The Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
... is heated to a high temperature, electrons will “boil” off its surface, creating a cloud of electrons (called a space charge) over the surface of the hot cathode. The electric field between anode and cathode will subsequently accelerate the electrons in the space charge towards the anode. If there i ...
... is heated to a high temperature, electrons will “boil” off its surface, creating a cloud of electrons (called a space charge) over the surface of the hot cathode. The electric field between anode and cathode will subsequently accelerate the electrons in the space charge towards the anode. If there i ...
on Fast Moving Electrons
... THE MINIMUM ENERGY REQUIRED TO EMIT AN ELECTRON FROM THE METAL SURFACE IS CALLED THE WORK FUNCTION. LOWER THE WORK FUNCTION, BETTER THE METAL IS AS A THERMION EMITTER. ...
... THE MINIMUM ENERGY REQUIRED TO EMIT AN ELECTRON FROM THE METAL SURFACE IS CALLED THE WORK FUNCTION. LOWER THE WORK FUNCTION, BETTER THE METAL IS AS A THERMION EMITTER. ...
Nothing would demonstrate your love of, and dedication to physics
... Last time: Fields from Moving Charges & Current-carrying wires ...
... Last time: Fields from Moving Charges & Current-carrying wires ...
Medical Physics I: Basics of medical imaging and radiotherapy
... 1) Operation of an x-ray tube Consider an x-ray tube in which the electrons are created by a heated cathode of lead or tungsten. These electrons are then accelerated by an electric potential of Ua = 80kV (Distance cathode – anode: 2 cm). Determine the following quantities for the operation of this x ...
... 1) Operation of an x-ray tube Consider an x-ray tube in which the electrons are created by a heated cathode of lead or tungsten. These electrons are then accelerated by an electric potential of Ua = 80kV (Distance cathode – anode: 2 cm). Determine the following quantities for the operation of this x ...
circuits 1.notebook
... Circuit- any path in which electrons flow series - a circuit in which there is only one path that the electrons can travel ****a break in the series circuit causes all current to stop**** parallel- the devices are connected to the same two points of an electrical circuit providing more than one path ...
... Circuit- any path in which electrons flow series - a circuit in which there is only one path that the electrons can travel ****a break in the series circuit causes all current to stop**** parallel- the devices are connected to the same two points of an electrical circuit providing more than one path ...
Chapter28 - Academic Program Pages
... We set this force equal to zero and use the relation between (uniform) electric field and potential difference. Thus, ...
... We set this force equal to zero and use the relation between (uniform) electric field and potential difference. Thus, ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
... the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
Physics_A2_37_GeneratingElectricity
... the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
... the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
Answer on Question #66811, Physics / Electromagnetism An
... Answer on Question #66811, Physics / Electromagnetism An electron moving parallel to the x-axis has an initial speed of 3.70×(10)^6 m/s at the origin. It's speed is reduced to 1.40×(10)^5 m/s at the point x=2c.m -calculate the electric potenial difference between the origin and that point? Find: vE ...
... Answer on Question #66811, Physics / Electromagnetism An electron moving parallel to the x-axis has an initial speed of 3.70×(10)^6 m/s at the origin. It's speed is reduced to 1.40×(10)^5 m/s at the point x=2c.m -calculate the electric potenial difference between the origin and that point? Find: vE ...
High Energy Electron Current Measurement Techniques for µ10
... between cathode and anode. The current experiment setup is applied to the neutralizer rather than on the thruster itself, to make it easier to develop the method without requiring too many ad-hoc components. Just like in the VFD displays, there’s a grid in front of the fluorescent material, but the ...
... between cathode and anode. The current experiment setup is applied to the neutralizer rather than on the thruster itself, to make it easier to develop the method without requiring too many ad-hoc components. Just like in the VFD displays, there’s a grid in front of the fluorescent material, but the ...
057500201 (doc, 36 KiB) - Infoscience
... differing shapes. Beam trajectory calculations have been done to maximize the observable areas of the plasma cross-sections with special emphasis on radial profiles extending from the plasma center up to the edge. As far as correlation measurements are concerned, it is important to be able to observ ...
... differing shapes. Beam trajectory calculations have been done to maximize the observable areas of the plasma cross-sections with special emphasis on radial profiles extending from the plasma center up to the edge. As far as correlation measurements are concerned, it is important to be able to observ ...
Cathode ray deflection tube
... A bar magnet can now be held at the side of the tube and you will see that the beam of electrons is deflected up or down depending which way round you hold the magnet. The same thing will happen of course if you use an electromagnet (see Figure 3). Magnetic field at right angles to the paper ...
... A bar magnet can now be held at the side of the tube and you will see that the beam of electrons is deflected up or down depending which way round you hold the magnet. The same thing will happen of course if you use an electromagnet (see Figure 3). Magnetic field at right angles to the paper ...
Quiz 3 Solution
... Two flat plates with charge density σ = +5nC/m2 and −σ = −5nC/m2 , respectively, lie parallel to the xy plane, separated by a distance d = 2 cm. An electron (charge −1.6 × 10−19 C, mass 9.11 × 10−31 kg) enters the plates at height d/2 = 1 cm moving in the positive ŷ direction with speed 106 m/s. Wh ...
... Two flat plates with charge density σ = +5nC/m2 and −σ = −5nC/m2 , respectively, lie parallel to the xy plane, separated by a distance d = 2 cm. An electron (charge −1.6 × 10−19 C, mass 9.11 × 10−31 kg) enters the plates at height d/2 = 1 cm moving in the positive ŷ direction with speed 106 m/s. Wh ...
Classical theory of atomic structure
... theory fails to explain the stability of atomic structure as accelerated electron radiates energy in the form of electromagnetic waves and consequently it will loose energy gradually and at last fall into the nucleus due to gravitational and coulombic attractions. Secondly classical theory fails to ...
... theory fails to explain the stability of atomic structure as accelerated electron radiates energy in the form of electromagnetic waves and consequently it will loose energy gradually and at last fall into the nucleus due to gravitational and coulombic attractions. Secondly classical theory fails to ...
Physics 105 - Multiple Choice Questions Ch 16
... move an electron 1 meter C) the energy gained by an electron in moving through a potential difference of 1 volt D) the energy needed to move an electron through 1 meter in any electric field E) the work done when 1 coulomb of charge is moved through a potential difference of 1 volt ...
... move an electron 1 meter C) the energy gained by an electron in moving through a potential difference of 1 volt D) the energy needed to move an electron through 1 meter in any electric field E) the work done when 1 coulomb of charge is moved through a potential difference of 1 volt ...
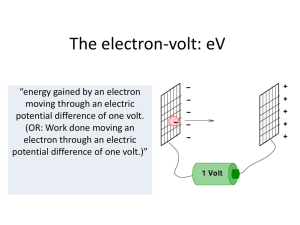
The electron-volt - Hockerill Students
... moving through an electric potential difference of one volt. (OR: Work done moving an electron through an electric potential difference of one volt.)” ...
... moving through an electric potential difference of one volt. (OR: Work done moving an electron through an electric potential difference of one volt.)” ...
Electrodynamic tether

Electrodynamic tethers (EDTs) are long conducting wires, such as one deployed from a tether satellite, which can operate on electromagnetic principles as generators, by converting their kinetic energy to electrical energy, or as motors, converting electrical energy to kinetic energy. Electric potential is generated across a conductive tether by its motion through a planet's magnetic field.