Urinary tract infection in children
... Other tests are only required in the following cases:• In babies or if your child has an abnormal ultrasound scan • Strong family history of kidney problems • Multiple infections • If the UTI was a bad one with a fever or back pain around the kidneys Other Tests DMSA Scan This involves the injec ...
... Other tests are only required in the following cases:• In babies or if your child has an abnormal ultrasound scan • Strong family history of kidney problems • Multiple infections • If the UTI was a bad one with a fever or back pain around the kidneys Other Tests DMSA Scan This involves the injec ...
Drugs Used to Treat Urinary System Disorders
... infection in one area can involve entire system microbes enter system through urethra common causes: catheterization urological exams intercourse poor perineal hygiene immobility poor fluid intake UTI is a common healthcare associated infection (HAI), this is an infection that develops i ...
... infection in one area can involve entire system microbes enter system through urethra common causes: catheterization urological exams intercourse poor perineal hygiene immobility poor fluid intake UTI is a common healthcare associated infection (HAI), this is an infection that develops i ...
Excretory and Urinary Systems
... • What are some examples from the other human body systems? – Digestive – Respiratory ...
... • What are some examples from the other human body systems? – Digestive – Respiratory ...
Human Excretion - Mrs. Tyler's Advanced Placement Biology
... the tubule of nephron water, minerals, and digestion end products are reabsorbed Urine is what is left and then leaves the kidneys through ureters to the urinary bladder ...
... the tubule of nephron water, minerals, and digestion end products are reabsorbed Urine is what is left and then leaves the kidneys through ureters to the urinary bladder ...
Urinary Tract Infection
... 6. UTI’s are a different situation than soft tissue infections and sinus infections which are closed cavities within bone, and where good antibiotic levels can be more difficult to achieve (see # 3 above). Those areas also do not offer the same drainage to de-bulk the infection as the urinary tract ...
... 6. UTI’s are a different situation than soft tissue infections and sinus infections which are closed cavities within bone, and where good antibiotic levels can be more difficult to achieve (see # 3 above). Those areas also do not offer the same drainage to de-bulk the infection as the urinary tract ...
Urinary Tract Infection
... These symptoms can range from mild to severe. Signs of a urinary tract infection in children also include fever, irritability, wetting in a previously ‘dry’ child and feeding problems in babies. Urethritis commonly causes burning during urination, but usually the urine is not bloody or cloudy. Pyelo ...
... These symptoms can range from mild to severe. Signs of a urinary tract infection in children also include fever, irritability, wetting in a previously ‘dry’ child and feeding problems in babies. Urethritis commonly causes burning during urination, but usually the urine is not bloody or cloudy. Pyelo ...
When do I need antibiotics
... understand about wanting to get well sooner. The choice of antibiotic is determined by the most likely bacterial cause for the specific infection. The dose is often weight based, sometimes age based. Using a “stronger” or broader spectrum antibiotic than is necessary can do more harm than good. Inap ...
... understand about wanting to get well sooner. The choice of antibiotic is determined by the most likely bacterial cause for the specific infection. The dose is often weight based, sometimes age based. Using a “stronger” or broader spectrum antibiotic than is necessary can do more harm than good. Inap ...
Urinary tract Infections
... usually over years. -Glomerular involvement is much more common in chronic nephritis than acute type. ...
... usually over years. -Glomerular involvement is much more common in chronic nephritis than acute type. ...
Lecture 3- Acute pyelonephritis
... • neurogenic bladder (e.g. due to spinal cord damage, spina bifida or multiple sclerosis) and • prostate disease (e.g. benign prostatic hyperplasia) in men • bladder tumours • urethral strictures ...
... • neurogenic bladder (e.g. due to spinal cord damage, spina bifida or multiple sclerosis) and • prostate disease (e.g. benign prostatic hyperplasia) in men • bladder tumours • urethral strictures ...
examen 2005 - Di-Et-Tri
... b. Describe briefly how GORD (Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease) can lead to oesophageal cancer. c. ...
... b. Describe briefly how GORD (Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease) can lead to oesophageal cancer. c. ...
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI`s)
... • Infrequent bowel movements or constipation • Wiping back to front after using the toilet – for girls • Poor water intake Some children are simply prone to getting UTI’s even though they have good habits. A child may have a defect where the ureter joins the bladder, causing urine to flow backwards ...
... • Infrequent bowel movements or constipation • Wiping back to front after using the toilet – for girls • Poor water intake Some children are simply prone to getting UTI’s even though they have good habits. A child may have a defect where the ureter joins the bladder, causing urine to flow backwards ...
Urinary tract infections in young women
... ● Preventive medication, when required. Taken after a sexual intercourse or swimming or getting cold, the drug reduces the risk of infection provoked by these situations (e.g., 100-300 mg of trimethoprim or 50-75 mg of nitrofurantoin). Preventive medication can also be used during a (sports) holiday ...
... ● Preventive medication, when required. Taken after a sexual intercourse or swimming or getting cold, the drug reduces the risk of infection provoked by these situations (e.g., 100-300 mg of trimethoprim or 50-75 mg of nitrofurantoin). Preventive medication can also be used during a (sports) holiday ...
Introduction – Urinary tract Infection (UTI)
... • 3. ≥ 105 uropathogens/mL in midstream urine of women or 104 uropathogens/mL of midstream urine in men (or in straight catheter urine in women) with complicated UTI. • 4. In a suprapubic bladder puncture specimen, any count of bacteria is relevant. • 5. Asymptomatic bacteriuria = two positive urine ...
... • 3. ≥ 105 uropathogens/mL in midstream urine of women or 104 uropathogens/mL of midstream urine in men (or in straight catheter urine in women) with complicated UTI. • 4. In a suprapubic bladder puncture specimen, any count of bacteria is relevant. • 5. Asymptomatic bacteriuria = two positive urine ...
Reducing Infections
... Cather Associated Urinary Tract Infections ( CAUTI)- Get all devices out as soon as possible to reduce the risk of infections. Do a daily assessment of the need for a Foley catheter and/ or central line and document the reason for not removing the device in the patient’s medical record. ...
... Cather Associated Urinary Tract Infections ( CAUTI)- Get all devices out as soon as possible to reduce the risk of infections. Do a daily assessment of the need for a Foley catheter and/ or central line and document the reason for not removing the device in the patient’s medical record. ...
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
... Even though UTIs are very common, they should be taken seriously. Severe cases of urinary tract infections, left untreated, may cause kidney infection. What Are the Symptoms of a UTI? While not everyone with a urinary tract infection (UTI) will notice symptoms, common symptoms include o o o o o o o ...
... Even though UTIs are very common, they should be taken seriously. Severe cases of urinary tract infections, left untreated, may cause kidney infection. What Are the Symptoms of a UTI? While not everyone with a urinary tract infection (UTI) will notice symptoms, common symptoms include o o o o o o o ...
Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Tract
... be spread into the abdomen during surgery • Surgery may result in a cure, if the mass can be removed completely • Wide surgical excision (that is, surgically removing the tumor and wide borders of apparently normal tissue) is necessary; up to 50% of the urinary bladder may be removed surgically with ...
... be spread into the abdomen during surgery • Surgery may result in a cure, if the mass can be removed completely • Wide surgical excision (that is, surgically removing the tumor and wide borders of apparently normal tissue) is necessary; up to 50% of the urinary bladder may be removed surgically with ...
Recurrent Bladder Infections in Females
... infection occur • take by mouth AND place in vagina • who: women with recurrent UTI that for vaginal use, you can cut off the end have identifiable symptoms of a gel-cap and • take as directed when you have AMinsert / PMthe capsule with lubricant or purchase Purfem symptoms – usually 3 days of treat ...
... infection occur • take by mouth AND place in vagina • who: women with recurrent UTI that for vaginal use, you can cut off the end have identifiable symptoms of a gel-cap and • take as directed when you have AMinsert / PMthe capsule with lubricant or purchase Purfem symptoms – usually 3 days of treat ...
FAQ050 -- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
... though your symptoms may go away before you finish your prescription. If you stop treatment early, the infection may still be present or it could come back after a short time. For more severe infections, such as a kidney infection, you may need to stay in the hospital. These infections take longer t ...
... though your symptoms may go away before you finish your prescription. If you stop treatment early, the infection may still be present or it could come back after a short time. For more severe infections, such as a kidney infection, you may need to stay in the hospital. These infections take longer t ...
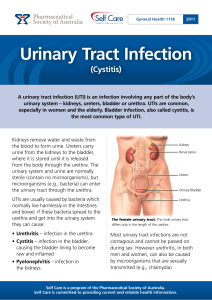
Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI), also known as acute cystitis or bladder infection, is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a simple cystitis (a bladder infection) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as pyelonephritis (a kidney infection). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract include painful urination and either frequent urination or urge to urinate (or both); while the symptoms of pyelonephritis include fever and flank pain in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. In some cases, a painful burning sensation in the urethra may be present even when not urinating. In the elderly and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The main causal agent of both types is Escherichia coli, though other bacteria, viruses or fungi may rarely be the cause.Urinary tract infections occur more commonly in women than men, with half of women having at least one infection at some point in their lives. Recurrences are common. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse and family history. Pyelonephritis, if it occurs, usually follows a bladder infection but may also result from a blood-borne infection. Diagnosis in young healthy women can be based on symptoms alone. In those with vague symptoms, diagnosis can be difficult because bacteria may be present without there being an infection. In complicated cases or if treatment has failed, a urine culture may be useful. In those with frequent infections, low dose antibiotics may be taken as a preventative measure.In uncomplicated cases, urinary tract infections are easily treated with a short course of antibiotics, although resistance to many of the antibiotics used to treat this condition is increasing. In complicated cases, a longer course or intravenous antibiotics may be needed, and if symptoms have not improved in two or three days, further diagnostic testing is needed. In women, urinary tract infections are the most common form of bacterial infection with 10% developing urinary tract infections yearly. In those who have bacteria or white blood cells in their urine but have no symptoms, antibiotics are generally not needed, although pregnant women are an exception to this recommendation.