Word - University of Georgia
... The exponent, m, may also be a rational number as long as its denominator (when the number is reduced to lowest terms) is odd. This is because if the exponent is a fraction with an even denominator (such as ½), the exponent indicates an even root. An even root of a negative number does not give a re ...
... The exponent, m, may also be a rational number as long as its denominator (when the number is reduced to lowest terms) is odd. This is because if the exponent is a fraction with an even denominator (such as ½), the exponent indicates an even root. An even root of a negative number does not give a re ...
Lecture 9: Integers, Rational Numbers and Algebraic Numbers
... There exists 0 ∈ F such that a + 0 = a for all a ∈ F . For each a ∈ F there is an element −a ∈ F such that a + (−a) = 0. a(bc) = (ab)c for all a, b, c ∈ F . ab = ba for all a, b ∈ F . There exists 1 ∈ F such that a · 1 = a for all a ∈ F . For each a ∈ F , there exists a−1 ∈ F such that aa−1 = 1. a(b ...
... There exists 0 ∈ F such that a + 0 = a for all a ∈ F . For each a ∈ F there is an element −a ∈ F such that a + (−a) = 0. a(bc) = (ab)c for all a, b, c ∈ F . ab = ba for all a, b ∈ F . There exists 1 ∈ F such that a · 1 = a for all a ∈ F . For each a ∈ F , there exists a−1 ∈ F such that aa−1 = 1. a(b ...
1346386692
... Draw a histogram and use it to estimate the mode. Calculate the median. A triangle ABC with vertices A2, 5 , B2, 1 and C5, 1 is rotated through a half turn by a matrix M to form the image A' B' C ' . a) Determine the matrix M and the coordinates of A' B' C ' . b) A' B' C ' is then reflec ...
... Draw a histogram and use it to estimate the mode. Calculate the median. A triangle ABC with vertices A2, 5 , B2, 1 and C5, 1 is rotated through a half turn by a matrix M to form the image A' B' C ' . a) Determine the matrix M and the coordinates of A' B' C ' . b) A' B' C ' is then reflec ...
here
... S 1.3.3 – Know and use the fact that about 68%, 95%, and 99.7% of the data lie within one, two, and three standard deviations of the mean, respectively in a normal distribution. S 1.3.4 – Calculate z-scores, use z-scores to recognize outliers, and use z-scores to make ...
... S 1.3.3 – Know and use the fact that about 68%, 95%, and 99.7% of the data lie within one, two, and three standard deviations of the mean, respectively in a normal distribution. S 1.3.4 – Calculate z-scores, use z-scores to recognize outliers, and use z-scores to make ...
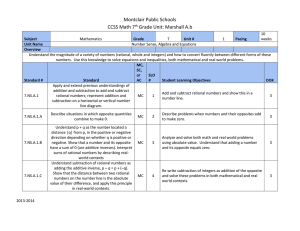
Montclair Public Schools CCSS Math 7th Grade Unit: Marshall A.b
... Apply properties of operations as strategies to add, subtract, factor, and expand linear expressions with rational coefficients. Understand that rewriting an expression in different forms in a problem context can shed light on the problem and how the quantities in it are related. Solve multi-step re ...
... Apply properties of operations as strategies to add, subtract, factor, and expand linear expressions with rational coefficients. Understand that rewriting an expression in different forms in a problem context can shed light on the problem and how the quantities in it are related. Solve multi-step re ...