Waves, incl. Electromagnetic Waves, Light
... (b) strong constructive interference, crests of twice the amplitude of each individual wave, followed by troughs twice as deep. (c) a succession of only troughs and no crests. (d) a succession of only crests and no troughs. ...
... (b) strong constructive interference, crests of twice the amplitude of each individual wave, followed by troughs twice as deep. (c) a succession of only troughs and no crests. (d) a succession of only crests and no troughs. ...
Charged Particles in Electric Fields
... • An electric field shows the direction and relative magnitude of an electric force. (Field theory, E = F/q) • The electric force will cause an acceleration. (Newton's Second Law) • An acceleration will cause an object to start moving one direction or another. (Newton's First Law) • So, if we place ...
... • An electric field shows the direction and relative magnitude of an electric force. (Field theory, E = F/q) • The electric force will cause an acceleration. (Newton's Second Law) • An acceleration will cause an object to start moving one direction or another. (Newton's First Law) • So, if we place ...
Monday, Apr. 11, 2005
... – Thus the accepted convention is to assign +1 intrinsic parity to proton, neutron and the L hyperon. • The parities of other particles are determined relative to these assignments through the analysis of parity conserving interactions involving these particles. ...
... – Thus the accepted convention is to assign +1 intrinsic parity to proton, neutron and the L hyperon. • The parities of other particles are determined relative to these assignments through the analysis of parity conserving interactions involving these particles. ...
TEST I 2-12-09
... Hints about exam I on Thursday 2/12/09-----I will not be able to answer emails till Monday next week. Please bring small blue Scranton that has 50 answers on one side. That way you all are at the same page. Do not bring a big one. May be just bring two of these. Just in case one goes bad or you may ...
... Hints about exam I on Thursday 2/12/09-----I will not be able to answer emails till Monday next week. Please bring small blue Scranton that has 50 answers on one side. That way you all are at the same page. Do not bring a big one. May be just bring two of these. Just in case one goes bad or you may ...
Wave as particle 2
... When photon with energy above the rest mass of two electrons ( 2me c 2 ) interact with the electric field of a nucleus, this photon may be turned into a pair of electron and positron. This process is called pair production through which energy gets turned into mass. Positron is the anti-particle of ...
... When photon with energy above the rest mass of two electrons ( 2me c 2 ) interact with the electric field of a nucleus, this photon may be turned into a pair of electron and positron. This process is called pair production through which energy gets turned into mass. Positron is the anti-particle of ...
A Gravity Model for Superconductors & (Non
... • Place electric field along radius direction, particles with opposite charges will accumulate on boundary and horizon, giving a charged balck hole • Voltage established between them can be interpretated as chemical potential (q)μ,which is the work done by moving a unit charge from horizon to bounda ...
... • Place electric field along radius direction, particles with opposite charges will accumulate on boundary and horizon, giving a charged balck hole • Voltage established between them can be interpretated as chemical potential (q)μ,which is the work done by moving a unit charge from horizon to bounda ...
HW4 - SMU Physics
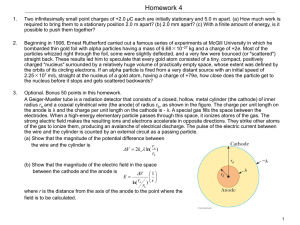
... Optional. Bonus 50 points in this homework. A Geiger-Mueller tube is a radiation detector that consists of a closed, hollow, metal cylinder (the cathode) of inner radius ra and a coaxial cylindrical wire (the anode) of radius rb, as shown in the figure. The charge per unit length on the anode is λ a ...
... Optional. Bonus 50 points in this homework. A Geiger-Mueller tube is a radiation detector that consists of a closed, hollow, metal cylinder (the cathode) of inner radius ra and a coaxial cylindrical wire (the anode) of radius rb, as shown in the figure. The charge per unit length on the anode is λ a ...
Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics and Reflectionless Potentials
... – My mentors during spring semester at Howard University Dr. James Lindesay and Dr. Marcus ...
... – My mentors during spring semester at Howard University Dr. James Lindesay and Dr. Marcus ...
Slide 1
... a) The electric field component in a particular direction. b) The magnetic field component in a particular direction. c) Either a or b above. d) The displacement of a charged particle in a direction transverse to the wave velocity direction. ...
... a) The electric field component in a particular direction. b) The magnetic field component in a particular direction. c) Either a or b above. d) The displacement of a charged particle in a direction transverse to the wave velocity direction. ...