Quantization of the Hall conductivity of a two
... of u,,. In the region of frequencies much higher than the characteristic frequencies of the drift motion, a,, ( w ) coincides with the conductivity tensor of an ideal impurity-free system. For the estimation of the conductivity in the region of low and intermediate frequencies we put forward a simpl ...
... of u,,. In the region of frequencies much higher than the characteristic frequencies of the drift motion, a,, ( w ) coincides with the conductivity tensor of an ideal impurity-free system. For the estimation of the conductivity in the region of low and intermediate frequencies we put forward a simpl ...
POP4e: Ch. 20 Problems
... 19.55. Four identical point charges (q = +10.0 μC) are located on the corners of a rectangle as shown in Figure P19.55. The dimensions of the rectangle are L = 60.0 cm and W = 15.0 cm. Calculate the change in electric potential energy of the system as the charge at the lower left corner in Figure P1 ...
... 19.55. Four identical point charges (q = +10.0 μC) are located on the corners of a rectangle as shown in Figure P19.55. The dimensions of the rectangle are L = 60.0 cm and W = 15.0 cm. Calculate the change in electric potential energy of the system as the charge at the lower left corner in Figure P1 ...
Electron and hole wave functions in self
... of this ring deforms the piezoelectric potential, pushing the extrema out from the corners of the ring, which reduces the overlap between the piezoelectric potential and the groundstate electron and hole wave functions. The piezoelectricinduced deformations of the ground-state wave functions are con ...
... of this ring deforms the piezoelectric potential, pushing the extrema out from the corners of the ring, which reduces the overlap between the piezoelectric potential and the groundstate electron and hole wave functions. The piezoelectricinduced deformations of the ground-state wave functions are con ...
Landau-level mixing and spin degeneracy in the quantum Hall effect *
... The system of two coupled extended states was also studied in the context of a spin-split Landau band.13–17 In the absence of a Zeeman term it was found that two separate extended states appear, each with a localization exponent of '2.3. Allowing for a finite Zeeman term leads to level attraction at ...
... The system of two coupled extended states was also studied in the context of a spin-split Landau band.13–17 In the absence of a Zeeman term it was found that two separate extended states appear, each with a localization exponent of '2.3. Allowing for a finite Zeeman term leads to level attraction at ...
contribution to the quantum theory of light scattering
... field vanishes, then the field th at appears at t > 0 can only be due to emission by the atom. Hence, such a non-stationary state serves to describe spontaneous emission. Again the phase shift (as a function of the incom ing frequency) is sufficient to find all data about the emission process. The s ...
... field vanishes, then the field th at appears at t > 0 can only be due to emission by the atom. Hence, such a non-stationary state serves to describe spontaneous emission. Again the phase shift (as a function of the incom ing frequency) is sufficient to find all data about the emission process. The s ...
The Dirac Equation and the Superluminal Electron Model
... Also in 1925, Werner Heisenberg and his colleagues developed a more accurate quantum mechanics called matrix mechanics. This approach was based on measured light frequencies and intensities coming from atoms when electrons transition from one energy level to another in an atom. With this abstract ma ...
... Also in 1925, Werner Heisenberg and his colleagues developed a more accurate quantum mechanics called matrix mechanics. This approach was based on measured light frequencies and intensities coming from atoms when electrons transition from one energy level to another in an atom. With this abstract ma ...
A Motivation of Quantum Mechanics
... In principle, there is nothing that stops macroscopic systems from behaving quantum mechanical, from showing interference effects etc. However, the larger the difference in action (measured in h̄) the larger the effect of small perturbations (from interactions with the environment) on the phase. Th ...
... In principle, there is nothing that stops macroscopic systems from behaving quantum mechanical, from showing interference effects etc. However, the larger the difference in action (measured in h̄) the larger the effect of small perturbations (from interactions with the environment) on the phase. Th ...
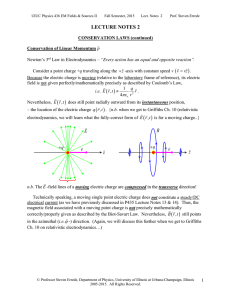
Lecture Notes 02: Conservation Laws (Continued): Conservation of Linear Momentum, Maxwell's Stress Tensor
... n.b. In electrostatics and in magnetostatics, Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion always holds. In electrodynamics, Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion does not hold for the apparent relative motion of two electric charges! (n.b. Isaac Newton could not have forseen this {from an apple falling on his head} because gra ...
... n.b. In electrostatics and in magnetostatics, Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion always holds. In electrodynamics, Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion does not hold for the apparent relative motion of two electric charges! (n.b. Isaac Newton could not have forseen this {from an apple falling on his head} because gra ...
B.Sc. PHYSICS Honours Syllabus Under CHOICE BASED CREDIT
... 1.Each University/Institute should provide a brief write-up about each paper outlining the salient features, utility, learning objectives and prerequisites. 2. University/Institute can add/delete some experiments of similar nature in the Laboratory ...
... 1.Each University/Institute should provide a brief write-up about each paper outlining the salient features, utility, learning objectives and prerequisites. 2. University/Institute can add/delete some experiments of similar nature in the Laboratory ...
Student Material
... separated by a distance of 20 m is 417 N. (1 tonne = 1000 kg) 2 Calculate the gravitational force of attraction between the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom. Assume the electron is describing a circular orbit with a radius of 5.3 x 10-11 m. (mass of proton = 1.67 x 10-27 kg; mass of electr ...
... separated by a distance of 20 m is 417 N. (1 tonne = 1000 kg) 2 Calculate the gravitational force of attraction between the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom. Assume the electron is describing a circular orbit with a radius of 5.3 x 10-11 m. (mass of proton = 1.67 x 10-27 kg; mass of electr ...
Unit 21
... contemporaries, Henry Cavendish, did a direct experiment to determine the nature of the gravitational force between two spherical masses in a laboratory. This confirmed Newton's gravitational force law and allowed him to determine the gravitational constant, G. A fact emerges that is quite amazing. ...
... contemporaries, Henry Cavendish, did a direct experiment to determine the nature of the gravitational force between two spherical masses in a laboratory. This confirmed Newton's gravitational force law and allowed him to determine the gravitational constant, G. A fact emerges that is quite amazing. ...
public schools of edison township
... Program based on backward design use desired results to drive decisions. With this design, there are questions to consider, such as: What should students understand, know, and be able to do? What does it look like to meet those goals? What kind of program will result in the outcomes stated? How will ...
... Program based on backward design use desired results to drive decisions. With this design, there are questions to consider, such as: What should students understand, know, and be able to do? What does it look like to meet those goals? What kind of program will result in the outcomes stated? How will ...
Chapter 14 Near-to-Far-Field Transformation
... However, this singularity is integrable. A volume integral of any region of space that includes the Dirac delta function at the origin (i.e., r = 0) will yield unit volume. For any observation point other than the origin, (14.20) can be written ∇2 Az (r) + k 2 Az (r) = 0 ...
... However, this singularity is integrable. A volume integral of any region of space that includes the Dirac delta function at the origin (i.e., r = 0) will yield unit volume. For any observation point other than the origin, (14.20) can be written ∇2 Az (r) + k 2 Az (r) = 0 ...