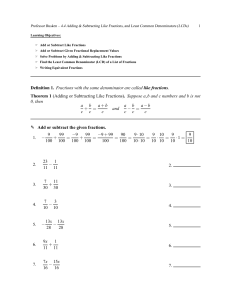
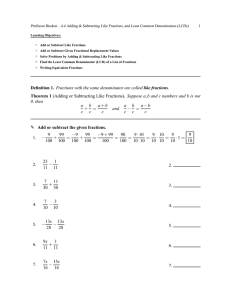
Full text
... A bi-unitary aliquot sequence is said to be periodic if there is an index k such that (nk; nk+1; ... ; n k + t - 1 ) is a bi-unitary t-cycle. A bi-unitary aliquot sequence which is neither terminating nor periodic is (obviously) unbounded. Whether or not unbounded bi-unitary aliquot sequences exist ...
... A bi-unitary aliquot sequence is said to be periodic if there is an index k such that (nk; nk+1; ... ; n k + t - 1 ) is a bi-unitary t-cycle. A bi-unitary aliquot sequence which is neither terminating nor periodic is (obviously) unbounded. Whether or not unbounded bi-unitary aliquot sequences exist ...
1stSamplePacingGuide..
... to the quantities they represent. N.ME.01.03 Order numbers to 110; compare using the phrases: same as, more than, greater than, fewer than; use = symbol. Arrange small sets of numbers in increasing order, e.g., write the following from smallest to largest: 21, 16, 35, 8. N.ME.01.06 Count backward by ...
... to the quantities they represent. N.ME.01.03 Order numbers to 110; compare using the phrases: same as, more than, greater than, fewer than; use = symbol. Arrange small sets of numbers in increasing order, e.g., write the following from smallest to largest: 21, 16, 35, 8. N.ME.01.06 Count backward by ...
A6 Quadratic equations
... Jenny drives 24 miles to get to work. On the way home she is caught in traffic and drives 20 miles per hour more slowly than on the way there. If her total journey time to work and back is 1 hour, what was her average speed on the way to work? ...
... Jenny drives 24 miles to get to work. On the way home she is caught in traffic and drives 20 miles per hour more slowly than on the way there. If her total journey time to work and back is 1 hour, what was her average speed on the way to work? ...
AS/A Level Physics Presentation
... more important than others. They represent the number of digits in a number, starting with the fist non zero number and ending with any other number or trailing zero’s They usually represent the accuracy and precision of a number. ...
... more important than others. They represent the number of digits in a number, starting with the fist non zero number and ending with any other number or trailing zero’s They usually represent the accuracy and precision of a number. ...
8.2.3 Arithmetic Coding (cont.)
... between 0 and 1. As the number of symbols in the message increases, the interval used to represent it becomes smaller and the number of information units (say, bits) required to represent the interval becomes larger. Each symbol of the message reduces the size of the interval in accordance with the ...
... between 0 and 1. As the number of symbols in the message increases, the interval used to represent it becomes smaller and the number of information units (say, bits) required to represent the interval becomes larger. Each symbol of the message reduces the size of the interval in accordance with the ...
Full text
... where p F (0) = 1 in accordance with the power series (1). This yields a recursion for p (n) with all coefficients ak equal to 1, -1, or 0. ...
... where p F (0) = 1 in accordance with the power series (1). This yields a recursion for p (n) with all coefficients ak equal to 1, -1, or 0. ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.