Section 1: The theory of evolution by natural selection
... Traits of individuals best suited to survive will become [more/ less] common in each new generation. [Genes/ natural selection] is (are) responsible for inherited traits. [Natural selection/ genes] cause(s) the frequency of certain alleles in a population to vary over time. [Isolation/ extinction] i ...
... Traits of individuals best suited to survive will become [more/ less] common in each new generation. [Genes/ natural selection] is (are) responsible for inherited traits. [Natural selection/ genes] cause(s) the frequency of certain alleles in a population to vary over time. [Isolation/ extinction] i ...
Natural Selection and the Evidence of Evolution Study Guide
... Vocab: Briefly explain how each of the following pairs of vocab words are different from each other: natural selection & selected breeding species & speciation ...
... Vocab: Briefly explain how each of the following pairs of vocab words are different from each other: natural selection & selected breeding species & speciation ...
Photo by “davemee” flickr creative commons
... G. Theories are inferred explanations, strongly supported by evidence • H. A scientific law has been proven and a theory has not. • I. Theories are used to make predictions • J. Laws are more important to science than theories Answers A, D, G, I best describe scientific theories ...
... G. Theories are inferred explanations, strongly supported by evidence • H. A scientific law has been proven and a theory has not. • I. Theories are used to make predictions • J. Laws are more important to science than theories Answers A, D, G, I best describe scientific theories ...
Evolution
... Host and guest cells come to depend upon one another for essential metabolic processes Mitochondria and chloroplasts may have evolved by endosymbiosis Early Discoveries 19th century ...
... Host and guest cells come to depend upon one another for essential metabolic processes Mitochondria and chloroplasts may have evolved by endosymbiosis Early Discoveries 19th century ...
EVOLUTION BY NATURAL SELECTION
... Some fossils extinct? ! Why same fossils on different continents? ...
... Some fossils extinct? ! Why same fossils on different continents? ...
File - Steckelberg Science
... perfect for them? _______________ were there no kangaroos in England? Living Organisms and Fossils Darwin collected the preserved remains of ancient organisms, called ___________________________________ Some of those fossils resembled organisms that were still alive today. ...
... perfect for them? _______________ were there no kangaroos in England? Living Organisms and Fossils Darwin collected the preserved remains of ancient organisms, called ___________________________________ Some of those fossils resembled organisms that were still alive today. ...
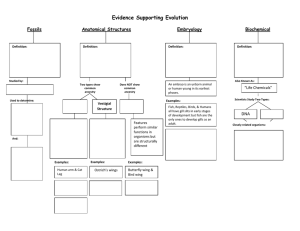
Evidence Supporting Evolution
... A remnant or trace of an organism of a past geologic age, such as a skeleton or leaf imprint, embedded and preserved in earth’s crust. ...
... A remnant or trace of an organism of a past geologic age, such as a skeleton or leaf imprint, embedded and preserved in earth’s crust. ...
chapter 15 test
... d. variations best suited to the environment. 7. The number and location of bones of many fossil vertebrates are similar to those in living vertebrates. Most biologists would probably explain this fact on the basis of a. the needs of the organisms. c. the struggle for existence. b. a common ancestor ...
... d. variations best suited to the environment. 7. The number and location of bones of many fossil vertebrates are similar to those in living vertebrates. Most biologists would probably explain this fact on the basis of a. the needs of the organisms. c. the struggle for existence. b. a common ancestor ...
Evolution Test Review- key
... When something geographic separates a species (canyon, river) 2 separate species evolve. What does it mean to be “fit” in terms of evolution? best traits optimal for survival: fastest, strongest, etc. Define: Survival of the fittest. Fit the best to survive What type of evolutionary evidence is show ...
... When something geographic separates a species (canyon, river) 2 separate species evolve. What does it mean to be “fit” in terms of evolution? best traits optimal for survival: fastest, strongest, etc. Define: Survival of the fittest. Fit the best to survive What type of evolutionary evidence is show ...
evolution
... The process by which species have changed over time Supporting Observations indicate certain organisms may have a common ancestor, not that one organism changed into another ...
... The process by which species have changed over time Supporting Observations indicate certain organisms may have a common ancestor, not that one organism changed into another ...
Evidence for Evolution
... If this mechanism of change has been shaping the organisms on this planet, then there should be evidence of it occurring 5 major types of evidence used to support the theory of evolution. ...
... If this mechanism of change has been shaping the organisms on this planet, then there should be evidence of it occurring 5 major types of evidence used to support the theory of evolution. ...
The 2 fundamental questions: Linneaus and Kirchner
... Evidence for Evolution – prior to 1830 • Enormous diversity of life – WHY ??? JBS Haldane " The Creator, if He exists, has "an inordinate fondness for beetles" ". ...
... Evidence for Evolution – prior to 1830 • Enormous diversity of life – WHY ??? JBS Haldane " The Creator, if He exists, has "an inordinate fondness for beetles" ". ...
Vertebrates
... having been originally breathed by the Creator into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being evolved. Parts of last paragraph of ...
... having been originally breathed by the Creator into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being evolved. Parts of last paragraph of ...
Evolution and Natural Selection
... developed from more simple life forms and have changed (evolved) over time ...
... developed from more simple life forms and have changed (evolved) over time ...
ppt
... The History of Evolution • Evolution is defined as change over time • The theory that all organisms on Earth are related by common ancestry and that they have changed over time (adapted) mostly because of natural selection. • Charles Darwin is one of the most famous scientists associated with the t ...
... The History of Evolution • Evolution is defined as change over time • The theory that all organisms on Earth are related by common ancestry and that they have changed over time (adapted) mostly because of natural selection. • Charles Darwin is one of the most famous scientists associated with the t ...
Evolution - Coach Blair`s Biology Website
... An analogous structure is any body part that is similar ...
... An analogous structure is any body part that is similar ...
Darwin
... EX: earthquake in CA creates a huge crevasse in the ground, isolating a population of lizards Since the two populations cannot mate, they begin to have subtle changes over time that make them different species ...
... EX: earthquake in CA creates a huge crevasse in the ground, isolating a population of lizards Since the two populations cannot mate, they begin to have subtle changes over time that make them different species ...
A. History of Evolutionary Theory
... time. The population of organisms scientist considered to be the founder of modern evolutionary theory is ______________. Charles Darwin ...
... time. The population of organisms scientist considered to be the founder of modern evolutionary theory is ______________. Charles Darwin ...
Ecology Unit Outline - nnhsbiology
... 2. We often discuss “life” and assume that we collectively know what the term “life” means. a. To a biologist such as yourself (yes you are) how do you determine that something is alive? b. How did “life” come into being on earth? c. How did first life alter the planet’s landscape and atmosphere an ...
... 2. We often discuss “life” and assume that we collectively know what the term “life” means. a. To a biologist such as yourself (yes you are) how do you determine that something is alive? b. How did “life” come into being on earth? c. How did first life alter the planet’s landscape and atmosphere an ...
More Than An EyeWitness
... Why do these structures occur? • May be homologous to useful structures in other organisms and thus suggest evolution from an ancestor in which they do have a use. ...
... Why do these structures occur? • May be homologous to useful structures in other organisms and thus suggest evolution from an ancestor in which they do have a use. ...
Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution
... Aristotle observes that dolphins and whales come to the surface for air, fish do not. Therefore, dolphins must once have lived on land. Early 18th C (1700’s) Geological and fossil evidence for change over time is discovered, discussed and published by many geologists and early paleontologists. ...
... Aristotle observes that dolphins and whales come to the surface for air, fish do not. Therefore, dolphins must once have lived on land. Early 18th C (1700’s) Geological and fossil evidence for change over time is discovered, discussed and published by many geologists and early paleontologists. ...
What is Evolution?
... • The diverse forms of life have arisen by descent with modification from ancestral species. • The mechanism of modification has been natural selection working over enormous tracts of time. ...
... • The diverse forms of life have arisen by descent with modification from ancestral species. • The mechanism of modification has been natural selection working over enormous tracts of time. ...
EVOLUTION!
... sudden changes in genes results in new types of plants and animals accounts for the variations suggested by Darwin mutations can be good, bad, or have no current value lethal genes which leaves organism with no chance of survival (almost always recessive) ...
... sudden changes in genes results in new types of plants and animals accounts for the variations suggested by Darwin mutations can be good, bad, or have no current value lethal genes which leaves organism with no chance of survival (almost always recessive) ...
Transitional fossil

A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that transitional fossils are direct ancestors of more recent groups, though they are frequently used as models for such ancestors.In 1859, when Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species was first published, the fossil record was poorly known. Darwin described the perceived lack of transitional fossils as, ""...the most obvious and gravest objection which can be urged against my theory,"" but explained it by relating it to the extreme imperfection of the geological record. He noted the limited collections available at that time, but described the available information as showing patterns that followed from his theory of descent with modification through natural selection. Indeed, Archaeopteryx was discovered just two years later, in 1861, and represents a classic transitional form between dinosaurs and birds. Many more transitional fossils have been discovered since then, and there is now abundant evidence of how all classes of vertebrates are related, much of it in the form of transitional fossils. Specific examples include humans and other primates, tetrapods and fish, and birds and dinosaurs.The term ""missing link"" has been used extensively in popular writings on human evolution to refer to a perceived gap in the hominid evolutionary record. It is most commonly used to refer to any new transitional fossil finds. Scientists, however, do not use the term, as it refers to a pre-evolutionary view of nature.