The Inner Ear - Lectures For UG-5
... • On the basilar membrane sits the sensory organ of the ear, the organ of Corti which acts as a transducer (converting sound energy into electrical energy) • It is composed of a complex of supporting cells and sensory or hair cells atop the thin basilar membrane • There are some 16,000 -20,000 of th ...
... • On the basilar membrane sits the sensory organ of the ear, the organ of Corti which acts as a transducer (converting sound energy into electrical energy) • It is composed of a complex of supporting cells and sensory or hair cells atop the thin basilar membrane • There are some 16,000 -20,000 of th ...
Frequency Compression through Beltone Sound Shifter
... comparison, each hearing instrument was programmed for 3 hearing losses: mild flat, mild sloping to moderatelysevere, and mild sloping to profound. Gains were set according to the default prescriptive targets in the respective ...
... comparison, each hearing instrument was programmed for 3 hearing losses: mild flat, mild sloping to moderatelysevere, and mild sloping to profound. Gains were set according to the default prescriptive targets in the respective ...
The Power of Sound!
... As sound enters your ear the first thing it encounters is your ear drum. The ear drum detects these tiny ripples and sends the vibrations to the middle ear and on to the inner ear, or Cochlea. The Cochlea contains tiny hairs which send electrical impulse to the brain which converts this Impulse to s ...
... As sound enters your ear the first thing it encounters is your ear drum. The ear drum detects these tiny ripples and sends the vibrations to the middle ear and on to the inner ear, or Cochlea. The Cochlea contains tiny hairs which send electrical impulse to the brain which converts this Impulse to s ...
2906_lect5
... For instance, dogs can hear higherfrequency sounds and elephants can hear lower-frequency sounds than humans can ...
... For instance, dogs can hear higherfrequency sounds and elephants can hear lower-frequency sounds than humans can ...
DOSITS Booklet.indd
... Because water is an effective medium for the transmission of sound, both marine animals and people use sound as a tool for finding objects, navigating, and communicating under water. Sound travels far greater distances than light under water. Light travels only a few hundred meters in the ocean befor ...
... Because water is an effective medium for the transmission of sound, both marine animals and people use sound as a tool for finding objects, navigating, and communicating under water. Sound travels far greater distances than light under water. Light travels only a few hundred meters in the ocean befor ...
(770k ppt)
... “weather” would be deafeningly loud. • 20kHz is not a firm “cutoff” for human hearing. Children appear to hear above 20kHz, as do some teens who haven’t been noise-exposed. • Age and noise exposure reduce high-frequency hearing ability. • At high power levels, ultrasonic signals are perceived on the ...
... “weather” would be deafeningly loud. • 20kHz is not a firm “cutoff” for human hearing. Children appear to hear above 20kHz, as do some teens who haven’t been noise-exposed. • Age and noise exposure reduce high-frequency hearing ability. • At high power levels, ultrasonic signals are perceived on the ...
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
... Ÿ Force amplification by a factor of about 20 (Fig. 13.4) ù Lever action amplifies the force by a factor of about 1.3 between M and S ù Piston action amplifies the force by a factor of about 15 between the eardrum and S m Ossicles and their sensory ligaments Protection against loud sounds: loud soun ...
... Ÿ Force amplification by a factor of about 20 (Fig. 13.4) ù Lever action amplifies the force by a factor of about 1.3 between M and S ù Piston action amplifies the force by a factor of about 15 between the eardrum and S m Ossicles and their sensory ligaments Protection against loud sounds: loud soun ...
Signal Transmission in the Auditory System
... Chapter 40. Signal Transmission in the Auditory System the TM, creating an osmotic pressure gradient across the TM boundary. Although the osmotic pressure exerted by PEG is a nonlinear function of concentration and MW1, calibration experiments confirm that we can exert a known osmotic pressure usin ...
... Chapter 40. Signal Transmission in the Auditory System the TM, creating an osmotic pressure gradient across the TM boundary. Although the osmotic pressure exerted by PEG is a nonlinear function of concentration and MW1, calibration experiments confirm that we can exert a known osmotic pressure usin ...
3D Simulation of the Human Middle Ear with Multi
... The dynamic behavior of the middle ear in the steady state condition was examined for both the normal model of the middle ear (Fig. 3) and the middle ear model coupled with a active implant with two different types of stimulation on the tympanum: a "click" sound excitation in the form of a Gaussian ...
... The dynamic behavior of the middle ear in the steady state condition was examined for both the normal model of the middle ear (Fig. 3) and the middle ear model coupled with a active implant with two different types of stimulation on the tympanum: a "click" sound excitation in the form of a Gaussian ...
SENSO P38 SENSO
... • M, MT, and T settings available. The “T” and “MT” responses are compensated to preserve the frequency and output level of the acoustic signal. • The microphone and telecoil inputs each have their own Sigma-Delta converter allowing a telecoil with a digital anti-hum filter to reduce interference fr ...
... • M, MT, and T settings available. The “T” and “MT” responses are compensated to preserve the frequency and output level of the acoustic signal. • The microphone and telecoil inputs each have their own Sigma-Delta converter allowing a telecoil with a digital anti-hum filter to reduce interference fr ...
10 Sensation
... sound, taste, etc. are made to test for reactions in people. Tone tests (hearing) are an example. ...
... sound, taste, etc. are made to test for reactions in people. Tone tests (hearing) are an example. ...
pcp_binaural
... • Forward and backward masking of weak segments by strong ones • Reduced ability to discriminate sub-phonemic segments like noise bursts, voice-onset-time, and formant transitions ...
... • Forward and backward masking of weak segments by strong ones • Reduced ability to discriminate sub-phonemic segments like noise bursts, voice-onset-time, and formant transitions ...
Teacher notes
... sounds in the frequency range 20Hertz (very low pitch) to 20,000Hertz (very high pitch). It is particularly sensitive to sounds in the frequency range 500Hz to 5000Hertz – the so-called speech frequencies that are vital for human communication. The ear is able to deal with a wide range of volume (so ...
... sounds in the frequency range 20Hertz (very low pitch) to 20,000Hertz (very high pitch). It is particularly sensitive to sounds in the frequency range 500Hz to 5000Hertz – the so-called speech frequencies that are vital for human communication. The ear is able to deal with a wide range of volume (so ...
Slide 1
... SLMs have electronic circuits which convert the microphone signal to an RMS sound pressure. ...
... SLMs have electronic circuits which convert the microphone signal to an RMS sound pressure. ...
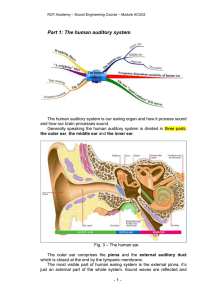
The Human Ear and Simple Tests of Hearing
... THE HUMAN EAR AND SIMPLE TESTS OF HEARING Ear Anatomy ...
... THE HUMAN EAR AND SIMPLE TESTS OF HEARING Ear Anatomy ...
2 nail illusion Fletcher-Munson Curves Characterizing simple and
... – Allows a complex sound wave to be decomposed into constituent sinusoidal frequencies, each an integer multiple of the original’s (fundamental) frequency – Fundamental frequency (or first harmonic) determines the pitch of a complex sound ...
... – Allows a complex sound wave to be decomposed into constituent sinusoidal frequencies, each an integer multiple of the original’s (fundamental) frequency – Fundamental frequency (or first harmonic) determines the pitch of a complex sound ...
Ear is the Excellent Acoustic Reader: The Effect of
... and 20,000 Hz (20 kHz), Both limits, especially the upper limit, decrease with age. Other species have a different range of hearing. For example, dogs can perceive vibrations higher than 20 kHz, but are deaf below 40 Hz. As a signal perceived by one of the major senses, sound is used by many species ...
... and 20,000 Hz (20 kHz), Both limits, especially the upper limit, decrease with age. Other species have a different range of hearing. For example, dogs can perceive vibrations higher than 20 kHz, but are deaf below 40 Hz. As a signal perceived by one of the major senses, sound is used by many species ...
Ear is the Excellent Acoustic Reader: The Effect of Acoustics on this
... and 20,000 Hz (20 kHz), Both limits, especially the upper limit, decrease with age. Other species have a different range of hearing. For example, dogs can perceive vibrations higher than 20 kHz, but are deaf below 40 Hz. As a signal perceived by one of the major senses, sound is used by many species ...
... and 20,000 Hz (20 kHz), Both limits, especially the upper limit, decrease with age. Other species have a different range of hearing. For example, dogs can perceive vibrations higher than 20 kHz, but are deaf below 40 Hz. As a signal perceived by one of the major senses, sound is used by many species ...
Hearing and Testing - Medical Home Portal
... Hearing “threshold” is the lowest intensity at which we begin to hear sound. The normal hearing threshold is between –10dB and 25 dB. Some examples of the sounds around us Sounds around us have a wide range of frequency and intensity. For example, leaves rustling are very soft, or very low intensity ...
... Hearing “threshold” is the lowest intensity at which we begin to hear sound. The normal hearing threshold is between –10dB and 25 dB. Some examples of the sounds around us Sounds around us have a wide range of frequency and intensity. For example, leaves rustling are very soft, or very low intensity ...
The Ear: Hearing and Balance
... Sound and Mechanisms of Hearing • Sound vibrations beat against the eardrum • The eardrum pushes against the ossicles, which presses fluid in the inner ear against the oval and round windows – This movement sets up shearing forces that pull on hair cells – Moving hair cells stimulates the cochlear ...
... Sound and Mechanisms of Hearing • Sound vibrations beat against the eardrum • The eardrum pushes against the ossicles, which presses fluid in the inner ear against the oval and round windows – This movement sets up shearing forces that pull on hair cells – Moving hair cells stimulates the cochlear ...
CREATING SPATIAL DEPTH USING DISTORTION
... effect as, “tactile in presence, [sounds] appear both larger than life and small enough to touch, heard as though miles away, or felt inside the listener” [2]. The tactile quality of sound and the auditory depth of field in Amacher’s work inform the methods used for composing with otoacoustic emissi ...
... effect as, “tactile in presence, [sounds] appear both larger than life and small enough to touch, heard as though miles away, or felt inside the listener” [2]. The tactile quality of sound and the auditory depth of field in Amacher’s work inform the methods used for composing with otoacoustic emissi ...
Human Body Project Auditory System
... The three types of ossicles bones are: Malleus, Incus, and Stapes. The Middle ears bones overcome the lost of sound by increasing sound pressure(+34dB) this process is known as impendence matching When the stapes move in and out of the oval window, it creates a fluid motion, which is called hydrodyn ...
... The three types of ossicles bones are: Malleus, Incus, and Stapes. The Middle ears bones overcome the lost of sound by increasing sound pressure(+34dB) this process is known as impendence matching When the stapes move in and out of the oval window, it creates a fluid motion, which is called hydrodyn ...
Weighting curves
... generally find keys which allow to choose which frequency weighting to use in sound analysis. We will discuss only about A-weighting and Cweighting. ...
... generally find keys which allow to choose which frequency weighting to use in sound analysis. We will discuss only about A-weighting and Cweighting. ...
brainstem lesion. Sound movement detection deficit due to a
... loss and asymmetry to the deficit is still possible, however. There was a mild impairment in the detection of fixed timing differences between the ears shown by the difficulty with fixed phase difference detection. Such difficulty would contribute to the sound localisation deficit, although we were ...
... loss and asymmetry to the deficit is still possible, however. There was a mild impairment in the detection of fixed timing differences between the ears shown by the difficulty with fixed phase difference detection. Such difficulty would contribute to the sound localisation deficit, although we were ...