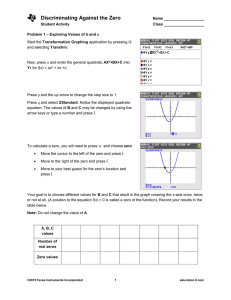
... Explain how the discriminant of a quadratic equation can be used to determine the nature of the solutions of a quadratic equation. ...
... Explain how the discriminant of a quadratic equation can be used to determine the nature of the solutions of a quadratic equation. ...
Document
... • Analytic geometry, usually called coordinate geometry or analytical geometry, is the study of geometry using the principles of algebra • The link between algebra and geometry was made possible by the development of a coordinate system which allowed geometric ideas, such as point and line, to be de ...
... • Analytic geometry, usually called coordinate geometry or analytical geometry, is the study of geometry using the principles of algebra • The link between algebra and geometry was made possible by the development of a coordinate system which allowed geometric ideas, such as point and line, to be de ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.