Development of emotional facial recognition in late
... including changes in the PFC and regions related to emotion such as the anterior cingulate cortex and temporal pole. Monk and colleagues (Monk, McClure, Nelson, Zarahn, Bilder, Leibenluft, Charney, Ernst & Pine, 2003) demonstrated greater orbital frontal cortex activation in adults relative to adole ...
... including changes in the PFC and regions related to emotion such as the anterior cingulate cortex and temporal pole. Monk and colleagues (Monk, McClure, Nelson, Zarahn, Bilder, Leibenluft, Charney, Ernst & Pine, 2003) demonstrated greater orbital frontal cortex activation in adults relative to adole ...
unit2
... Split-brain subjects could not name objects shown only to the right hemisphere. If asked to select these objects with their left hand, they succeeded. The left hemisphere controls speech, the right does not. ©2006 Prentice Hall ...
... Split-brain subjects could not name objects shown only to the right hemisphere. If asked to select these objects with their left hand, they succeeded. The left hemisphere controls speech, the right does not. ©2006 Prentice Hall ...
Chapter 6: Summary and Discussion
... modulation depends on feedback from higher visual and perhaps frontal areas (Matsumoto et al., 2003; Padoa-Schioppa and Assad, 2006), which explains why it is expressed during a delayed phase of the neuronal response. The results presented in chapter 3, in combination with previous studies (Dorris a ...
... modulation depends on feedback from higher visual and perhaps frontal areas (Matsumoto et al., 2003; Padoa-Schioppa and Assad, 2006), which explains why it is expressed during a delayed phase of the neuronal response. The results presented in chapter 3, in combination with previous studies (Dorris a ...
Brain_stemCh45
... Raphe magnus (serotonergic) in rostral medulla<= opiodergic periaqueductal grey Noradrenergic neurons in pons ...
... Raphe magnus (serotonergic) in rostral medulla<= opiodergic periaqueductal grey Noradrenergic neurons in pons ...
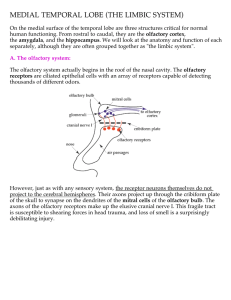
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
... CA1 region. Below is a photograph of the hippocampus of an Alzheimer's patient, with the CA1 region magnified. Both extracellular plaques and intracellular tangles are visible - these are the pathological hallmarks of the disease. ...
... CA1 region. Below is a photograph of the hippocampus of an Alzheimer's patient, with the CA1 region magnified. Both extracellular plaques and intracellular tangles are visible - these are the pathological hallmarks of the disease. ...
The Brain and Behaviour
... The sensory area that receives and processes visual information is called the primary visual cortex. It is located in the occipital lobe. The sensory area that processes auditory information is called the primary auditory cortex and is located in the temporal lobe. Sensory information from the skin ...
... The sensory area that receives and processes visual information is called the primary visual cortex. It is located in the occipital lobe. The sensory area that processes auditory information is called the primary auditory cortex and is located in the temporal lobe. Sensory information from the skin ...
VIII. Functional Brain Systems
... superiorly and the central canal inferiorly 4. Cranial nerves __________ arise from the MO 5. Important nuclei in the MO include the nucleus __________ & ________, which relay sensory info. to the thalamus, then to the cerebral cortex via thalamic nuclei 6. Three other nuclei function as ___________ ...
... superiorly and the central canal inferiorly 4. Cranial nerves __________ arise from the MO 5. Important nuclei in the MO include the nucleus __________ & ________, which relay sensory info. to the thalamus, then to the cerebral cortex via thalamic nuclei 6. Three other nuclei function as ___________ ...
Topic Option A Neurobio
... 2. The anterior part of the neural tube expands to 11. Application: Visual cortex, Broca’s area, nucleus form the brain. accumbens as areas of the brain with specific 3. Different parts of the brain have specific roles. functions. 4. The autonomic nervous system controls 12. Application: Swallowing, ...
... 2. The anterior part of the neural tube expands to 11. Application: Visual cortex, Broca’s area, nucleus form the brain. accumbens as areas of the brain with specific 3. Different parts of the brain have specific roles. functions. 4. The autonomic nervous system controls 12. Application: Swallowing, ...
4. Notes on the Brain and Plasticity
... Although plasticity occurs over an individual’s lifetime, different types of plasticity dominate during certain periods of one’s life and are less prevalent during other periods. FACT 3: Neuroplasticity occurs in the brain under two primary conditions: 1. During normal brain development when the imm ...
... Although plasticity occurs over an individual’s lifetime, different types of plasticity dominate during certain periods of one’s life and are less prevalent during other periods. FACT 3: Neuroplasticity occurs in the brain under two primary conditions: 1. During normal brain development when the imm ...
A.P. Psychology 3-B (C)
... Located at front of parietal lobes Registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (Input) ...
... Located at front of parietal lobes Registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (Input) ...
Robin Balbernie
... As brains evolved and became more complicated their formation became more patterned by the surroundings in which they must function – the ‘knowledge networks of culture’– so that specialised circuits are formed in response to the demands of the local environment. The structural organisation of the b ...
... As brains evolved and became more complicated their formation became more patterned by the surroundings in which they must function – the ‘knowledge networks of culture’– so that specialised circuits are formed in response to the demands of the local environment. The structural organisation of the b ...
biological bases of behavior
... Forebrain- controls what we think of as thought and reason. a. Thalamus- portion of the lower brain that functions primarily as a central relay station for incoming and outgoing messages from the body to the brain and the brain to the body b. Hypothalamus- portion of the lower brain that regulates b ...
... Forebrain- controls what we think of as thought and reason. a. Thalamus- portion of the lower brain that functions primarily as a central relay station for incoming and outgoing messages from the body to the brain and the brain to the body b. Hypothalamus- portion of the lower brain that regulates b ...
Alba Hernandez
... day. Subsequent visits for upper respiratory infections are noted. On 12/29/06 migraine headaches were diagnoses and the patient was given a trial of Topamax. It was noted that her blood pressure was increasing and that she had increasing GERD. 2/6/06 (Rivera) – MRI brain: no evidence for acute trau ...
... day. Subsequent visits for upper respiratory infections are noted. On 12/29/06 migraine headaches were diagnoses and the patient was given a trial of Topamax. It was noted that her blood pressure was increasing and that she had increasing GERD. 2/6/06 (Rivera) – MRI brain: no evidence for acute trau ...
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... Because he liked what he heard, he began to move to the music. Which nervous system allowed him to respond in that way? A. Autonomic B. Parasympathetic C. Somatic D. Sympathetic While walking in the woods, Amy sees a bear. The sympathetic branch of her autonomic nervous system activates. What is the ...
... Because he liked what he heard, he began to move to the music. Which nervous system allowed him to respond in that way? A. Autonomic B. Parasympathetic C. Somatic D. Sympathetic While walking in the woods, Amy sees a bear. The sympathetic branch of her autonomic nervous system activates. What is the ...
The Brain and Behaviour
... The sensory neurons then transmit the information to the . The brain then organises and interprets the information in a meaningful way, which enables you to know how hot the flame is. If you decide it is too hot, the brain sends messages via the neurons which are part of the and then the which are p ...
... The sensory neurons then transmit the information to the . The brain then organises and interprets the information in a meaningful way, which enables you to know how hot the flame is. If you decide it is too hot, the brain sends messages via the neurons which are part of the and then the which are p ...
fMRI - Rackcdn.com
... activation of a sound-based representation of the target word (phonological processing). thus there is considerable overlap in the brain regions activated by production and comprehension tasks. The main goal of fMRI language mapping for presurgical planning is to: a) cerebral hemispheric language LA ...
... activation of a sound-based representation of the target word (phonological processing). thus there is considerable overlap in the brain regions activated by production and comprehension tasks. The main goal of fMRI language mapping for presurgical planning is to: a) cerebral hemispheric language LA ...
Hemispheric Differences in the Activation of
... picture processing, and visual imagery. For example, Marsolek and colleagues showed hemispheric differences when the perceptual form of objects was altered on repeated presentation using a visual half-field technique in combination with a repetition priming procedure (Marsolek, 1995, 1999). In one s ...
... picture processing, and visual imagery. For example, Marsolek and colleagues showed hemispheric differences when the perceptual form of objects was altered on repeated presentation using a visual half-field technique in combination with a repetition priming procedure (Marsolek, 1995, 1999). In one s ...
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy and Neuroscience:
... combining basic assumptions of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) with neuroscience research results. In recent years, interdisciplinary research in the field of neuroscience has expanded our knowledge about neurobiological correlates of mental processes and changes occurring in the brain due to the ...
... combining basic assumptions of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) with neuroscience research results. In recent years, interdisciplinary research in the field of neuroscience has expanded our knowledge about neurobiological correlates of mental processes and changes occurring in the brain due to the ...
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... – The primary motor cortex allows conscious control of skilled voluntary movement of skeletal muscles – The premotor cortex is the region controlling learned motor skills – Broca’s area is a motor speech area that controls muscles involved in speech production – The frontal eye field controls eye mo ...
... – The primary motor cortex allows conscious control of skilled voluntary movement of skeletal muscles – The premotor cortex is the region controlling learned motor skills – Broca’s area is a motor speech area that controls muscles involved in speech production – The frontal eye field controls eye mo ...
Predictability Modulates Human Brain Response to Reward
... temporal-differences (TD), which postulates that a synaptically reinforcing substance, e.g. dopamine, is released in response to errors in reward prediction (Schultz et al., 1997). This model has been used in a wide variety of applications including complex learning tasks, like backgammon (Sutton, 1 ...
... temporal-differences (TD), which postulates that a synaptically reinforcing substance, e.g. dopamine, is released in response to errors in reward prediction (Schultz et al., 1997). This model has been used in a wide variety of applications including complex learning tasks, like backgammon (Sutton, 1 ...
Demonstrating the Implicit Processing of Visually Presented Words
... have legitimate word forms with semantic and phonological representations; related activity was detected in the left medial extrastriate visual cortex and a left prefrontal area. Pseudowords have legitimate word forms from which phonological but not semantic associations can be computed; related act ...
... have legitimate word forms with semantic and phonological representations; related activity was detected in the left medial extrastriate visual cortex and a left prefrontal area. Pseudowords have legitimate word forms from which phonological but not semantic associations can be computed; related act ...
Chapter 2 Functional Neuroanatomy
... Although these approaches can yield useful information about the developing brain, they are not without shortcomings. For example, because of the plasticity of the developing brain following damage, injury in a specific brain region may produce behavioral losses that vary greatly depending on the ag ...
... Although these approaches can yield useful information about the developing brain, they are not without shortcomings. For example, because of the plasticity of the developing brain following damage, injury in a specific brain region may produce behavioral losses that vary greatly depending on the ag ...
A.P. Psychology Rubric: Chapter 2 10 point question Question: You
... Parietal lobes Temporal lobes Hippocampus Amygdala Medulla ...
... Parietal lobes Temporal lobes Hippocampus Amygdala Medulla ...