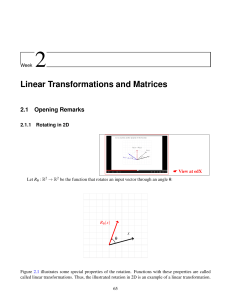
Document
... • When comparing different forms of rational and irrational numbers, convert the numbers to the same ...
... • When comparing different forms of rational and irrational numbers, convert the numbers to the same ...
Algebra I - Denise Kapler
... reflective, symmetric and transitive 2. Equality: Substitution 3. Property of Distribution 4. Simplify (Arithmetic) ...
... reflective, symmetric and transitive 2. Equality: Substitution 3. Property of Distribution 4. Simplify (Arithmetic) ...
File
... 2. Construct medians AD, BE, and CF of triangle ABC and have their intersection be G. Let the midpoint of AG be X, the midpoint of EG be Y, and the midpoint of FG be Z. If the area of XYZ is 1, what is the area of ABC? 3. There are six blank fish drawn in a line on a piece of paper. Lucy wants to co ...
... 2. Construct medians AD, BE, and CF of triangle ABC and have their intersection be G. Let the midpoint of AG be X, the midpoint of EG be Y, and the midpoint of FG be Z. If the area of XYZ is 1, what is the area of ABC? 3. There are six blank fish drawn in a line on a piece of paper. Lucy wants to co ...
Full text
... Define Al = sl-sQ. Let r^ be the least n such that sn-sn_l & Al5 and let A2 = sni -sni-h Continue inductively, so that nh is, for each h > 2, the least n such that sn - sn_l is not among the numbers Al3 A 2 ,..., Ah_t, and A^ = snh -snh-h It will be helpful to provide single Indexing for the doubly- ...
... Define Al = sl-sQ. Let r^ be the least n such that sn-sn_l & Al5 and let A2 = sni -sni-h Continue inductively, so that nh is, for each h > 2, the least n such that sn - sn_l is not among the numbers Al3 A 2 ,..., Ah_t, and A^ = snh -snh-h It will be helpful to provide single Indexing for the doubly- ...
Revised Version 080113
... If n is odd, then n + 1 is even and therefore divisible by 2. Hence natural number. If n is even, then it is divisible by 2. And hence natural number. ...
... If n is odd, then n + 1 is even and therefore divisible by 2. Hence natural number. If n is even, then it is divisible by 2. And hence natural number. ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.