Intermediate Algebra, 5ed
... Simplifying Complex Fractions Simplifying a Complex Fraction (Method 1) 1) Simplify the numerator and the denominator of the complex fraction so that each is a single fraction. 2) Perform the indicated division by multiplying the numerator of the complex fraction by the reciprocal of the denominato ...
... Simplifying Complex Fractions Simplifying a Complex Fraction (Method 1) 1) Simplify the numerator and the denominator of the complex fraction so that each is a single fraction. 2) Perform the indicated division by multiplying the numerator of the complex fraction by the reciprocal of the denominato ...
TUNED LNA FOR RFICs - Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell
... developed prototype chip fabricated in a 20 GHz cut-off frequency bipolar process. The measured center frequency of the amplifier is tunable between 0.96-1.026 GHz with a transducer power gain greater than 27 dB and a quality factor (Q) greater than 15. Based on the same boot-strapped inductor and o ...
... developed prototype chip fabricated in a 20 GHz cut-off frequency bipolar process. The measured center frequency of the amplifier is tunable between 0.96-1.026 GHz with a transducer power gain greater than 27 dB and a quality factor (Q) greater than 15. Based on the same boot-strapped inductor and o ...
y6 block e plan - School
... division facts involving decimals (e.g. 0.8 7, 4.8 6) Use efficient written methods to add and subtract integers and decimals, to multiply and divide integers and decimals by a onedigit integer, and to multiply twodigit and three-digit integers by a two-digit integer Express one quantity as a pe ...
... division facts involving decimals (e.g. 0.8 7, 4.8 6) Use efficient written methods to add and subtract integers and decimals, to multiply and divide integers and decimals by a onedigit integer, and to multiply twodigit and three-digit integers by a two-digit integer Express one quantity as a pe ...
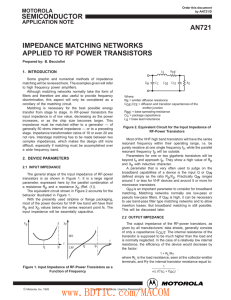
IMPEDANCE MATCHING NETWORKS APPLIED TO RF POWER TRANSISTORS 1. INTRODUCTION
... Figure 10. Z-Plane Representation of the Circuit of Figure 9(a) Exact transformation from R1 into R2 occurs at the points of intersection M and N. Impedances are then conjugate or Z′ = R′ + jX′ and Z″ = R″ + jX″ with R′ = R″ and X′ = – X″. The only possible solution is obtained when X′ and – X″ are ...
... Figure 10. Z-Plane Representation of the Circuit of Figure 9(a) Exact transformation from R1 into R2 occurs at the points of intersection M and N. Impedances are then conjugate or Z′ = R′ + jX′ and Z″ = R″ + jX″ with R′ = R″ and X′ = – X″. The only possible solution is obtained when X′ and – X″ are ...
Number Operations and Integers
... KEY: addition, multiplication, properties, whole numbers NOT: /A/Correct! /B/Look at the ones digits. Do any of these digits multiplied together produce a product that is a multiple of 10? /C/Look at the ones digits. Do any of these digits multiplied together produce a product that is a multiple of ...
... KEY: addition, multiplication, properties, whole numbers NOT: /A/Correct! /B/Look at the ones digits. Do any of these digits multiplied together produce a product that is a multiple of 10? /C/Look at the ones digits. Do any of these digits multiplied together produce a product that is a multiple of ...
PDF
... transmission and distribution of electric systems as well as nonlinear loads such as electric drives, arc furnace, all kind of lighting devices produce harmonics in the power networks and an accurate model of power system components is essential. Modeling of electric loads in the presence of harmoni ...
... transmission and distribution of electric systems as well as nonlinear loads such as electric drives, arc furnace, all kind of lighting devices produce harmonics in the power networks and an accurate model of power system components is essential. Modeling of electric loads in the presence of harmoni ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.