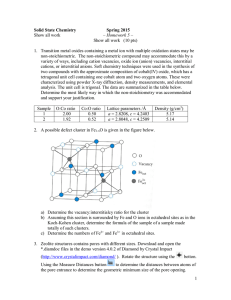
Magnetic susceptibility measurements of transition metal containing
... effects including Van Vleck paramagnetism, can be described in terms of the effective magnetic moment µeff, where k = Boltzmann’s constant, T = absolute temperature, β = Bohr Magneton, N is Avogardo’s number, and χA is the susceptibility per gram of the paramagnetic ion. ...
... effects including Van Vleck paramagnetism, can be described in terms of the effective magnetic moment µeff, where k = Boltzmann’s constant, T = absolute temperature, β = Bohr Magneton, N is Avogardo’s number, and χA is the susceptibility per gram of the paramagnetic ion. ...
Experiment 3: Dynamic NMR spectroscopy
... In general spectroscopic experiments are divided into two categories: optical spectroscopy and magnetic spectroscopy. In previous experiments optical spectroscopy based techniques (e.g., UV/VIS absorption and fluorescence) were applied to obtain information about molecules. In this experiment Nuclea ...
... In general spectroscopic experiments are divided into two categories: optical spectroscopy and magnetic spectroscopy. In previous experiments optical spectroscopy based techniques (e.g., UV/VIS absorption and fluorescence) were applied to obtain information about molecules. In this experiment Nuclea ...
Spin Hall Effect in
... Rashba term induces an energy level crossing in the lowest heavy hole sub-band, which gives rise to a resonant spin Hall conductance. The resonance may be used to identify the intrinsic spin Hall effect. In collaboration with X. Dai, Z. Fang, Y. G. Yao ...
... Rashba term induces an energy level crossing in the lowest heavy hole sub-band, which gives rise to a resonant spin Hall conductance. The resonance may be used to identify the intrinsic spin Hall effect. In collaboration with X. Dai, Z. Fang, Y. G. Yao ...
Zeeman effect – Studying magnetic fields in star
... of 9 hf-components (of which 7 are strong and of these 4 have a strong Zeeman effect) • The very different Z values of the hf. lines helps to distinguish the real Zeeman effect and instrumental ...
... of 9 hf-components (of which 7 are strong and of these 4 have a strong Zeeman effect) • The very different Z values of the hf. lines helps to distinguish the real Zeeman effect and instrumental ...
Contents - Center for Ultracold Atoms
... The moments of the nucleus couple to its spin which interacts with the angular momentum of the rest of the atom. This splits the energy levels of the atom according to the magnitude |F|, where F = I+J. The resulting hyperfine structure can be measured with almost limitless precision (certainly < 10− ...
... The moments of the nucleus couple to its spin which interacts with the angular momentum of the rest of the atom. This splits the energy levels of the atom according to the magnitude |F|, where F = I+J. The resulting hyperfine structure can be measured with almost limitless precision (certainly < 10− ...
Slide 1
... In the case of resonance with the electric field, the material will exhibit a negative permittivity ε (as is the case with metals at optical frequencies). At resonance with a driving magnetic field, the material will exhibit a negative permeability . ...
... In the case of resonance with the electric field, the material will exhibit a negative permittivity ε (as is the case with metals at optical frequencies). At resonance with a driving magnetic field, the material will exhibit a negative permeability . ...
Effects of high static magnetic fields in magnetic resonance imaging
... structures or functions of tissues and organs using their different magnetic properties. A better signalto-noise ratio led to growing magnetic field strengths in today’s MR scanners resulting in a better resolution of images and shorter examination times. The question has come up if static magnetic ...
... structures or functions of tissues and organs using their different magnetic properties. A better signalto-noise ratio led to growing magnetic field strengths in today’s MR scanners resulting in a better resolution of images and shorter examination times. The question has come up if static magnetic ...
5_2_Magnetism basics
... Another way of saying this is that the application of H lowers the energy of the spin parallel states by an amount 2βH. The total magnetic moment of the system is 2xβ, where x is the number of electrons transferred from the anti-parallel to the parallel orientation... ...note that it is 2x times the ...
... Another way of saying this is that the application of H lowers the energy of the spin parallel states by an amount 2βH. The total magnetic moment of the system is 2xβ, where x is the number of electrons transferred from the anti-parallel to the parallel orientation... ...note that it is 2x times the ...
Electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a technique for studying materials with unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but it is electron spins that are excited instead of the spins of atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes or organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford.