Full text
... where hn - hn_1 = 5n - 4«, Heptagonal numbers are represented geometrically by regular heptagons homothetic with respect to one of the vertices and containing 2, 3, 4, ..., n points at equal distances along each side. The sum of all the points for a given n yields hn. Both Dickson [3] and LeVeque [4 ...
... where hn - hn_1 = 5n - 4«, Heptagonal numbers are represented geometrically by regular heptagons homothetic with respect to one of the vertices and containing 2, 3, 4, ..., n points at equal distances along each side. The sum of all the points for a given n yields hn. Both Dickson [3] and LeVeque [4 ...
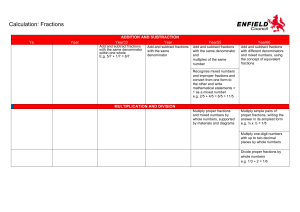
Example
... Simplifying Rational Expressions and Stating Domain Restrictions Investigate and explain characteristics of rational functions including domain, range, zeros, points of discontinuity, intervals of increase and decrease, rates of change, local and absolute extrema, symmetry, asymptotes, and end behav ...
... Simplifying Rational Expressions and Stating Domain Restrictions Investigate and explain characteristics of rational functions including domain, range, zeros, points of discontinuity, intervals of increase and decrease, rates of change, local and absolute extrema, symmetry, asymptotes, and end behav ...
Ch.5, Section 3
... relationship between input values (domain, “x”) and output values (range, “f (x)”) in such a way that exactly one output or range value is assigned to each number in the domain. We’ve seen that functions pass the Vertical Line Test. It turns out that a polynomial function is a function whose equatio ...
... relationship between input values (domain, “x”) and output values (range, “f (x)”) in such a way that exactly one output or range value is assigned to each number in the domain. We’ve seen that functions pass the Vertical Line Test. It turns out that a polynomial function is a function whose equatio ...
Math 142 Group Projects
... 1. Define the complex number i. 2. Explain Euler’s formula and show how it can be derived using the Maclaurin series for sine, cosine, and ex . 3. Show that Euler’s formula immediately implies Euler’s identity eiπ + 1 = 0 which relates the five most important numbers in all of mathematics. 4. Introd ...
... 1. Define the complex number i. 2. Explain Euler’s formula and show how it can be derived using the Maclaurin series for sine, cosine, and ex . 3. Show that Euler’s formula immediately implies Euler’s identity eiπ + 1 = 0 which relates the five most important numbers in all of mathematics. 4. Introd ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.