2-1 - SPX.org
... Adding zero to any number will not change the value of that number. a+0=a * The additive identity is zero. Additive Inverse Property (Add Inv. Prop.) Adding a number to its inverse will result in zero. a + (–a) = 0 * If two numbers are opposites, they are additive inverses of each other. Simplify. S ...
... Adding zero to any number will not change the value of that number. a+0=a * The additive identity is zero. Additive Inverse Property (Add Inv. Prop.) Adding a number to its inverse will result in zero. a + (–a) = 0 * If two numbers are opposites, they are additive inverses of each other. Simplify. S ...
the review sheet for the final exam
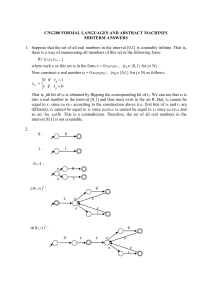
... Section 2.1: What is a Function? 1. Definitions: A function f is a rule that assigns to each element x in a set A exactly one element f(x), in a set B. The set A is the domain of the function. f(x) is the image of x under f. The range is the set of all possible values of f(x) as x varies through the ...
... Section 2.1: What is a Function? 1. Definitions: A function f is a rule that assigns to each element x in a set A exactly one element f(x), in a set B. The set A is the domain of the function. f(x) is the image of x under f. The range is the set of all possible values of f(x) as x varies through the ...
Document
... If d|b, we use the following strategy to find solutions: 1. Reduce the equation by dividing both sides by d. 2. Multiply both sides of the reduced equation by multiplicative inverse of a (including the modulus) to find the particular solution x0. 3. The general solutions are x = x0 + k(n/d) ...
... If d|b, we use the following strategy to find solutions: 1. Reduce the equation by dividing both sides by d. 2. Multiply both sides of the reduced equation by multiplicative inverse of a (including the modulus) to find the particular solution x0. 3. The general solutions are x = x0 + k(n/d) ...
ON THE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION OF THE ∗
... random linear functional defined over the solutions and apply this theory for our original problem concerning random linear programs. Our approximation formulas for the characteristics of μ, especially for the dispersion, will be particularly simple, as simple as possible in this general formulation ...
... random linear functional defined over the solutions and apply this theory for our original problem concerning random linear programs. Our approximation formulas for the characteristics of μ, especially for the dispersion, will be particularly simple, as simple as possible in this general formulation ...
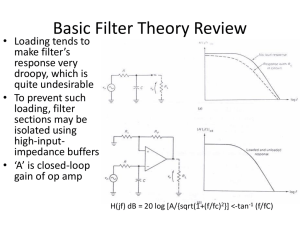
Equivalent Circuit Description 8.2.2 Small Signal Response of p-n Junctions
... Dimensions in real (Si) devices, especially integrated circuits, are much, much smaller than the diffusion length L. For the excess minority carrier distribution as shown for a large diode, this has profound consequences. The excess concentration must go down to zero at the contact, i.e. after a dis ...
... Dimensions in real (Si) devices, especially integrated circuits, are much, much smaller than the diffusion length L. For the excess minority carrier distribution as shown for a large diode, this has profound consequences. The excess concentration must go down to zero at the contact, i.e. after a dis ...
AP Physics C
... AC Circuits and Impedance 25. Voltage across the terminals of an ac power supply varies with time according the following: V = 45 cos(πt). What is the rms voltage? 26. An ac current varies with time according the following: I = 2 cos(2πt). What is the rms current? 27. A 5000 Ω resistor is connected ...
... AC Circuits and Impedance 25. Voltage across the terminals of an ac power supply varies with time according the following: V = 45 cos(πt). What is the rms voltage? 26. An ac current varies with time according the following: I = 2 cos(2πt). What is the rms current? 27. A 5000 Ω resistor is connected ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.