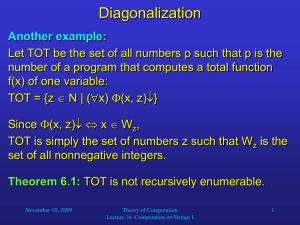
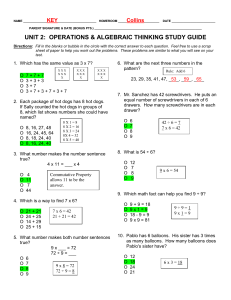
MATH 0301 - The University of Texas at El Paso
... The expression 3 8 is called a radical expression, where 3 is called the index, is the radical sign, and 8 is called the radicand. The index of a radical expression must always be a positive integer greater than 1. When no index is written it is assumed to be 2, or a square root; as noted in example ...
... The expression 3 8 is called a radical expression, where 3 is called the index, is the radical sign, and 8 is called the radicand. The index of a radical expression must always be a positive integer greater than 1. When no index is written it is assumed to be 2, or a square root; as noted in example ...
Finding Reference Angles
... Trigonometric Functions of Real Numbers So, it follows that sin and sin are equal, except possibly in sign. The same is true for tan and tan and for the other four trigonometric functions. In all cases, the sign of the function value can be determined by the quadrant in which lies. ...
... Trigonometric Functions of Real Numbers So, it follows that sin and sin are equal, except possibly in sign. The same is true for tan and tan and for the other four trigonometric functions. In all cases, the sign of the function value can be determined by the quadrant in which lies. ...
ALGEBRA I Lesson 9-3
... Trinomial: A polynomial with three parts (the sum of three monomials) “FOIL”: First, Outside, Inside, and Last (to multiply two binomials) Now: We will learn to factor, then solve trinomials with a leading coefficient of “1” attached to x 2 term TERM: Factor Pair: Two numbers multiplied together to ...
... Trinomial: A polynomial with three parts (the sum of three monomials) “FOIL”: First, Outside, Inside, and Last (to multiply two binomials) Now: We will learn to factor, then solve trinomials with a leading coefficient of “1” attached to x 2 term TERM: Factor Pair: Two numbers multiplied together to ...
Multiplying and dividing algebraic fractions
... Algebraic Fractions – Core 3, Chapter 1 Session 1 LO: ...
... Algebraic Fractions – Core 3, Chapter 1 Session 1 LO: ...
NRF 10 - 3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers Where does
... Method 2: Finding the GCF using the prime factorizations of each numbers Step 1 : Break each number into the product of its primes (prime factorization) 76 = 2 x 38 = 2 x 2 x 19 148 = 2 x 74 = 2 x 2 x 37 Step 2 : Multiply the common factors of each prime factorization list Since both have two 2’s in ...
... Method 2: Finding the GCF using the prime factorizations of each numbers Step 1 : Break each number into the product of its primes (prime factorization) 76 = 2 x 38 = 2 x 2 x 19 148 = 2 x 74 = 2 x 2 x 37 Step 2 : Multiply the common factors of each prime factorization list Since both have two 2’s in ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.