Old Physics GRE Problems Based on content from Chapter 2 of your
... 3. Which of the following statements most accurately describes how an electromagnetic field behaves under a Lorentz transformation? A. The electric field transforms completely into a magnetic field. B. If initially there is only an electric field, after the transformation there may be both an electr ...
... 3. Which of the following statements most accurately describes how an electromagnetic field behaves under a Lorentz transformation? A. The electric field transforms completely into a magnetic field. B. If initially there is only an electric field, after the transformation there may be both an electr ...
some aspects of strange matter : stars and strangelets
... photo-electric effect. Later in 1923 scattering of X-rays and γrays on electrons in atoms was explained again with the quantum nature of light by Compton. Photons as particles or quantum of the electromagnetic field was established. Bose formulated the statistical mechanics of photons around 1924. ...
... photo-electric effect. Later in 1923 scattering of X-rays and γrays on electrons in atoms was explained again with the quantum nature of light by Compton. Photons as particles or quantum of the electromagnetic field was established. Bose formulated the statistical mechanics of photons around 1924. ...
Physics 30 Atomic Model Review
... A Millikan wannabe set up an experiment using 2 parallel plates 6.0 cm apart with a potential difference of 1500 V. The mass of the hovering oil drop is calculated to be 1.63 x 10 -12g. a. Calculate the electric field strength. (2) ...
... A Millikan wannabe set up an experiment using 2 parallel plates 6.0 cm apart with a potential difference of 1500 V. The mass of the hovering oil drop is calculated to be 1.63 x 10 -12g. a. Calculate the electric field strength. (2) ...
Perturbed Chern-Simons Theory, Fractional Statistics, and Yang-Baxter Algebra
... Thus we have the important new result that the structure functions o f the operator algebra of the matter fields coupled to a Chern-Simons gauge field furnish solutions o f the YBE. The fact that the arguments o f R(u, v) in eq. (27) are not scalars and that the functional dependence is not through ...
... Thus we have the important new result that the structure functions o f the operator algebra of the matter fields coupled to a Chern-Simons gauge field furnish solutions o f the YBE. The fact that the arguments o f R(u, v) in eq. (27) are not scalars and that the functional dependence is not through ...
Physics 2DL Lectures
... If incoming electron does not have enough energy to transfer =E2-E1 then Elastic scattering, if electron has atleast KE= then inelastic scattering and the electron does not make it to the plate P Loss of current ...
... If incoming electron does not have enough energy to transfer =E2-E1 then Elastic scattering, if electron has atleast KE= then inelastic scattering and the electron does not make it to the plate P Loss of current ...
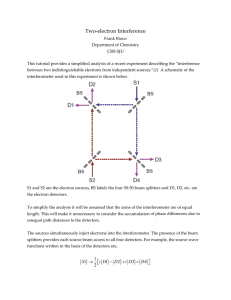
Two-electron Interference
... quantum interference of two independent, but indistinquishable, particles is also possible. For a single particle, the interference is between the amplitudes of the particle’s wave function, whereas the interference between two particles is a direct result of quantum exchange statistics. Such int ...
... quantum interference of two independent, but indistinquishable, particles is also possible. For a single particle, the interference is between the amplitudes of the particle’s wave function, whereas the interference between two particles is a direct result of quantum exchange statistics. Such int ...
General formula of effective potential in 5D SU(N) - www
... symmetry SU(3) is broken down to SU(2)×U(1) and a doublet scalar appears from A5 at the low energy effective theory. If this doublet scalar acquires an appropriate VEV, ...
... symmetry SU(3) is broken down to SU(2)×U(1) and a doublet scalar appears from A5 at the low energy effective theory. If this doublet scalar acquires an appropriate VEV, ...
Electricity Magnetism
... between the cylinders is V . The capacitor is spinning around the z-axis at an angular velocity of ω radians/sec. For each of the three regions (inside the inner sylinder, between the two cylinders and outisde the outer cylinder) find: ...
... between the cylinders is V . The capacitor is spinning around the z-axis at an angular velocity of ω radians/sec. For each of the three regions (inside the inner sylinder, between the two cylinders and outisde the outer cylinder) find: ...
is the accelerating voltage of 1000 V)
... into a region of perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. If the electric field is generated by two parallel plates separated by 2.0 cm, what would the voltage between the two plates have to be so that the alpha particle passes through undeflected in a magnetic field of 0.92T? ; need to find ...
... into a region of perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. If the electric field is generated by two parallel plates separated by 2.0 cm, what would the voltage between the two plates have to be so that the alpha particle passes through undeflected in a magnetic field of 0.92T? ; need to find ...
EMlecture203
... once sinusoidal fields are created they can propagate on their own. These propagating fields are called electromagnetic waves. ...
... once sinusoidal fields are created they can propagate on their own. These propagating fields are called electromagnetic waves. ...
Atomic Structure
... energy emitted by atoms or molecules is always in whole number multiples of energy of certain well-defined quantities. The word Quanta or Quantum refers to the smallest quantity of energy that can be emitted or absorbed in the form of electromagnetic radiation. E=h, where h is Planck’s constant = 6 ...
... energy emitted by atoms or molecules is always in whole number multiples of energy of certain well-defined quantities. The word Quanta or Quantum refers to the smallest quantity of energy that can be emitted or absorbed in the form of electromagnetic radiation. E=h, where h is Planck’s constant = 6 ...