Ch 11 lec 1
... Lesions of the amygdala decrease emotional responses. Lesions interfere with effects of emotions on memory. ...
... Lesions of the amygdala decrease emotional responses. Lesions interfere with effects of emotions on memory. ...
• Ch 49 • Nervous Systems • Neuronal Circuits • Each single
... In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNSThe PNS has two efferent components: the motor system and the ...
... In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNSThe PNS has two efferent components: the motor system and the ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... The chemical component of neural communication is accomplished through neurotransmitters released at the synapse ...
... The chemical component of neural communication is accomplished through neurotransmitters released at the synapse ...
Affective Computing
... (unconditioned stimulus) • Pair audio tone (conditioned stimulus) with electric shock (unconditioned stimulus) • Rat eventually learns to react aversively just to tone • Then study learned pathways and role of various brain regions via • Staining of neurons and dissection • Impact of lesions on beha ...
... (unconditioned stimulus) • Pair audio tone (conditioned stimulus) with electric shock (unconditioned stimulus) • Rat eventually learns to react aversively just to tone • Then study learned pathways and role of various brain regions via • Staining of neurons and dissection • Impact of lesions on beha ...
J15 Environment and working with children
... Evoked Response Potentials (ERP’s) Polygraphs HR BP ...
... Evoked Response Potentials (ERP’s) Polygraphs HR BP ...
1. 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter
... the stimuli was routed to the left hemisphere, the subjects could describe the stimuli verbally. In trials where the right hemisphere received the stimulus, subjects were unable to verbalize their observations, but could communicate the received information in other ways e.g., by drawing or pointing ...
... the stimuli was routed to the left hemisphere, the subjects could describe the stimuli verbally. In trials where the right hemisphere received the stimulus, subjects were unable to verbalize their observations, but could communicate the received information in other ways e.g., by drawing or pointing ...
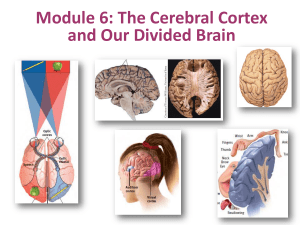
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neu ...
... This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neu ...
E4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses (and drugs!)
... After the brain has been altered of the situation, pain can ...
... After the brain has been altered of the situation, pain can ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. Association Cortex - Region of the cortex in which the highest intellectual functions occur 75% of the cor ...
... The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. Association Cortex - Region of the cortex in which the highest intellectual functions occur 75% of the cor ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers
... Sensory Functions of the Cortex The sensory strip deals with information from touch stimuli. The occipital lobe deals with visual information. Auditory information is sent to the temporal lobe. Auditory areas are also active when someone in a psychotic state is experiencing “voices” or audi ...
... Sensory Functions of the Cortex The sensory strip deals with information from touch stimuli. The occipital lobe deals with visual information. Auditory information is sent to the temporal lobe. Auditory areas are also active when someone in a psychotic state is experiencing “voices” or audi ...
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... Paul Broca (1824 – 1880) demonstrates that highly localized brain lesions (damage) correlated with specific cognitive dysfunctions for the patient. Injuries to a small area in the frontal lobe of the cortex on the left hemisphere only resulted in speech impairment. Korbinian Brodmann (18681918) defi ...
... Paul Broca (1824 – 1880) demonstrates that highly localized brain lesions (damage) correlated with specific cognitive dysfunctions for the patient. Injuries to a small area in the frontal lobe of the cortex on the left hemisphere only resulted in speech impairment. Korbinian Brodmann (18681918) defi ...
Frontal Lobes
... Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body AND is aware of the visual field on that opposite side. Without the corpus callosum, the halves of the body and the halves of the visual field do not work together. Only the left half of the brain has enough verbal ability to express its t ...
... Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body AND is aware of the visual field on that opposite side. Without the corpus callosum, the halves of the body and the halves of the visual field do not work together. Only the left half of the brain has enough verbal ability to express its t ...
PsychSim5: Neural Messages 1 PsychSim 5: NEURAL MESSAGES
... This activity describes what researchers have learned about the special abilities of the left and right sides of the brain. You will learn how information is transmitted to these two hemispheres and about the unique function of each. Hemispheric Connections What is the name of the band of fibers c ...
... This activity describes what researchers have learned about the special abilities of the left and right sides of the brain. You will learn how information is transmitted to these two hemispheres and about the unique function of each. Hemispheric Connections What is the name of the band of fibers c ...
General Psychology - K-Dub
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
Chapter Two Part Three - K-Dub
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
Emotions The issues • Innate or learned? • Voluntary or involuntary
... and emotional learning, also involved in long term stress • Specifically: lateral hypothalamus, ventral tegmental area, locus coeruleus (NE), PAG, facial motor nuclei Amygdala and Fear • Evidence o Animal: stimulation of the hypothalamus: fear/attack expression (sham rage) o Human: stimulation of am ...
... and emotional learning, also involved in long term stress • Specifically: lateral hypothalamus, ventral tegmental area, locus coeruleus (NE), PAG, facial motor nuclei Amygdala and Fear • Evidence o Animal: stimulation of the hypothalamus: fear/attack expression (sham rage) o Human: stimulation of am ...
Nervous system
... You are a neurologist in a large hospital. The wife of a construction worker visits you and describes that her husband has experienced a serious injury to his frontal lobe. She is perplexed by his behavior. Which of the following would you tell her is “normal behavior” for a person with frontal lob ...
... You are a neurologist in a large hospital. The wife of a construction worker visits you and describes that her husband has experienced a serious injury to his frontal lobe. She is perplexed by his behavior. Which of the following would you tell her is “normal behavior” for a person with frontal lob ...
The role of Amygdala
... When a tone is paired a few times with a foot-shock, rat freezing responses start at the tone, prior to the onset of the shock. ...
... When a tone is paired a few times with a foot-shock, rat freezing responses start at the tone, prior to the onset of the shock. ...
4.BiologicalPsycholo..
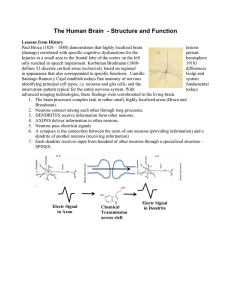
... positively charged sodium ions (Na+) rush into the cell, its interior briefly becomes positive. This is the action potential. After the action potential, positive potassium ions (K+) flow out of the axon and restore its negative charge (see Fig. 2.3 for further explanation). ...
... positively charged sodium ions (Na+) rush into the cell, its interior briefly becomes positive. This is the action potential. After the action potential, positive potassium ions (K+) flow out of the axon and restore its negative charge (see Fig. 2.3 for further explanation). ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... 4. Cerebral cortex: Largest and most complex part of the human brain. Includes the brain areas that are responsible for the most complex mental activities, including learning, remembering, thinking, and consciousness. LOBES OF THE BRAIN Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes. Each is de ...
... 4. Cerebral cortex: Largest and most complex part of the human brain. Includes the brain areas that are responsible for the most complex mental activities, including learning, remembering, thinking, and consciousness. LOBES OF THE BRAIN Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes. Each is de ...
Intro Chap 2n.ppt
... and remembering the location of objects • The Amygdala – manages emotions, our fear response, and memories of fearful stimuli • Cingulate Cortex – helps us with emotional and cognitve processing ...
... and remembering the location of objects • The Amygdala – manages emotions, our fear response, and memories of fearful stimuli • Cingulate Cortex – helps us with emotional and cognitve processing ...
Ch.02 - Biology of the Mind
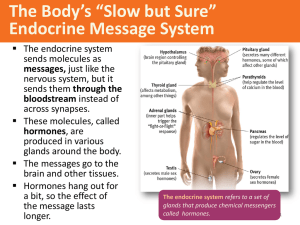
... (hypo) the thalamus; directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking body temperature, and emotions. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. ...
... (hypo) the thalamus; directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking body temperature, and emotions. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. ...
Chapter 4 - (www.forensicconsultation.org).
... Neurons: nerve cells- send and receive information • Glial cells: support and protect the neurons • Myelination: coats the neural pathways, allows for efficient and fast signals to travel • Reflex behavior: controlled by lower brain centers, ...
... Neurons: nerve cells- send and receive information • Glial cells: support and protect the neurons • Myelination: coats the neural pathways, allows for efficient and fast signals to travel • Reflex behavior: controlled by lower brain centers, ...